nginx 命令详解
location
语法
location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ | @ ] uri { ... }
匹配方式(优先级由高到低):
- 精确匹配:使用修饰符
=。 - 前缀匹配:使用修饰符
^~。 - 正则匹配:使用修饰符
~(区分大小写)和~*(不区分大小写)。 - 最长匹配:没有修饰符,使用匹配到的最长记录。
- @,nginx内部跳转
location /img/ {
error_page 404 @img_err;
}
#以 /img/ 开头的请求,如果链接的状态为 404, 则会匹配到 @img_err 这条规则上。
location @img_err {
# 规则
}
示例
# 精确匹配
# 只匹配请求/
location = / {
[ configuration A ]
}
# 正则匹配,不区分大小写
# 通过后缀匹配图片, /images/.../1.jpg
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
[ configuration B ]
}
# 前缀匹配
# 匹配 /images/xxx/yyyy
location ^~ /images/ {
[ configuration C ]
}
# 前缀匹配
# 匹配 /img/xxx/yyyy, /imgx,/imgy/abc/1
location ^~ /img {
[ configuration D ]
}
location / {
[ configuration E ]
}
location /user/ {
[ configuration F ]
}
-
请求
/精准匹配A,不再往下查找。 -
请求
/index.html匹配B。首先找到最长匹配B,接着又按照顺序查找匹配的正则。结果没有找到,因此使用先前标记的最长匹配,即配置B。 -
请求
/user/index.html匹配C。首先找到最长匹配C,由于后面没有匹配的正则,所以使用最长匹配C。 -
请求
/user/1.jpg匹配E。首先找到最长匹配项C,继续进行正则查找,找到匹配项E。因此使用E。 -
请求
/images/1.jpg匹配D。首先进行前缀字符的查找,找到最长匹配D。但是,特殊的是它使用了^~修饰符,不再进行接下来的正则的匹配查找,因此使用D。这里,如果没有前面的修饰符,其实最终的匹配是E。大家可以想一想为什么。 -
请求
/documents/about.html匹配B。因为B表示任何以/开头的URL都匹配。在上面的配置中,只有B能满足,所以匹配B。
proxy_pass
语法
location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri {
proxy_pass http://host:port[uri0]
}
# uri0可以是 /, /www, /www/
# 不存在uri0
actualUrl = requestUrl
# 存在uri0
actualUrl = uri0 + requestUrl.remove(uri)
以请求http://localhost:8080/api/values/ccc为例:
不存在uri0
# 实际请求: http://localhost:5000/api/values/ccc
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000;
}
# 实际请求: http://localhost:5000/api/values/ccc
location /api {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000;
}
# 实际请求: http://localhost:5000/api/values/ccc
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000;
}
存在uri0:
# 实际请求: http://localhost:5000/api/values/ccc
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000/;
}
# 实际请求: http://localhost:5000//values/ccc
location /api {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000/;
}
# 实际请求: http://localhost:5000/values/ccc
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000/;
}
# 实际请求: http://localhost:5000/www/values/ccc
location /api {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000/www;
}
# 实际请求: http://localhost:5000/wwwvalues/ccc
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000/www;
}
rewrite
语法
server {
rewrite 规则 定向路径 重写类型;
}
规则:可以是字符串或者正则,来表示想匹配的目标url
定向路径:表示匹配到规则后要定向的路径,如果规则里有正则,则可以使用$index来表示正则里的捕获分组
重写类型:
- last :表示完成rewrite,浏览器地址栏URL地址不变
- break;本条规则匹配完成后,终止匹配,不再匹配后面的规则,浏览器地址栏URL地址不变
- redirect:返回302临时重定向,浏览器地址会显示跳转后的URL地址
- permanent:返回301永久重定向,浏览器地址栏会显示跳转后的URL地址
:::tip 302和301的区别
301是永久重定向,比较常用的场景是使用域名跳转,旧域名指向新域名。比如,我们访问 http://www.baidu.com 会跳转到 https://www.baidu.com,301请求是可以缓存的。
302是临时重定向,未登陆的用户重定向到登录页面。
:::
示例
server {
# 访问 /last.html 的时候,页面内容重写到 /index.html 中
rewrite /last.html /index.html last;
# 访问 /break.html 的时候,页面内容重写到 /index.html 中,并停止后续的匹配
rewrite /break.html /index.html break;
# 访问 /redirect.html 的时候,页面直接302定向到 /index.html中
rewrite /redirect.html /index.html redirect;
# 访问 /permanent.html 的时候,页面直接301定向到 /index.html中
rewrite /permanent.html /index.html permanent;
# 把 /html/*.html => /post/*.html ,301定向
rewrite ^/html/(.+?).html$ /post/$1.html permanent;
# 把 /search/key => /search.html?keyword=key
rewrite ^/search\/([^\/]+?)(\/|$) /search.html?keyword=$1 permanent;
}
try_files
语法
try_files file1 file2 ... uri
try_files file1 file2 ... =code
依次尝试指定的文件,以及目录下的默认文件。如果都不存在,则返回最后一个参数
- 作用域: location, server
- $uri/ 表示目录
示例
location / {
# 依次尝试:$url, $url/index.html, html/index.html, abc.html
# 如果都不存在,则返回notFound.html
try_files $url $url/ html/ abc.html notFound.html
index index.html
}
location / {
# 如果$url不存在,则返回状态码502
try_files $url =502;
}
location / {
# 如果$url不存在,则执行新规则 @notFound
try_files $url @notFound;
}
location @notFound {
...
}
内置变量
请求行
以请求http://invo.com/nginx-var/request-line?a=1&b=2为例
| 变量 | 含义 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| $request | 整个请求行 | GET /nginx-var/request-line?a=1&b=2 HTTP/1.1 |
| $request_method | 请求方法(如GET、POST) | GET |
| $request_uri | 完整的请求URI | /nginx-var/request-line?a=1&b=2 |
| $uri | URI,除去查询字符串 | /nginx-var/request-line |
| $document_uri | 同$uri | /nginx-var/request-line |
| $args | 查询字符串 | a=1&b=2 |
| $query_string | 同$args | a=1&b=2 |
| $server_protocol | 请求协议(如HTTP/1.0 HTTP/1.1) | HTTP/1.1 |
| $arg_name | 请求行中name参数的值 | $arg_a = 1 , $arg_b = 2 |
请求头
| 变量 | 含义 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| $host | 该变量按如下优先级获得:请求行中解析到的host、请求头“Host”中的host、配置文件中匹配到的server_name | invo.com |
| $remote_addr | 客户端ip地址 | 127.0.0.1 |
| $remote_port | 客户端端口 | 4204 |
| $http_user_agent | 用户代理(“User-Agent”请求头的值) | Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv:50.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/50.0 |
| $http_cookie | “Cookie”请求头的值 | CA=abc;CB=123 |
| $cookie_name | Cookie中名为name的值 | $cookie_CA=abc, $cookie_CB=123 |
| $http_referer | “Http-Referer”请求头的值 | http://invo.com |
其他
| 变量 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| $body_bytes_sent | 发给客户端的数据大小,以字节计,不包括http报头 |
| $bytes_sent | 发给客户端的数据大小,以字节计 |
| $status | http响应状态码 |
| $request_time | 请求处理时间 |
| $http_cookie | “Cookie”请求头的值 |
| $upstream_response_time | 从与upstream建立连接到收到最后一个字节所经历的时间(nginx做反向代理服务器时可用) |
| $upstream_connect_time | 与upstream建立连接所消耗的时间(nginx做反向代理服务器时可用) |
常见场景实例
https 配置
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name abc.example.com;
#HTTP_TO_HTTPS_START
if ($server_port !~ 443){
rewrite ^(/.*)$ https://$host$1 permanent;
}
ssl on;
ssl_certificate abc.example.com.pem;
ssl_certificate_key abc.example.com.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers AWSGCM:ALL:!DH:!EXPORT:!RC4:+HIGH:!MEDIUM:!LOW:!aNULL:!eNULL;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.57:80;
}
}
文件上传大小
location / {
// 最大允许50M
client_max_body_size 50m;
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.57:80;
}
k8s的Ingress添加注解:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 50M
跨域
location / {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods 'GET, POST, OPTIONS';
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Headers 'DNT,X-Mx-ReqToken,Keep-Alive,User-Agent,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Authorization';
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
return 204;
}
}
k8s的Ingress添加注解:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-headers: *
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-methods: GET, POST, OPTIONS
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-origin: *
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/enable-cors: true
根据参数重写url
// 实际请求: url=/DataServer?T=img_w&x=1701&y=837&l=11&tk=fcdf3d8f7124f72fb0e09c71174723c3
location ^~ /DataServer {
// 根据参数 T,x,y,l重写url = /img_w/11/1701/837.jpeg
rewrite .* /$arg_T/$arg_l/$arg_x/$arg_y.jpeg last;
}
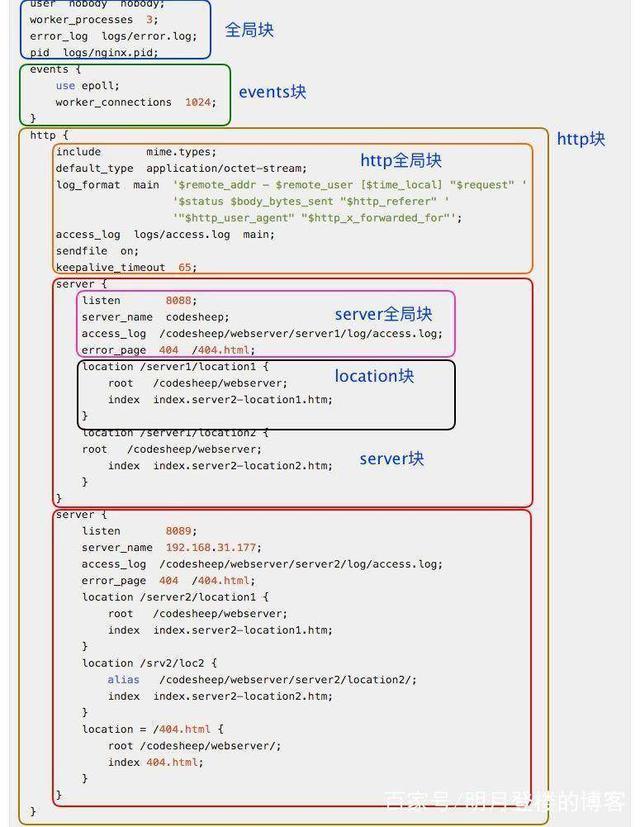
配置清单


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号