NetCore 入门 (八) : 管道
1. 入门
ASP.NET Core是一个Web开发平台,而不是一个单纯的开发框架。这是因为它具有一个极具扩展性的请求处理管道,我们可以通过对这个管道的定制来满足各种场景下的HTTP处理需求。ASP. NET Core应用的很多特性,比如路由、认证、会话、缓存等,都是通过管道的定制来实现的。
1.1 管道机制
HTTP协议自身的特性决定了任何一个Web应用的工作方式都是监听、接收并处理HTTP请求,并在最终对请求予以响应。在ASP.NET Core应用中,用户的每次请求,都会对应一个请求管道。在这个请求管道中,我们可以动态配置各种业务逻辑对应的中间件,可以针对不同用户做出不同的请求响应。
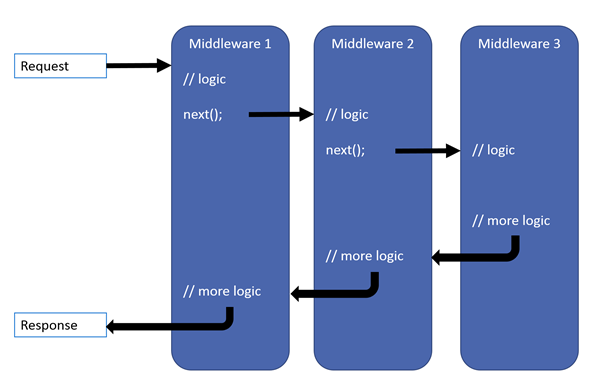
当用户发出一起请求后,应用程序都会为其创建一个请求管道,在这个请求管道中,每一个中间件都会按顺序进行处理(可能会执行,也可能不会被执行,取决于具体的业务逻辑),等最后一个中间件处理完毕后请求又会以相反的方向返回给用户最终的处理结果。
1.2 NuGet包
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting.Abstractions; // 抽象依赖包
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; // 默认实现包
1.3 入门示例
1. 新建一个简单的控制台应用
控制台应用的SDK是Microsoft.NET.Sdk,而ASP.NET Core Web应用的SDK一般都是Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web,所以在这里做个简单的修改。这个SDK会自动把Web应用相关的包添加进来,不需要再去添加其他依赖了。
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web">
<PropertyGroup>
<OutputType>Exe</OutputType>
<TargetFramework>netcoreapp3.1</TargetFramework>
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>
2. 新建Startup
在Startup类中定义3个中间件。
internal class Startup
{
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
// Middleware A
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("A (in)");
await next();
Console.WriteLine("A (out)");
});
// Middleware B
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("B (in)");
await next();
Console.WriteLine("B (out)");
});
// Middleware C
app.Run(async context =>
{
Console.WriteLine("C");
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World from the terminal middleware");
});
}
}
3. Program
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>();
});
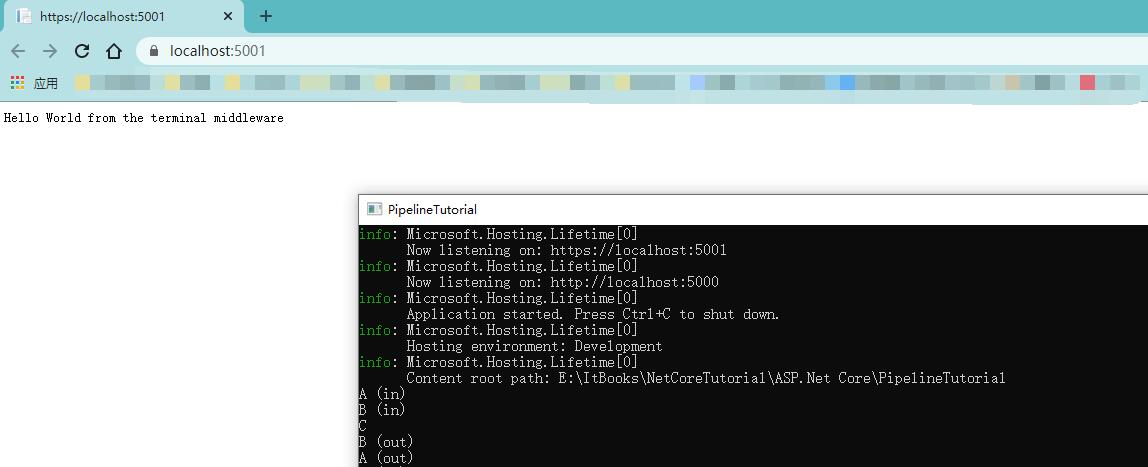
}从上面的代码可以看出,这里利用了IHost承载系统搭建了一个ASP.NET Core Web应用。ConfigureWebHostDefaults方法做了一些默认的配置,包括:使用服务器Kestrel、监听端口(5000、5001)、添加路由等。
输出结果如下:
2. 中间件
ASP.NET Core的请求处理管道有一个服务器和一组中间件组成。服务器负责请求的监听、接收、分发和最终的响应,而当前请求的处理由后续的中间件来完成。本节重点来剖析一下中间件和管道的原理。
2.1 准备
HttpContext
用户的每一次请求,服务器都会创建一个只针对当前请求的HttpContext上下文。在管道中流通的正是此对象。在组成管道的每个中间件中,可以通过HttpContext上下文获取当前请求的信息,也可以利用Response属性完成当前请求的响应。
public abstract class HttpContext
{
public abstract IServiceProvider RequestServices { get; set; }
public abstract HttpRequest Request { get; }
public abstract HttpResponse Response { get; }
public abstract ISession Session { get; set; }
...
}
Request:可以获得当前请求的所有信息。Response:利用Response完成当前请求的响应工作。
IApplicationBuilder
用于配置当前应用的请求管道。
public interface IApplicationBuilder
{
IServiceProvider ApplicationServices { get; set; }
IDictionary<string, object> Properties { get; }
IFeatureCollection ServerFeatures { get; }
RequestDelegate Build();
IApplicationBuilder New();
IApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware);
}
ApplicationServices:当前应用的依赖注入服务。Build:构建请求管道。Use:添加中间件。
2.2 原理
中间件的职责包括2个部分:
- 业务逻辑。即中间件本身要完成的业务功能,由
RequestDelegate表示。 - 构建管道。中间件要与前后相连的中间件组成流水线式的管道,方便请求的处理,由
Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>表示。
RequestDelegate
定义一个委托对象RequestDelegate,表示一次对HttpContext上下文的处理,即中间件的业务逻辑。这是中间件的核心功能。
public delegate Task RequestDelegate(HttpContext context);
构建管道
中间件有多种表现形式,可以是一个类,也可以是基于RequestDelegate的委托函数,但最终都要转换成最基本的形式:
Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware;
下面通过一个简单的示例,来演示管道的构建和请求的处理过程。
// 定义一个变量中间件middlewareA,这个变量是个委托函数
static Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middlewareA =
(RequestDelegate next) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Link A");
return async context =>
{
Console.WriteLine("process in A");
await next(context);
Console.WriteLine("back from A");
};
};
// 定义一个函数中间件middlewareB
static RequestDelegate middlewareB(RequestDelegate next)
{
Console.WriteLine("Link B");
return async context =>
{
Console.WriteLine("process in B");
await next(context);
Console.WriteLine("back from B");
};
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 定义最后一个中间件,如果之前的中间件没有对请求做出响应,则此中间件执行
RequestDelegate last = (context) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("process in last middleware");
context.Response.StatusCode = 404;
return Task.CompletedTask;
};
Console.WriteLine("==========Build the Pipeline============");
// 组建管道: A ==> B ==> last
var next = middlewareB(last);
next = middlewareA(next);
Console.WriteLine("==========A Request Arrived============");
HttpContext context = new DefaultHttpContext();
// 处理请求
next(context);
}输出结果如下:
==========Build the Pipeline============
Link B
Link A
==========A Request Arrived============
process in A
process in B
process in last middleware
back from B
back from A
2.3 定义中间件
2.3.1 强类型定义
如果采用强类型的方式定义中间件,只需实现接口IMiddleware即可。
public interface IMiddleware
{
Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context, RequestDelegate next);
}
context: 代表当前请求的HttpContext对象next: 代表后续中间件的RequestDelegate对象。如果要将当前请求分发给后续中间件处理,调用此委托即可。
2.3.2 基于约定的定义
这种方式比较自由,不需要实现某个接口或继承某个基类,只需要遵循一些约定即可。
::: tip 约定
- 中间件类型需要有一个公共的构造函数,且该构造函数必须包含一个
RequestDelegate的参数。 - 针对请求的处理实现在返回类型为
Task的InvokeAsync或Invoke方法中,该方法的第一个参数必须是代表当前请求上下文的HttpContext对象。
:::
简单示例
public class StringContentMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
private readonly string _content;
public StringContentMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, string content)
{
_next = next;
_content = content;
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync(_content);
await next(context);
}
}
2.4 注册中间件
提供了以下方式,将中间件添加到请求管道中。
2.4.1 Use
public interface IApplicationBuilder
{
IApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware);
}
public static class UseExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder Use(this IApplicationBuilder app, Func<HttpContext, Func<Task>, Task> middleware);
}
示例
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
// other
await next();
});
2.4.2 Run
该方法通常用于指定管道的最后一个中间件。如果在此之后又注册了其他的中间件,后续中间件将不会被调用。
public static class RunExtensions
{
public static void Run(this IApplicationBuilder app, RequestDelegate handler);
}
示例
app.Run(context => context.Response.WriteAsync("hello,world"));
2.4.3 UseMiddleware
public static class UseMiddlewareExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMiddleware(this IApplicationBuilder app, Type middleware, params object[] args);
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMiddleware<TMiddleware>(this IApplicationBuilder app, params object[] args);
}
2.5 中间件委托链
// nuget: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Abstractions
// namespace: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder
public interface IApplicationBuilder
{
IServiceProvider ApplicationServices { get; set; }
IFeatureCollection ServerFeatures { get; }
IDictionary<string, object> Properties { get; }
IApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware);
IApplicationBuilder New();
RequestDelegate Build();
}
// nuget: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http
// namespace: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder
public class ApplicationBuilder : IApplicationBuilder
{
private const string ServerFeaturesKey = "server.Features";
private const string ApplicationServicesKey = "application.Services";
private readonly IList<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>> _components =
new List<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>();
public ApplicationBuilder(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
this.Properties = new Dictionary<string, object>(StringComparer.Ordinal);
this.ApplicationServices = serviceProvider;
}
public ApplicationBuilder(IServiceProvider serviceProvider, object server) : this(serviceProvider)
{
this.SetProperty<object>("server.Features", server);
}
private ApplicationBuilder(ApplicationBuilder builder)
{
this.Properties = new CopyOnWriteDictionary<string, object>(builder.Properties, StringComparer.Ordinal);
}
public IServiceProvider ApplicationServices
{
get
{
return this.GetProperty<IServiceProvider>("application.Services");
}
set
{
this.SetProperty<IServiceProvider>("application.Services", value);
}
}
public IFeatureCollection ServerFeatures
{
get
{
return this.GetProperty<IFeatureCollection>("server.Features");
}
}
public IDictionary<string, object> Properties { get; }
private T GetProperty<T>(string key)
{
object obj;
if (!this.Properties.TryGetValue(key, out obj))
{
return default(T);
}
return (T)((object)obj);
}
private void SetProperty<T>(string key, T value)
{
this.Properties[key] = value;
}
public IApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware)
{
this._components.Add(middleware);
return this;
}
public IApplicationBuilder New()
{
return new ApplicationBuilder(this);
}
public RequestDelegate Build()
{
RequestDelegate requestDelegate = delegate(HttpContext context)
{
Endpoint endpoint = context.GetEndpoint();
if (((endpoint != null) ? endpoint.RequestDelegate : null) != null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("The request reached the end of the pipeline without executing the endpoint: '" + endpoint.DisplayName + "'. Please register the EndpointMiddleware using 'IApplicationBuilder.UseEndpoints(...)' if using routing.");
}
context.Response.StatusCode = 404;
return Task.CompletedTask;
};
foreach (Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> func in this._components.Reverse<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>())
{
requestDelegate = func(requestDelegate);
}
return requestDelegate;
}
}
// nuget: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting
// namespace: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting.Builder
public interface IApplicationBuilderFactory
{
IApplicationBuilder CreateBuilder(IFeatureCollection serverFeatures);
}
// nuget: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting
// namespace: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting.Builder
public class ApplicationBuilderFactory : IApplicationBuilderFactory
{
public ApplicationBuilderFactory(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
this._serviceProvider = serviceProvider;
}
public IApplicationBuilder CreateBuilder(IFeatureCollection serverFeatures)
{
return new ApplicationBuilder(this._serviceProvider, serverFeatures);
}
private readonly IServiceProvider _serviceProvider;
}
3. Startup
ASP.NET Core应用在启动过程中,要进行特定的初始化工作。包括:
- 注册依赖服务
- 注册中间件
3.1 Startup类
定义
Startup类是基于约定的方式创建的,一般包括如下3个函数:
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services);
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app);
public void ConfigureContainer(XXXContainerBuilder container);
}
ConfigureServices: 注册依赖服务,这个函数是必须的。Configure: 注册中间件,可选函数。ConfigureContainer: 对第三方依赖注入容器的配置,可选函数。
::: tip
Startup类的创建和调用,在框架内部是基于依赖注入服务的。所以,可以在构造函数和方法中添加Startup类依赖的服务。
:::
::: tip 承载环境
Startup类优先使用与承载环境名称EnvironmentName一致的函数,如下所示:
Configure{EnvironmentName}ServicesConfigure{EnvironmentName}Configure{EnvironmentName}Container
:::
示例
public class Startup
{
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
// 在Development环境下优先执行
public void ConfigureDevelopmentServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc();
}
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddSingleton<IFoo,Foo>();
services.AddMvc();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
// Middleware B
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("B (in)");
await next();
Console.WriteLine("B (out)");
});
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
}
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
}
}
}注册
public static class WebHostBuilderExtensions
{
public static IWebHostBuilder UseStartup(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, Type startupType);
public static IWebHostBuilder UseStartup<TStartup>(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder) where TStartup : class;
}
示例
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>();
});3.2 IStartupFilter
使用IStartupFilter同样可以添加中间件。如果说在Startup中添加的中间件负责业务逻辑(比如Mvc,路由,SignalR等),那么IStartupFilter添加的中间件负责应用程序的通用功能(比如认证授权、异常处理、日志等)。IStartupFilter的编程模式类似于AOP。
public interface IStartupFilter
{
Action<IApplicationBuilder> Configure(Action<IApplicationBuilder> next);
}
在IStartupFilter中添加的中间件放置在管道的最前面,所以可以通过这种方式在业务中间件执行之前或之后,添加特定的功能。
示例
- 定义
IStartupFilter,注册中间件
public class FooStartupFilter : IStartupFilter
{
public Action<IApplicationBuilder> Configure(Action<IApplicationBuilder> next)
{
return app =>
{
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
Console.Write("Foo==>");
await next();
Console.Write("==>Foo");
});
//app.UseMiddleware<FooMiddleware>();
next(app);
};
}
}- 注册IStartupFilter
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureServices(services =>
{
services.TryAddEnumerable(ServiceDescriptor.Singleton<IStartupFilter, FooStartupFilter>());
})
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.Configure(app =>
{
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
{
Console.Write("A==>");
await next();
Console.Write("==>A");
};
});
app.Run(context =>
{
Console.Write("Hello, World");
context.Response.WriteAsync("hello,world");
return Task.CompletedTask;
});
});
});一个应用可以注册多个IStartupFilter服务,它们会按照添加的顺序依次添加中间件。
输出结果
Foo==>A==>Hello, World==>A==>Foo
3.3 Startup程序集
如果在另外的一个程序集中定义了合法的Startup类型,可以通过配置的方式将它指定为启动程序集,对应的配置项名称为startupAssembly。
public static class WebHostDefaults
{
public static readonly string StartupAssemblyKey = "startupAssembly";
}
:::tip 类型筛选
Startup类型加载器将按照如下的顺序从启动程序集中进行筛选,如果没有找到满足条件的类型,则抛出异常。
Startup{EnvironmentName}Startup{startupAssembly}.Startup{EnvironmentName}{startupAssembly}.StartupXXX.Startup{EnvironmentName}任意命名空间XXX.Startup任意命名空间
:::
示例
- 新建一个名为
AppStartup的类库项目
public class StartupBase
{
public StartupBase()
{
Console.WriteLine($"{this.GetType().FullName} is Created");
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
Console.WriteLine("B (in)");
await next();
Console.WriteLine("B (out)");
});
}
}
public class Startup : StartupBase { }
public class StartupDevelopment : StartupBase { }
public class StartupStaging : StartupBase { }
- 主程序
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.ConfigureLogging(builder => builder.ClearProviders());
});
}
- 启动程序
dotnet run --startupAssembly=AppStartup
AppStartup.StartupDevelopment is Created
dotnet run --startupAssembly=AppStartup --environment=Staging
AppStartup.StartupStaging is Created
3.4 HostingStartup服务
如果第三方框架、类库或者工具需要在应用程序启动时做些初始化工作,可以通过IHostingStartup服务的形式进行。注册IHostingStartup服务需要经过以下3个步骤:
- 实现接口
IHostingStartup - 添加程序集特性
HostingStartupAttribute - 在应用程序中配置
IHostingStartup
public interface IHostingStartup
{
void Configure(IWebHostBuilder builder);
}
HostingStartupAttribute
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Assembly, Inherited = false, AllowMultiple = true)]
public sealed class HostingStartupAttribute : Attribute
{
public HostingStartupAttribute(Type hostingStartupType);
public Type HostingStartupType { get; }
}
从定义中可以看出:
- 这是针对程序集的特性。
AllowMultiple=true,一个程序集中可以定个多个IHostingStartup服务。
配置
public static class WebHostDefaults
{
public static readonly string HostingStartupAssembliesKey = "hostingStartupAssemblies";
public static readonly string HostingStartupExcludeAssembliesKey = "hostingStartupExcludeAssemblies";
public static readonly string PreventHostingStartupKey = "preventHostingStartup";
}
hostingStartupAssemblies: 通过该属性进行IHostingStartup服务的注册。多个程序集名称以英文分号(;)进行分隔。当前应用程序的名称会作为默认的值进行注册。hostingStartupExcludeAssemblies: 通过该属性将不希望启动的程序集排除在外。preventHostingStartup: 是否禁用IHostingStartup特性,默认False。对于Boolean类型的配置,true(不区分大小写)和1都表示True,其他值表示False。
:::warning
这些属性只能在以ASPNETCORE_为前缀的环境变量中进行配置。
:::
示例
- 新建名为
AppStartup的类库项目
[assembly: HostingStartup(typeof(AppStartup.Bar))]
[assembly: HostingStartup(typeof(AppStartup.Baz))]
namespace AppStartup
{
public class HostingStartupBase : IHostingStartup
{
public void Configure(IWebHostBuilder builder) =>
Console.WriteLine($"{GetType().Name}.Configure()");
}
public class Bar : HostingStartupBase { }
public class Baz : HostingStartupBase { }
}
- 配置环境
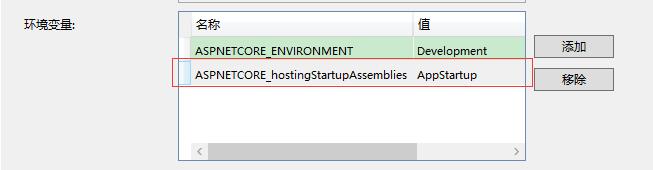
- 启动项目,输出如下:
Bar.Configure()
Baz.Configure()
4. 系统配置
4.1 承载环境
IWebHostEnvironment
::: tip 参考
IHostEnvironment
:::
public interface IWebHostEnvironment : IHostEnvironment
{
string WebRootPath { get; set; }
IFileProvider WebRootFileProvider { get; set; }
}
WebHostBuilderContext
public class WebHostBuilderContext
{
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; set; }
public IWebHostEnvironment HostingEnvironment { get; set; }
}
4.2 宿主配置
IWebHostBuilder
public interface IWebHostBuilder
{
// 构建IWebHost
IWebHost Build();
// 添加依赖注入服务
IWebHostBuilder ConfigureServices(Action<WebHostBuilderContext, IServiceCollection> configureServices);
IWebHostBuilder ConfigureServices(Action<IServiceCollection> configureServices);
// 配置Configuration
IWebHostBuilder ConfigureAppConfiguration(Action<WebHostBuilderContext, IConfigurationBuilder> configureDelegate);
// 读取或更改Configuration的值
string GetSetting(string key);
IWebHostBuilder UseSetting(string key, string value);
}
扩展
public static class WebHostBuilderExtensions
{
public static IWebHostBuilder Configure(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, Action<IApplicationBuilder> configureApp);
public static IWebHostBuilder Configure(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, Action<WebHostBuilderContext, IApplicationBuilder> configureApp);
public static IWebHostBuilder ConfigureAppConfiguration(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, Action<IConfigurationBuilder> configureDelegate);
public static IWebHostBuilder ConfigureLogging(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, Action<WebHostBuilderContext, ILoggingBuilder> configureLogging);
public static IWebHostBuilder ConfigureLogging(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, Action<ILoggingBuilder> configureLogging);
public static IWebHostBuilder UseDefaultServiceProvider(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, Action<WebHostBuilderContext, ServiceProviderOptions> configure);
public static IWebHostBuilder UseDefaultServiceProvider(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, Action<ServiceProviderOptions> configure);
public static IWebHostBuilder UseStartup(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder, Type startupType);
public static IWebHostBuilder UseStartup<TStartup>(this IWebHostBuilder hostBuilder) where TStartup : class;
public static IWebHostBuilder UseStaticWebAssets(this IWebHostBuilder builder);
}
4.3 管道配置
IApplicationBuilder
用于配置当前应用的请求管道。
public interface IApplicationBuilder
{
IServiceProvider ApplicationServices { get; set; }
IDictionary<string, object> Properties { get; }
IFeatureCollection ServerFeatures { get; }
RequestDelegate Build();
IApplicationBuilder New();
IApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware);
}
ApplicationServices:当前应用的依赖注入服务。Build:构建请求管道。Use:添加中间件。
4.4 属性配置
属性列表
| 属性 | 配置键 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
ApplicationName |
applicationName |
|
Environment |
environment |
WebHostOptions
public static class WebHostDefaults
{
public static readonly string ApplicationKey = "applicationName";
public static readonly string StartupAssemblyKey = "startupAssembly";
public static readonly string HostingStartupAssembliesKey = "hostingStartupAssemblies";
public static readonly string HostingStartupExcludeAssembliesKey = "hostingStartupExcludeAssemblies";
public static readonly string DetailedErrorsKey = "detailedErrors";
public static readonly string EnvironmentKey = "environment";
public static readonly string WebRootKey = "webroot";
public static readonly string CaptureStartupErrorsKey = "captureStartupErrors";
public static readonly string ServerUrlsKey = "urls";
public static readonly string ContentRootKey = "contentRoot";
public static readonly string PreferHostingUrlsKey = "preferHostingUrls";
public static readonly string PreventHostingStartupKey = "preventHostingStartup";
public static readonly string SuppressStatusMessagesKey = "suppressStatusMessages";
public static readonly string ShutdownTimeoutKey = "shutdownTimeoutSeconds";
public static readonly string StaticWebAssetsKey = "staticWebAssets";
}
5. HttpContext
:::tip
nuget : Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Abstractions
namespace : Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http
:::
public abstract class HttpContext
{
public abstract IFeatureCollection Features { get; }
public abstract HttpRequest Request { get; }
public abstract HttpResponse Response { get; }
...
}
public abstract class HttpRequest
{
public abstract HttpContext HttpContext { get; }
...
}
public abstract class HttpResponse
{
public abstract HttpContext HttpContext { get; }
...
}
5.1 默认实现
:::tip
nuget : Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http
namespace : Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http
:::
public sealed class DefaultHttpContext : HttpContext
{
public DefaultHttpContext(IFeatureCollection features);
}
internal sealed class DefaultHttpRequest : HttpRequest
{
public DefaultHttpRequest(DefaultHttpContext context);
}
internal sealed class DefaultHttpResponse : HttpResponse
{
public DefaultHttpResponse(DefaultHttpContext context)
}
5.2 特性Features
用于不同服务器和抽象的HttpContext适配。
:::tip
nuget : Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Features
namespace : Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Features
:::
public interface IFeatureCollection : IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<Type, object>>, IEnumerable
{
bool IsReadOnly { get; }
int Revision { get; }
object this[Type key] { get; set; }
TFeature Get<TFeature>();
void Set<TFeature>(TFeature instance);
}
public class FeatureCollection : IFeatureCollection
{
}
5.3 获取上下文
如果第三方组件需要获取表示当前请求上下文的HttpContext对象,就可以通过注入IHttpContextAccessor服务来实现。
// nuget: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Abstractions
// namespace: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http
public interface IHttpContextAccessor
{
HttpContext HttpContext { get; set; }
}
// nuget: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http
// namespace: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http
public class HttpContextAccessor : IHttpContextAccessor
{
public HttpContext HttpContext
{
get
{
HttpContextAccessor.HttpContextHolder value = HttpContextAccessor._httpContextCurrent.Value;
if (value == null)
{
return null;
}
return value.Context;
}
set
{
HttpContextAccessor.HttpContextHolder value2 = HttpContextAccessor._httpContextCurrent.Value;
if (value2 != null)
{
value2.Context = null;
}
if (value != null)
{
HttpContextAccessor._httpContextCurrent.Value = new HttpContextAccessor.HttpContextHolder
{
Context = value
};
}
}
}
private static AsyncLocal<HttpContextAccessor.HttpContextHolder> _httpContextCurrent =
new AsyncLocal<HttpContextAccessor.HttpContextHolder>();
private class HttpContextHolder
{
public HttpContext Context;
}
}
注册服务
// nuget: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http
// namespace: Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection
public static class HttpServiceCollectionExtensions
{
public static IServiceCollection AddHttpContextAccessor(this IServiceCollection services)
{
if (services == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("services");
}
services.TryAddSingleton<IHttpContextAccessor, HttpContextAccessor>();
return services;
}
}
5.4 创建和释放
// nuget: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Abstractions
// namespace: Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http
public interface IHttpContextFactory
{
HttpContext Create(IFeatureCollection featureCollection);
void Dispose(HttpContext httpContext);
}
public class DefaultHttpContextFactory : IHttpContextFactory
{
private readonly IHttpContextAccessor _httpContextAccessor;
private readonly FormOptions _formOptions;
private readonly IServiceScopeFactory _serviceScopeFactory;
public DefaultHttpContextFactory(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
this._httpContextAccessor = serviceProvider.GetService<IHttpContextAccessor>();
this._formOptions = serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<IOptions<FormOptions>>().Value;
this._serviceScopeFactory = serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<IServiceScopeFactory>();
}
}
5.5 RequestServices
ASP.NET Core框架存在两个用于提供所需服务的依赖注入容器:一个是针对应用程序,另一个是针对当前请求。IServiceProvidesFeature特性提供针对当前请求的IServiceProvider。绑定到HttpContext上下文的RequestServices属性正是来源于此。
//nuget : Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Features
//namespace : Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Features
public interface IServiceProvidersFeature
{
IServiceProvider RequestServices { get; set; }
}
//nuget : Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http
//namespace : Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Features
public class RequestServicesFeature : IServiceProvidersFeature, IDisposable, IAsyncDisposable
{
private readonly IServiceScopeFactory _scopeFactory;
private readonly HttpContext _context;
private IServiceProvider _requestServices;
private IServiceScope _scope;
private bool _requestServicesSet;
public RequestServicesFeature(HttpContext context, IServiceScopeFactory scopeFactory)
{
this._context = context;
this._scopeFactory = scopeFactory;
}
public IServiceProvider RequestServices
{
get
{
if (!this._requestServicesSet && this._scopeFactory != null)
{
this._context.Response.RegisterForDisposeAsync(this);
this._scope = this._scopeFactory.CreateScope();
this._requestServices = this._scope.ServiceProvider;
this._requestServicesSet = true;
}
return this._requestServices;
}
set
{
this._requestServices = value;
this._requestServicesSet = true;
}
}
public void Dispose()
{
this.DisposeAsync().ConfigureAwait(false).GetAwaiter().GetResult();
}
public ValueTask DisposeAsync(){}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号