SpringMVC(二):使用注解开发
-
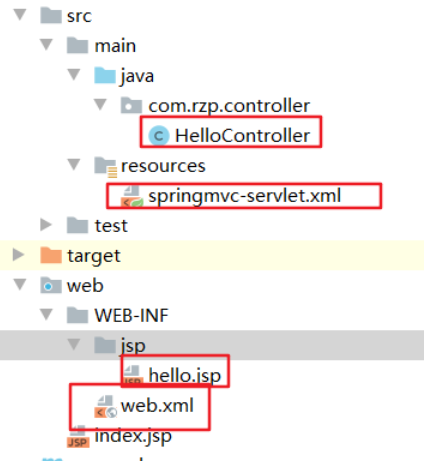
结构和前一篇是一样的
-
web.xml
-
也和原来的一样
-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <!--注册DispatcherServlet--> <!--这个类是Spring写好的,我们直接注册就可以了--> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!--导入spring的配置文件--> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml</param-value> </init-param> <!--启动级别--> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!--所有的请求都会经过这个类--> <!--/ 匹配所有的请求(不包括jsp)--> <!--/* 匹配所有的请求(包括jsp)--> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
-
springmvc-servlet.xml
-
和原来的不同点:
-
导入context依赖,使注解生效
-
使用mvc默认的handler,不过滤静态资源
-
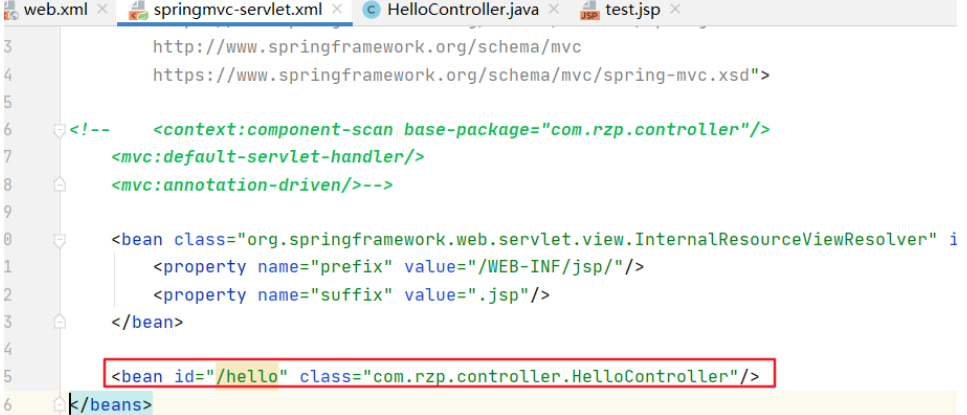
使用mvc:annotation-driven替代原来的映射器和适配器。
-
不再需要在spring里面注册类了
-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <!--自动扫描包,让指定包下的注解生效,由IOC容器管理--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.rzp.controller"/> <!--让SpringMVC不处理静态资源,过滤了.css .js .html .mp3这些静态资源,否则这些资源无法生效--> <mvc:default-servlet-handler/> <!-- 支持mvc注解驱动,其实就是直接替代了映射器和适配器 一般采用@RequestMapping注解来完成映射关系 要想使@RequestMapping注解生效 必须向上下文中注册DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping(映射器) 和一个AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter(适配器)实例 这两个实例分别在类级别和方法级别处理。 而annotation-driven配置帮助我们自动完成上述两个实例的注入。 --> <mvc:annotation-driven/> <!--视图解析器:DispatcherServlet给他的ModelAndView--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="InternalResourceViewResolver"> <!--页面前缀--> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/> <!--页面后缀--> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean> </beans>
-
hello
-
使用注解以后:
-
不再需要继承Controller接口,直接增加Controller,就相当于在spring中注册了。
-
因为原来的url输入是在springmvc-servlet.xml中配置的,现在我们不在xml中配置,而是增加RequestMapping注解,在这里写上要输入的url。
-
原来最终输出的页面地址我们封装到ModeAndView对象中,现在我们直接返回一个字符串就可以了,这个字符串就和原来的ModeAndView.setView方法一样,会被视图解析器拼接处理最终找到我们的页面。
-
package com.rzp.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; //加了Controller注解的类,这个类中所有的方法,如果返回值是String而且有具体的页面可以跳转,就会被视图解析器解析。 @Controller // 如果在类上添加,则url要输入..../hello/h1,否则就直接写..../h1就可以了 //@RequestMapping("/hello") public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/h1") public String hello(Model model){ //封装数据 model.addAttribute("msg","HelloSpingMVCAnnotation!"); return "hello"; //会被视图解析器处理 } //多个页面的时候,可以直接添加一个方法就可以了 @RequestMapping("/h2") public String hello2(Model model){ //封装数据 model.addAttribute("msg","HelloSpingMVCAnnotation2!"); return "hello2"; //会被视图解析器处理 }
-
hello.jsp
-
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
${msg}
</body>
</html>
使用注解开发以后,就彻底的比servlet优化,我们不再需要每个类都要在xml文件里面注册,开发更加简单了。而两个xml文件都是固定的。
与注册xml对比
-
使用注册的方式,每个页面都要在xml文件中注册,而且一个页面就要给一个类,而使用注解开发我们一个类就可以直接写多个页面。
RESTful风格
-
SpringMVC对RESTful风格的支持:
对于下面这个Controller,有输入参数a和b,要正确显示页面,我们的url中就需要通过?a=1&b=2传入参数
@Controller public class RestfulStyile { //原来的方式要在URI最后增加?并且录入参数 http://localhost:8080/s04/add?a=1&b=2 @RequestMapping(value = "/add") public String test0( int a, int b, Model model){ int res = a+b; model.addAttribute("msg","结果为"+res); return "test"; } }
或者某些URI会暴露我们的动作(例如下面左边的URI),而RESTful风格就是避免这种做法,比如上面的?a=1&b=2应该变成/1/2,或者下面的右边的URI。
GET /rest/api/getDogs --> GET /rest/api/dogs 获取所有小狗
GET /rest/api/addDogs --> POST /rest/api/dogs 添加一个小狗
-
在SpringMVC中:
-
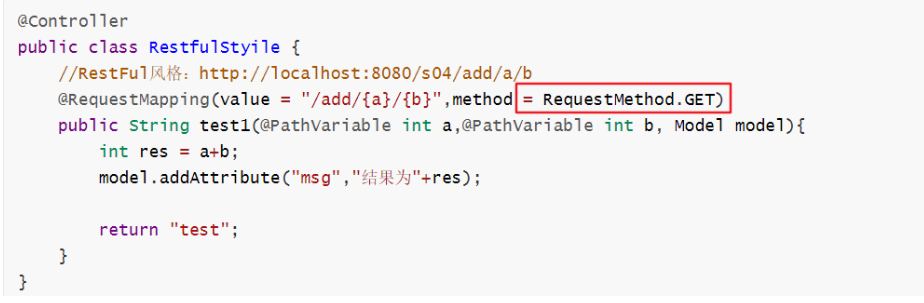
通过RequestMapping配置的value = "/add/{a}/{b}",以及在输入参数前面加入@PathVariable注解,就可以自动实现这种风格
-
@Controller public class RestfulStyile { //RestFul风格:http://localhost:8080/s04/add/a/b @RequestMapping(value = "/add/{a}/{b}",method = RequestMethod.GET) public String test1(@PathVariable int a,@PathVariable int b, Model model){ int res = a+b; model.addAttribute("msg","结果为"+res); return "test"; } }
-
测试

-
在RequestMapping中配置method = RequestMethod.GET可以指定我们的动作。
-
RequestMethod其实是RequestMapping下的枚举类。
-
-
除了通过枚举类以外,还可以直接把RequestMapping注解改为以下几种,达到同样的效果
@GetMapping
@PostMapping
@PutMapping
@DeleteMapping
@PatchMapping
例如:
@Controller public class RestfulStyile { @GetMapping(value = "/add/{a}/{b}") public String test1(@PathVariable int a,@PathVariable int b, Model model){ int res = a+b; model.addAttribute("msg","结果为"+res); return "test"; } }


