Spring (五):AOP
定义:
-
AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming) :面向切面编程
-
个人理解其实就是spring下的动态代理模式,说白了就是不影响原代码的情况下,横向增加代码扩充功能的设计思想.
-
-
AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容。是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
-
官方文档定义个人理解说明:
-
横切关注点:跨越应用程序多个模块的方法或功能。
-
切面(ASPECT) :横切关注点被模块化的特殊对象。
-
我们要自定义一个类,里面写上代理对象附加要实现的内容,这个类就是切面。
-
-
通知(Advice) :切面必须要完成的工作。
-
代理对象附加要实现的内容
-
-
目标(Target) :被通知对象。
-
真实对象。
-
-
代理(Proxy) :向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象。
-
代理对象,Spring AOP封装了代理对象的生成,我们不用管怎么生成的。
-
-
切入点(PointCut) :切面通知执行的“地点”的定义。
-
什么地方要执行代理对象的方法,比如定义某个类,那么这个类的所有方法都会执行代理方法。
-
-
连接点UointPoint) :与切入点匹配的执行点。
-
导入依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver --> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.5</version> </dependency>
方式一:使用原生Spring API接口
-
需要注入aop配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
-
真实对象接口
package com.rzp.service; public interface UserService { public void add(); public void delete(); public void update(); public void query(); }
-
真实对象
package com.rzp.service; //真实对象 public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { public void add() { System.out.println("增加用户"); } public void delete() { System.out.println("删除用户"); } public void update() { System.out.println("更新用户"); } public void query() { System.out.println("查询用户"); } }
-
LOG类
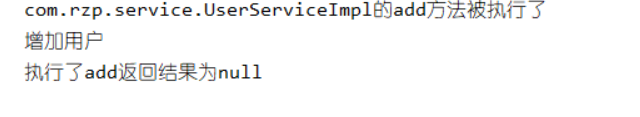
package com.rzp.log; import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice; import java.lang.reflect.Method; //继承MethodBeforeAdvice,重写的before方法会在真实对象方法执行前会执行 public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice { //method 要执行的目标对象的方法 //Object[] 参数 //target 目标对象 public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println(target.getClass().getName()+"的"+method.getName()+"方法被执行了"); } }
-
afterLog类
package com.rzp.log; import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice; import java.lang.reflect.Method; //继承AfterReturningAdvice,重写的afterReturning会在真实对象方法执行后执行 public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice { //returnValue 返回值 public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println("执行了"+method.getName()+"返回结果为"+returnValue); } }
-
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <bean id="userService" class="com.rzp.service.UserServiceImpl"/> <bean id="log" class="com.rzp.log.Log"/> <bean id="afterlog" class="com.rzp.log.AfterLog"/> <!--方式一,使用原生Spring API接口--> <!--配置aop--> <aop:config> <!--定义切入点,在什么地方切入 expression:表达式 executiion(要执行的位置)--> <!--1、execution(): 表达式主体。 2、第一个*号:表示返回类型,*号表示所有的类型。 3、包名:表示需要拦截的包名,后面的两个句点表示当前包和当前包的所有子孙包下所有类的方法。 4、第二个*号:表示类名,*号表示所有的类。 5、*(..):最后这个星号表示方法名,*号表示所有的方法,后面括弧里面表示方法的参数,两个句点表示任何参数--> <aop:pointcut id="pointc" expression="execution(* com.rzp.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/> <!--执行环绕增加--> <aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointc"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="afterlog" pointcut-ref="pointc"/> </aop:config> </beans>
-
测试
import com.rzp.service.UserService; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Mytest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext contest = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserService user = contest.getBean("userService", UserService.class); user.add(); } }
方式二:使用自定义类来实现AOP
-
自定义类
package com.rzp.diy; public class DiyPointCut { public void before(){ System.out.println("方法执行前"); } public void after(){ System.out.println("方法执行后"); } }
-
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <bean id="userService" class="com.rzp.service.UserServiceImpl"/> <bean id="log" class="com.rzp.log.Log"/> <bean id="afterlog" class="com.rzp.log.AfterLog"/> <!--方式二,使用自定义类--> <bean id="diy" class="com.rzp.diy.DiyPointCut"/> <aop:config> <!--自定义切面,ref引用的类--> <aop:aspect ref="diy"> <aop:pointcut id="point" expression="execution(* com.rzp.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/> <!--通知--> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="point"/> <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="point"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
-
测试
import com.rzp.service.UserService; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Mytest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext contest = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserService user = contest.getBean("userService", UserService.class); user.add(); } }

-
没有方式一好,因为方式一还能通过反射获取到真实对象的信息。
方式三:使用注解实现
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <bean id="userService" class="com.rzp.service.UserServiceImpl"/> <bean id="log" class="com.rzp.log.Log"/> <bean id="afterlog" class="com.rzp.log.AfterLog"/> <!--方式三:使用注解开发--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.rzp.*"/> <context:annotation-config/> <!--开启注解AOP支持,JDK5 默认proxy-target-class="false" Cglib proxy-target-class="true"--> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/> </beans>
-
自定义类
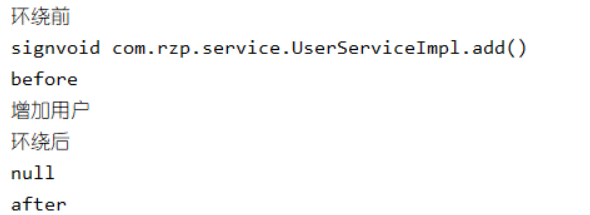
package com.rzp.diy; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.Signature; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect //标注这个类是一个切面 @Component public class AnnotationPointCut { @Before("execution(* com.rzp.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") public void before(){ System.out.println("before"); } @After("execution(* com.rzp.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") public void after(){ System.out.println("after"); } //在环绕增强中,我们可以给定一个参数,代表我们要获取处理切入的点 @Around("execution(* com.rzp.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("环绕前"); //获得签名--其实就是执行了真实对象的什么方法 Signature signature = jp.getSignature(); System.out.println("sign"+signature); //执行方法 Object proceed = jp.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕后"); System.out.println(proceed); } }
-
其他不变,测试结果