Spring(一):Spring入门程序和IoC初步理解
-
Spring是一个轻量级控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架。
-
Spring框架即以interface21框架为基础,经过重新设计,于2004年3月发布。
-
作者:Rod Johnson
-
目的:解决企业开发的复杂性。
-
理念:使现有的技术更加容易使用,本身是一个大杂烩,整合了现有的技术框架。
优点:Spring是一个开源免费的框架。
-
是一个轻量级、非入侵式的框架。
-
轻量级:本体很小。
-
非入侵式:不会印象原来的代码
-
-
控制反转(IOC),面向切面编程(AOP)
-
支持事务的处理,对框架整合的支持。
-
SSH:Struts2 Spring Hibernate
-
SSM:SpringMVC Spring Mybatis
Github:https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework
maven:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
Spring 7大功能模块

拓展

-
Spring Boot:一个快速开发的框架
-
基于Spring Boot可以快速的开发单个微服务。
-
-
Spring Cloud
-
Spring Cloud是基于Spring Boot实现的。
-
学习Spring Boot的前提,需要完全掌握Spring及SpringMVC。
弊端:发展了太久后,违背了原来的理念,配置十分繁琐。
IOC理论推导
-
Inversion of Control,控制反转。
-
控制反转是一种设计思想,依赖注入(DI)是实现IoC的一种方法。
-
没有IoC的程序中,我们使用面向对象编程,对象的创建与对象间的依赖关系完全硬编码在程序中,对象的创建由程序控制。
-
控制反转后将对象的创建转移给第三方---获得依赖对象的方式反转了。
原来写代码,我们这样写:
-
UserDao接口 ---限制了CRUD的方法规范,保证其他类能正确调用
public interface UserDao { void getUser(); }
-
UserDaoImpl实现类 ---具体实现了CRUD的方法,其他类不需要管如何实现的
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { public void getUser() { System.out.println("获取用户数据"); } }
-
UserService 业务接口 ---限制了业务操作的规范,保证了交互类能正确调用
public interface UserService { void getUser(); }
-
UserServiceImpl 业务实现类 ---业务操作的具体实现方法,通常在这里会调用UserDaoImpl的方法来执行数据库操作
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { private UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl(); public void getUser() { userDao.getUser(); } }
-
交互层 ---只需要调用业务类的方法
public class MyTest01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //用户实际调用的是业务层,dao层不需要接触 UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl(); userService.getUser(); } }
-
在这种情况下,用户的需求可能会影响我们原来的代码,比如增加了一个dao类
public class UserDaoMysqlImpl implements UserDao { public void getUser() { System.out.println("MySQL获取用户数据"); } }
-
这个时候我们就需要修改UserServiceImpl 的代码
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { //增加一个UserDaoMysqlImpl后,必须要修改这里的代码改成UserDaoMysqlImpl //private UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl(); private UserDao userDao = new UserDaoMysqlImpl(); public void getUser() { userDao.getUser(); } }
如果程序代码量大,就会导致程序修改量大。
-
如果UserServiceImpl 使用一个Set接口实现
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { private UserDao userDao; //利用set进行动态实现值的注入 public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; } public void getUser() { userDao.getUser(); } }
-
那么相应的,交互层就改成了:
public class MyTest01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl(); //交互层选择使用什么对象创建。 userService.setUserDao(new UserDaoMysqlImpl()); userService.getUser(); } }
-
原来UserServiceImpl的对象创建是写死的,现在通过set方法变成了由客户主动选择创建什么对象。
-
这就叫做控制反转,把主动权放在了客户手上。
-
这种思想,从本质上解决了问题,程序员不再需要管理对象的创建。系统的耦合性大大降低。可以更加专注在新业务的实现上。
IoC与Spring
-
IoC是Spring框架的核心内容,使用多种方式完美的实现了IoC,可以使用xml配置,也可以使用注解,新版本的Spring也可以零配置实现IoC。
-
Spring容器在初始化时先读取配置文件,根据配置文件和元数据创建与组织对象存入容器中,程序使用时再从IoC容器取出需要的对象。
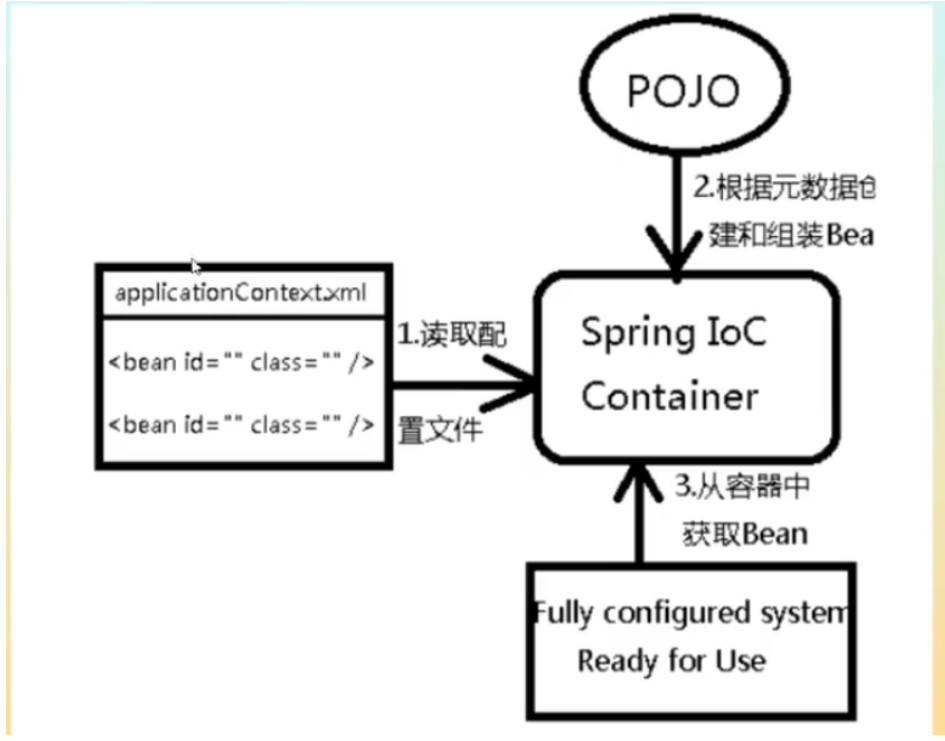
-
Spring有两种方式配置Bean:
-
采用xml的方式配置,Bean的定义信息和实现分离的。
-
采用注解的方式配置,可以把两者合为一体,Bean的定义信息直接以注解的行释定义在实现类中,从而达到零配置的目的。
-
-
控制反转是一种通过描述(XML或注解)并通过第三方生产或获取特定对象的方式,在Spring中实现控制反转的是IoC容器,其实现方法是依赖注入(Dependecy Injection,DI)。
示例程序
-
beans
package com.rzp.pojo; public class Hello { private String str; public String getStr() { return str; } public void setStr(String str) { this.str = str; } @Override public String toString() { return "Hello{" + "str='" + str + '\'' + '}'; } }
-
beans.xml(Spring推荐使用的名字是applicationContext.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--使用Spring来创建对象,在Spring中这些都成为Bean bean 相当于new了一个对象=====Hello hello = new Hello(); id = 变量名 class = new 的对象 property相当于给对象中的属性设置一个值 --> <bean id = "hello" class="com.rzp.pojo.Hello"> <!--Spring会利用set方法来赋值,因此没有set方法这行代码就不起作用--> <property name="str" value="Spring"/> </bean> </beans>
-
测试
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--使用Spring来创建对象,在Spring中这些都成为Bean bean 相当于new了一个对象=====Hello hello = new Hello(); id = 变量名 class = new 的对象 property相当于给对象中的属性设置一个值 --> <bean id = "hello" class="com.rzp.pojo.Hello"> <!--ref:引用Spring容器中创建好的对象 value : 具体的值,基本数据类型 如果是value,Spring会利用set方法来赋值,因此没有set方法这行代码就不起作用--> <property name="str" value="Spring"/> </bean> </beans>
-
这个过程就叫控制反转:
-
控制:传统应用程序的对象是由程序本身控制创建的,使用Spring后,对象是由Spring来创建的.
-
反转:程序本身不创建对象,而变成被动的接收对象.
-
依赖注入:就是利用set方法来进行注入的.
-
IOC是一种编程思想,由主动的编程变成被动的接收.
-
可以通过newClassPathXmlApplicationContext去浏览一下底层源码.
-
所谓的IoC:对象由IoC容器来创建,管理,装配!
示例程序2
如果使用Spring来实现最初的例子:
我们只需要增加配置beans.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id = "mysqlImpl" class="com.rzp.dao.UserDaoMysqlImpl"/> <bean id = "oracleImpl" class="com.rzp.dao.UserDaoOracleImpl"/> <bean id="UserServiceImpl" class="com.rzp.service.UserServiceImpl"> <property name="userDao" ref="mysqlImpl"/> </bean> </beans>
-
测试程序就不再需要new对象,对象的创建由xml文件决定。
-
这个时候如果需要修改mysqlImpl为oracleImpl,就不再需要改代码,完全可以由客户修改xml文件。
-
import com.rzp.dao.UserDaoImpl; import com.rzp.dao.UserDaoOracleImpl; import com.rzp.service.UserServiceImpl; import javafx.application.Application; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MyTest01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取Spring的容器 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserServiceImpl userServiceImpl = (UserServiceImpl) context.getBean("UserServiceImpl"); userServiceImpl.getUser(); } }


