Linux服务之nginx服务篇五(静态/动态文件缓存)
一、nginx实现静态文件缓存实战
1、nginx静态文件缓存
如果要熟练使用nginx来实现文件的缓存,那下面的几个指令你必须要牢记于心
(1)指令1:proxy_cache_path
作用:设置缓存数据的相关信息 Syntax: proxy_cache_path path [levels=levels] [use_temp_path=on|off] keys_zone=name:size [inactive=time] [max_size=size] [manager_files=number] [manager_sleep=time] [manager_threshold=time] [loader_files=number] [loader_sleep=time] [loader_threshold=time] [purger=on|off] [purger_files=number] [purger_sleep=time] [purger_threshold=time]; Default: — Context: http 值: path:缓存目录的位置 levels:指定使用几级缓存目录 keys_zone:指定缓存区域的名称和缓存空间的大小 例子: proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache levels=1:4 keys_zone=mycache:10m; 说明 1:表示一级目录可以由1个字符来构成 4:表示二级目录可以由4个字符来构成 mycache:是这个缓存区域的名称 10m:可以缓存10M大小的数据 缓存结果 /data/nginx/cache/c/29ad/b7f54b2df7773722d382f4809d65029c 说明 /data/nginx/cache/:这里是缓存目录 c:因为一级目录可以由1个字符构成,所有这里随机出现一个c 29ad:二级目录由4个随机字符构成 b7f54b2df7773722d382f4809d65029c:缓存的数据
(2)指令2:proxy_cache
作用:调用缓存 Syntax: proxy_cache zone | off; Default: proxy_cache off; Context: http, server, location 注意: 该指令写在不同的位置,缓存数据对象也不同
(3)指令3:proxy_cache_min_uses
作用:指定一个文件至少需要被用户访问多少次以后,才会被缓存,默认1 Syntax: proxy_cache_min_uses number; Default: proxy_cache_min_uses 1; Context: http, server, location
(4)指令4:proxy_cache_purge
Syntax: proxy_cache_purge string ...; Default: — Context: http, server, location 使用场景:上游服务器中的资源发生了更改,但是缓存中的数据尚未过去,这个时候就需要手动执行purge让缓存中的数据过去 使用举例: http { proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache levels=1:4 keys_zone=mycache:10m; server { listen 10.220.5.196:80; location / { proxy_pass http://10.220.5.180:80: proxy_cache mycache; .... .... } location = /cleanCache { allow= deny= proxy_cache_purge mycache; #这里需要指定上面定义的缓存名称 ... ... ... } } }
(5)指令5:proxy_cache_valid
作用:定义缓存数据的有效期 Syntax: proxy_cache_valid [code ...] time; Default: — Context: http, server, location 例子: proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m; proxy_cache_valid 301 1h; proxy_cache_valid any 1m;
(6)指令6:proxy_cache_key
作用:指定缓存的key的名称 Syntax: proxy_cache_key string; Default: proxy_cache_key $scheme$proxy_host$request_uri; Context: http, server, location 例子: proxy_cache_key "$host$request_uri $cookie_user"; proxy_cache_key "$uri"
2、nginx实现缓存配置
(1)环境准备
centos7.5
NGINX服务器端IP:172.20.10.8/28
HTTPD服务器端IP:172.20.10.7/28
HTTPD服务器端IP:172.20.10.9/28
客户端IP:172.20.10.4/28
(2)NGINX服务器端
使用yum下载nginx需要使用网络yum源,复制下面的代码到你的yum仓库即可下载
1 2 3 4 5 | [ken]name=kenenabled=1gpgcheck=0baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/epel/7Server/x86_64/ |
下载nginx
1 | [root@ken ~]# yum install nginx -y |
配置nginx文件
# For more information on configuration, see: # * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/ # * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/ user nginx; worker_processes auto; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; pid /run/nginx.pid; # Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/nginx/README.dynamic. include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; sendfile on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; keepalive_timeout 65; types_hash_max_size 2048; include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; # Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory. # See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include # for more information. #include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; proxy_cache_path /ken levels=1:2 keys_zone=kenken:100m; add_header host $server_addr; add_header cachestatus $upstream_cache_status; #添加本条可以在浏览器中看到是否命中缓存 server { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default_server; server_name _; root /var/www/html; # Load configuration files for the default server block. # include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; location / { proxy_pass http://172.20.10.7:80; proxy_set_header host $host; proxy_set_header realip $remote_addr; proxy_cache kenken; proxy_cache_min_uses 3; proxy_cache_valid any 10m; } } }
创建缓存目录
1 | [root@ken ~]# mkdir /ken |
更改缓存目录的属主和属组
1 | [root@ken ~]# chown -R nginx.nginx /ken |
启动nignx
1 2 3 4 | [root@ken ~]# systemctl start nginx[root@ken ~]# ss -tnl | grep 80LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:* LISTEN 0 128 :::80 :::* |
3、配置web服务端
下载httpd
[root@ken ~]# yum install httpd -y
准备测试文件
[root@ken ~]# echo "this is 172.20.10.7 for test">>/var/www/html/index.html
启动httpd
[root@ken ~]# systemctl restart httpd
4、浏览器测试
输入nginx服务器端的IP地址
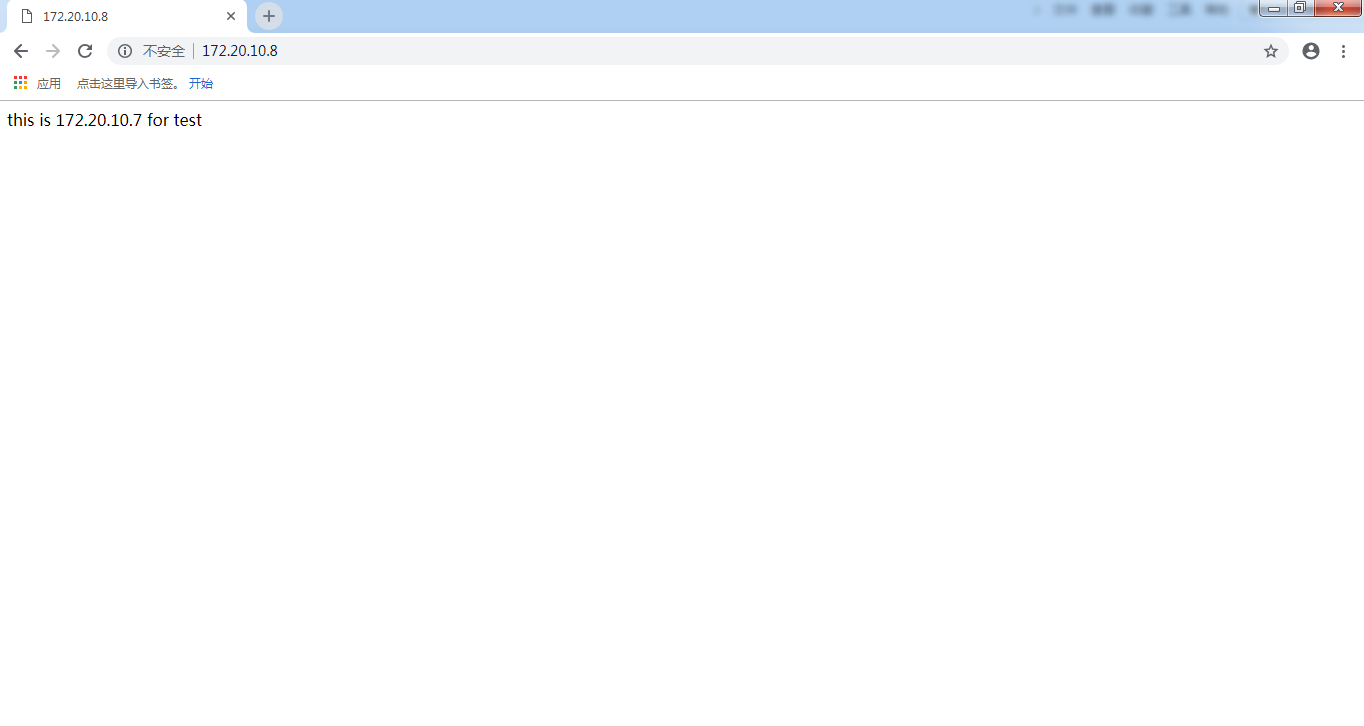
输入172.20.10.8的地址成功访问172.20.10.7的页面
查看web服务器端的访问日志
[root@ken ~]# tail -f /var/log/httpd/access_log 172.20.10.8 - - [02/Oct/2018:22:40:43 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.0" 200 29 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/69.0.3497.92 Safari/537.36"
成功捕捉到来自172.20.10.8的访问请求
我们去查看nginx服务端是否已经有缓存产生
[root@ken /]# ls /ken/e/55/58be92261b4ffa2c4fe7e92be2f0255e
测试成功!
在nginx服务器端已经产生了缓存,再次刷新浏览器界面,在web服务器端都不会再产生访问日志,因为现在客户请求是直接从缓存提取的,没有再往后方节点来访问文件,这样可以大大提高网站的负载和并发能力。
二、NGINX实现动态文件缓存实战
在完成了上面的静态文件缓存之后,相信动态文件的缓存对你来说也是轻而易举了,下面我们一鼓作气完成对动态文件的缓存吧。
1、环境准备
centos7.5
NGINX服务器端IP:172.20.10.8/28
WEB服务器端IP:172.20.10.9/28
2、配置NGINX服务器端
下载php
[root@ken ~]# yum install php php-fpm -y
配置nginx文件
# For more information on configuration, see:
# * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
# * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
#include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
fastcgi_cache_path /kenken levels=1:2 keys_zone=kenken:100m;
add_header host $server_addr;
add_header cachestatus $upstream_cache_status;
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name _;
root /var/www/html;
index index.php;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
# include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location ~^/.*(\.php)$ {
fastcgi_pass 172.20.10.9:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi.conf;
fastcgi_cache kenken;
fastcgi_cache_valid any 10m;
fastcgi_cache_key $request_uri;
}
}
}
创建缓存目录,并修改权限
[root@ken ~]# mkdir /kenken [root@ken ~]# chown -R nginx.nginx /kenken
nginx语法检测
[root@ken ~]# nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
启动nginx
[root@ken ~]# systemctl restart nginx
3、配置web服务器端
下载所需服务程序
[root@ken ~]# yum install httpd php-fpm php -y
配置php-fpm
[root@ken ~]# vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf ... 10 ; '/path/to/unix/socket' - to listen on a unix socket. 11 ; Note: This value is mandatory. 12 listen = 172.20.10.9:9000 #修改为本机ip地址 13 14 ; Set listen(2) backlog. A value of '-1' means unlimited. 15 ; Default Value: -1 16 ;listen.backlog = -1 17 18 ; List of ipv4 addresses of FastCGI clients which are allowed to connect. 19 ; Equivalent to the FCGI_WEB_SERVER_ADDRS environment variable in the original 20 ; PHP FCGI (5.2.2+). Makes sense only with a tcp listening socket. Each address 21 ; must be separated by a comma. If this value is left blank, connections will be 22 ; accepted from any ip address. 23 ; Default Value: any 24 listen.allowed_clients = 172.20.10.8 #修改为nginx服务端地址 ...
启动php-fpm
[root@ken ~]# systemctl restart php-fpm [root@ken ~]# ss -tnl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 172.20.10.9:9000 *:*
准备动态测试文件
[root@ken ~]# cd /var/www/html/ [root@ken html]# ls index.html [root@ken html]# vim index.php <?php phpinfo(); ?>
重启nginx
[root@ken ~]# systemctl restart nginx
浏览器输入nginx服务端ip地址进行测试
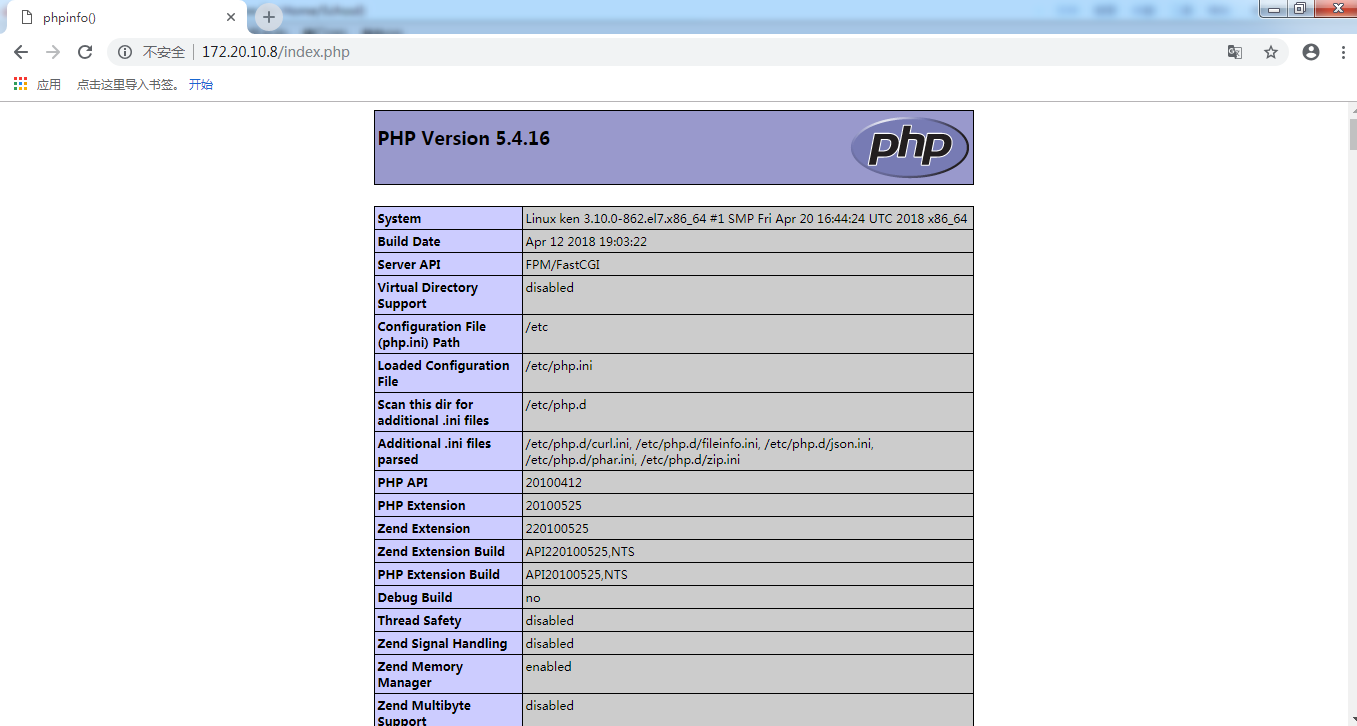
访问成功,刷新几次查看nginx是否已经产生缓存
[root@ken ~]# ls /kenken/ 1/ b/ e/ [root@ken ~]# ls /kenken/b/fe/c86156f7dcfecf44876ca30d1bac7feb
动态文件缓存成功!






【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux glibc自带哈希表的用例及性能测试
· 深入理解 Mybatis 分库分表执行原理
· 如何打造一个高并发系统?
· .NET Core GC压缩(compact_phase)底层原理浅谈
· 现代计算机视觉入门之:什么是图片特征编码
· 手把手教你在本地部署DeepSeek R1,搭建web-ui ,建议收藏!
· Spring AI + Ollama 实现 deepseek-r1 的API服务和调用
· 数据库服务器 SQL Server 版本升级公告
· 程序员常用高效实用工具推荐,办公效率提升利器!
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 23 期(2025年1.20-1.26)