Android 事件分发与责任链模式
一、责任链模式
责任链模式是一种行为模式,为请求创建一个接收者的对象链.这样就避免,一个请求链接多个接收者的情况.进行外部解耦.类似于单向链表结构。
优点:
1. 降低耦合度。它将请求的发送者和接收者解耦。
2. 简化了对象。使得对象不需要知道链的结构。
3. 增强给对象指派职责的灵活性。通过改变链内的成员或者调动它们的次 序,允许动态地新增或者删除责任。
4. 增加新的请求处理类很方便。
缺点:
1. 不能保证请求一定被接收。
2. 系统性能将受到一定影响,而且在进行代码调试时不太方便,可能会造成循环调用。
3. 可能不容易观察运行时的特征,有碍于除错。
在Android事件分发机制是责任链模式最典型的应用:
dispatchTouchEvent的,就是责任链中的将事件交给下一级处理的.
onInterceptTouchEvent ,就是责任链中,处理自己处理事务的方法.
onTouchEvent 是责任链中 事件上报的事件链。
下面我们来通过Android事件分发机制来感悟一下责任链模式在Android中的应用。
二、Android 事件分发传递机制
1. View事件传递分发层级结构
a). 事件收集之后最先传递给 Activity, 然后依次向下传递,大致如下:
Activity -> PhoneWindow -> DecorView -> ViewGroup -> ... -> View
这样的事件分发机制逻辑非常清晰,可是,你是否注意到一个问题?如果最后分发到View,如果这个View也没有处理事件怎么办,就这样让事件浪费掉?当然不会啦。
b). 如果没有任何View消费掉事件,那么这个事件会按照反方向回传,最终传回给Activity,如果最后 Activity 也没有处理,本次事件才会被抛弃:
Activity <- PhoneWindow <- DecorView <- ViewGroup <- ... <- View
可以看到,这是一个非常经典的责任链模式,如果我能处理就拦截下来自己干,如果自己不能处理或者不确定就交给责任链中下一个对象。 这种设计是非常精巧的,上层View既可以直接拦截该事件,自己处理,也可以先询问(分发给)子View,如果子View需要就交给子View处理,如果子View不需要还能继续交给上层View处理。既保证了事件的有序性,又非常的灵活。
View点击事件分发有三个关键流程方法:
1.dispatchTouchEvent:事件下发 --- View和ViewGroup都有的方法
2.onInterceptTouchEvent:拦截下发的事件,并交给自己OnTouchEvent处理处理 ---ViewGroup才有的方法
3.onTouchEvent:事件上报 --- View和ViewGroup都有的方法
以下是不同层级对事件的分发、拦截和消费的功能表:
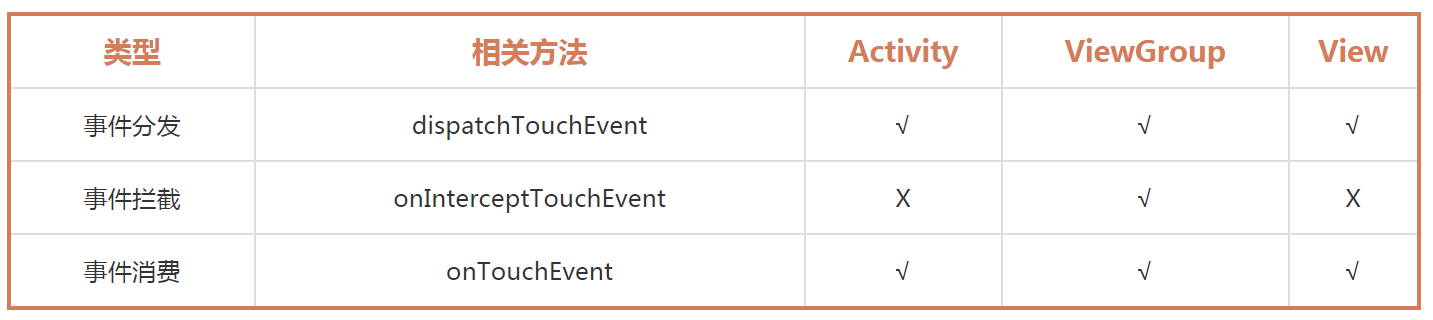
可以看到 Activity 和 View 都是没有事件拦截的:
a). Activity 作为原始的事件分发者,如果 Activity 拦截了事件会导致整个屏幕都无法响应事件,这肯定不是我们想要的效果。
b). View最为事件传递的最末端,要么消费掉事件,要么不处理进行回传,根本没必要进行事件拦截。
下图是点击View,事件传递但是都没有被处理,生成的一个完整的事件分发流程图:
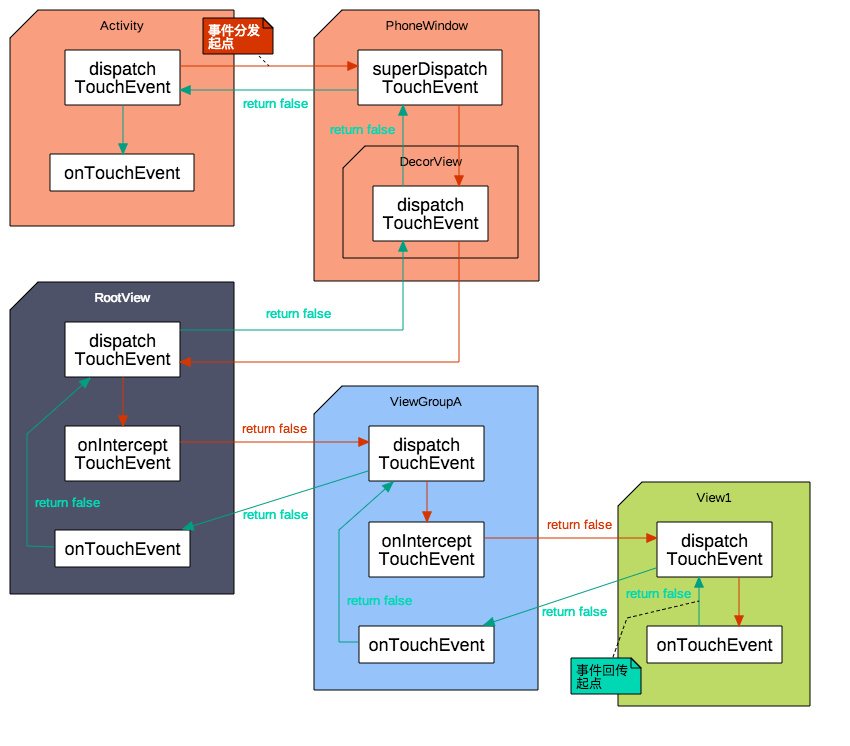
如果事件被View处理了,那么事件分发流程图应该如下:
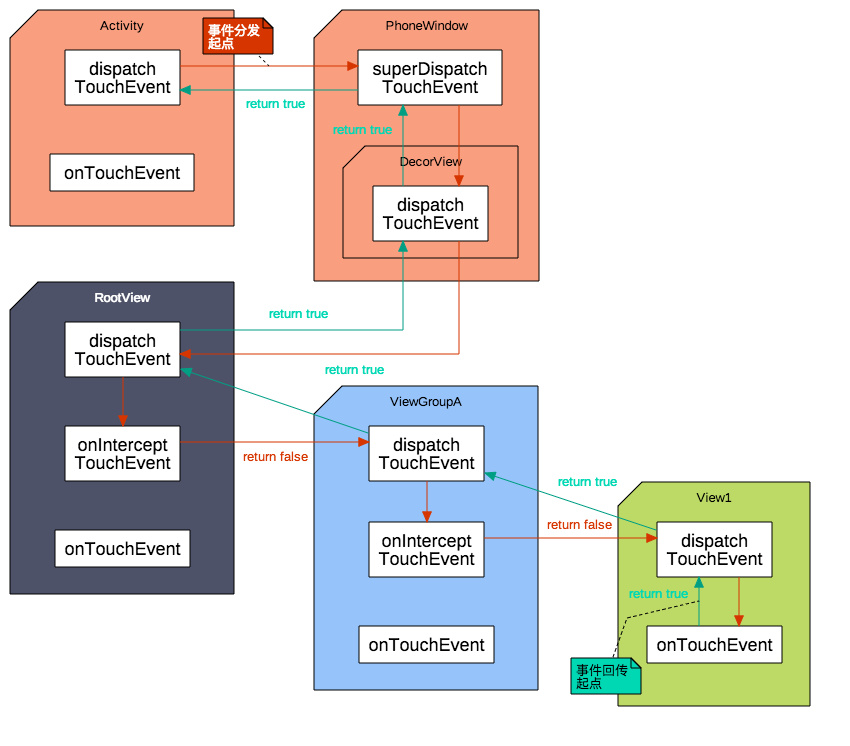
如果事件被ViewGroup拦截处理了, 那么事件分发流程图应该如下:

从上面的流程,我们可以概括Android的事件分发机制为:责任链模式,事件层层传递,直到被消费。
三、Q&A
上面我们讲解了一下Android的事件分发机制,可能很多人会有疑惑,下面我们针对部分疑惑进行分析和说明:
1. 为什么 View 会有 dispatchTouchEvent ?
答:我们知道 View 可以注册很多事件监听器,例如:单击事件(onClick)、长按事件(onLongClick)、触摸事件(onTouch),并且View自身也有 onTouchEvent 方法,那么问题来了,这么多与事件相关的方法应该由谁管理?毋庸置疑就是 dispatchTouchEvent,所以 View 也会有事件分发。
View的dispatchTouchEvent源码:

/** * Pass the touch screen motion event down to the target view, or this * view if it is the target. * * @param event The motion event to be dispatched. * @return True if the event was handled by the view, false otherwise. */ public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { // If the event should be handled by accessibility focus first. if (event.isTargetAccessibilityFocus()) { // We don't have focus or no virtual descendant has it, do not handle the event. if (!isAccessibilityFocusedViewOrHost()) { return false; } // We have focus and got the event, then use normal event dispatch. event.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false); } boolean result = false; if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) { mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onTouchEvent(event, 0); } final int actionMasked = event.getActionMasked(); if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) { // Defensive cleanup for new gesture stopNestedScroll(); } if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) { if ((mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED && handleScrollBarDragging(event)) { result = true; } //noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo; if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null && (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED && li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) { result = true; } if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) { result = true; } } if (!result && mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) { mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(event, 0); } // Clean up after nested scrolls if this is the end of a gesture; // also cancel it if we tried an ACTION_DOWN but we didn't want the rest // of the gesture. if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP || actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL || (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN && !result)) { stopNestedScroll(); } return result; }
2. View事件分发时各个方法调用顺序是怎样的?
a). 单击事件(onClickListener) 需要两个两个事件(ACTION_DOWN 和 ACTION_UP )才能触发,如果先分配给onClick判断,等它判断完再交由其他相应时间显然是不合理的,会造成 View 无法响应其他事件,应该最后调用。(所以此调用顺序最后)
b). 长按事件(onLongClickListener) 同理,也是需要长时间等待才能出结果,肯定不能排到前面,但因为不需要ACTION_UP,应该排在 onClick 前面。(onLongClickListener > onClickListener)
c). 触摸事件(onTouchListener) 如果用户注册了触摸事件,说明用户要自己处理触摸事件了,这个应该排在最前面。(最前)
d). View自身处理(onTouchEvent) 提供了一种默认的处理方式,如果用户已经处理好了,也就不需要了,所以应该排在 onClickListener 后面。(onTouchListener > onClickListener)
所以事件的调度顺序应该是 onTouchListener > onTouchEvent > onLongClickListener > onClickListener。
3. ViewGroup 的事件分发流程又是如何的呢?
在默认的情况下 ViewGroup 事件分发流程是这样的。
a). 判断自身是否需要(询问 onInterceptTouchEvent 是否拦截),如果需要,调用自己的 onTouchEvent。
b). 自身不需要或者不确定,则询问 ChildView ,一般来说是调用手指触摸位置的 ChildView。
c). 如果子 ChildView 不需要则调用自身的 onTouchEvent。
ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent源码:

@Override public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) { mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onTouchEvent(ev, 1); } // If the event targets the accessibility focused view and this is it, start // normal event dispatch. Maybe a descendant is what will handle the click. if (ev.isTargetAccessibilityFocus() && isAccessibilityFocusedViewOrHost()) { ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false); } boolean handled = false; if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(ev)) { final int action = ev.getAction(); final int actionMasked = action & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK; // Handle an initial down. if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) { // Throw away all previous state when starting a new touch gesture. // The framework may have dropped the up or cancel event for the previous gesture // due to an app switch, ANR, or some other state change. cancelAndClearTouchTargets(ev); resetTouchState(); } // Check for interception. final boolean intercepted; if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN || mFirstTouchTarget != null) { final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0; if (!disallowIntercept) { intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev); ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed } else { intercepted = false; } } else { // There are no touch targets and this action is not an initial down // so this view group continues to intercept touches. intercepted = true; } // If intercepted, start normal event dispatch. Also if there is already // a view that is handling the gesture, do normal event dispatch. if (intercepted || mFirstTouchTarget != null) { ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false); } // Check for cancelation. final boolean canceled = resetCancelNextUpFlag(this) || actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL; // Update list of touch targets for pointer down, if needed. final boolean split = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_SPLIT_MOTION_EVENTS) != 0; TouchTarget newTouchTarget = null; boolean alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = false; if (!canceled && !intercepted) { // If the event is targeting accessibility focus we give it to the // view that has accessibility focus and if it does not handle it // we clear the flag and dispatch the event to all children as usual. // We are looking up the accessibility focused host to avoid keeping // state since these events are very rare. View childWithAccessibilityFocus = ev.isTargetAccessibilityFocus() ? findChildWithAccessibilityFocus() : null; if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN || (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN) || actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) { final int actionIndex = ev.getActionIndex(); // always 0 for down final int idBitsToAssign = split ? 1 << ev.getPointerId(actionIndex) : TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS; // Clean up earlier touch targets for this pointer id in case they // have become out of sync. removePointersFromTouchTargets(idBitsToAssign); final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount; if (newTouchTarget == null && childrenCount != 0) { final float x = ev.getX(actionIndex); final float y = ev.getY(actionIndex); // Find a child that can receive the event. // Scan children from front to back. final ArrayList<View> preorderedList = buildTouchDispatchChildList(); final boolean customOrder = preorderedList == null && isChildrenDrawingOrderEnabled(); final View[] children = mChildren; for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) { final int childIndex = getAndVerifyPreorderedIndex( childrenCount, i, customOrder); final View child = getAndVerifyPreorderedView( preorderedList, children, childIndex); // If there is a view that has accessibility focus we want it // to get the event first and if not handled we will perform a // normal dispatch. We may do a double iteration but this is // safer given the timeframe. if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != null) { if (childWithAccessibilityFocus != child) { continue; } childWithAccessibilityFocus = null; i = childrenCount - 1; } if (!canViewReceivePointerEvents(child) || !isTransformedTouchPointInView(x, y, child, null)) { ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false); continue; } newTouchTarget = getTouchTarget(child); if (newTouchTarget != null) { // Child is already receiving touch within its bounds. // Give it the new pointer in addition to the ones it is handling. newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign; break; } resetCancelNextUpFlag(child); if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) { // Child wants to receive touch within its bounds. mLastTouchDownTime = ev.getDownTime(); if (preorderedList != null) { // childIndex points into presorted list, find original index for (int j = 0; j < childrenCount; j++) { if (children[childIndex] == mChildren[j]) { mLastTouchDownIndex = j; break; } } } else { mLastTouchDownIndex = childIndex; } mLastTouchDownX = ev.getX(); mLastTouchDownY = ev.getY(); newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign); alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true; break; } // The accessibility focus didn't handle the event, so clear // the flag and do a normal dispatch to all children. ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false); } if (preorderedList != null) preorderedList.clear(); } if (newTouchTarget == null && mFirstTouchTarget != null) { // Did not find a child to receive the event. // Assign the pointer to the least recently added target. newTouchTarget = mFirstTouchTarget; while (newTouchTarget.next != null) { newTouchTarget = newTouchTarget.next; } newTouchTarget.pointerIdBits |= idBitsToAssign; } } } // Dispatch to touch targets. if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) { // No touch targets so treat this as an ordinary view. handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null, TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS); } else { // Dispatch to touch targets, excluding the new touch target if we already // dispatched to it. Cancel touch targets if necessary. TouchTarget predecessor = null; TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget; while (target != null) { final TouchTarget next = target.next; if (alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget && target == newTouchTarget) { handled = true; } else { final boolean cancelChild = resetCancelNextUpFlag(target.child) || intercepted; if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, cancelChild, target.child, target.pointerIdBits)) { handled = true; } if (cancelChild) { if (predecessor == null) { mFirstTouchTarget = next; } else { predecessor.next = next; } target.recycle(); target = next; continue; } } predecessor = target; target = next; } } // Update list of touch targets for pointer up or cancel, if needed. if (canceled || actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP || actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) { resetTouchState(); } else if (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP) { final int actionIndex = ev.getActionIndex(); final int idBitsToRemove = 1 << ev.getPointerId(actionIndex); removePointersFromTouchTargets(idBitsToRemove); } } if (!handled && mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) { mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(ev, 1); } return handled; }
可能看这么长的代码,我们会比较懵,下面我们用伪代码来表示一下:
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { boolean consume = false; if (onInterceptTouchEvent(ev)) { consume = onTouchEvent(ev); } else { consume = child.dispatchTouchEvent(ev) } return consume; }
这样我们就能更直白的看懂View事件的传递机制了。
4. ViewGroup将事件分发给ChildView的机制
- ViewGroup分发事件时会遍历 ChildView,如果手指触摸的点在 ChildView 区域内就分发给这个View。当 ChildView 重叠时,一般会分配给显示在最上面的 ChildView。
- ViewGroup判断是否需要拦截,主要是根据onInterruptTouchEvent的返回值进行判断。
- 在Down事件中将touch事件分发给ChildView,如果有ChildView捕获消费了Down事件,就会对mFirstTouchTarget进行赋值。mFirstTouchTarget的作用就是记录消费事件的View。
- 在ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent方法中,会根据mFirstTouchTarget 是否为 null,决定是自己处理 touch 事件,还是分发给子 View。
- Down事件是touch事件序列的起点,决定了后续的事件由谁来消费处理。Cancel事件的触发场景为:父View先不拦截,但在MOVE事件中又重新拦截,此时子View会收到一个Cancel事件,
5. ViewGroup 和 ChildView 同时注册了事件监听器(onClick等),哪个会执行?
事件优先给 ChildView,会被 ChildView消费掉,ViewGroup 不会响应。
四、参考资料




