Go语言数据结构与算法-链表
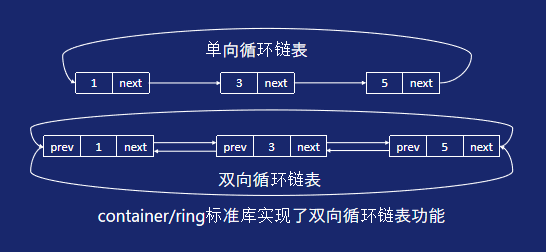
单双向链表

示例代码:
container/list标准库实现
package main
import (
"container/list"
"fmt"
)
func TraversList(lst *list.List) {
head := lst.Front()
for head.Next() != nil {
fmt.Printf("%v ", head.Value)
head = head.Next()
}
fmt.Println(head.Value)
}
func ReverseList(lst *list.List) {
tail := lst.Back()
for tail.Prev() != nil {
fmt.Printf("%v ", tail.Value)
tail = tail.Prev()
}
fmt.Println(tail.Value)
}
func main() {
lst := list.New()
lst.PushBack(1)
lst.PushBack(2)
lst.PushBack(3)
lst.PushBack(4)
lst.PushBack(5)
TraversList(lst)
ReverseList(lst)
_ = lst.Remove(lst.Back()) //移除尾元素,同时返回元素的值,注意元素不能是nil
_ = lst.Remove(lst.Front()) //移除首元素,Remove操作复杂度为O(1)
fmt.Printf("length %d\n\n", lst.Len())
TraversList(lst)
}
>>>>>>
1 2 3 4 5
5 4 3 2 1
length 3
2 3 4
自己动手实现
package main
import "fmt"
// ListNode 链表节点元素
type ListNode struct {
Value int //该节点数据
Prev *ListNode //上一个节点
Next *ListNode //下一个节点
}
// DoubleList 双向链表
type DoubleList struct {
Head *ListNode //头节点
Tail *ListNode //尾节点
Length int //节点数量
}
// NewDoubleList 初始化链表
func NewDoubleList() *DoubleList {
return &DoubleList{}
}
// Append 追加到链表尾部
func (l *DoubleList) Append(i int) {
n := &ListNode{Value: i}
t := l.Tail
if t == nil {
l.Head = n
l.Tail = n
} else {
t.Next = n
n.Prev = t
l.Tail = n
}
l.Length += 1
}
// Get 获取链表中id下标的节点
func (l *DoubleList) Get(index int) *ListNode {
if l.Length <= index {
return nil
}
pres := l.Head
for i := 0; i < index; i++ {
pres = pres.Next
}
return pres
}
// InsertAfter 链表插入节点
func (l *DoubleList) InsertAfter(i int, pNode *ListNode) {
n := &ListNode{Value: i}
if pNode.Next == nil {
pNode.Next = n
n.Prev = pNode
} else {
nNode := pNode.Next
nNode.Prev = n
n.Prev = pNode
n.Next = nNode
pNode.Next = n
}
l.Length += 1
}
// Traverse 链表正向值
func (l *DoubleList) Traverse() {
pres := l.Head
for pres != nil {
fmt.Printf("%d ", pres.Value)
pres = pres.Next
}
fmt.Println()
}
// Reverse 链表反向值
func (l *DoubleList) Reverse() {
t := l.Get(l.Length-1)
for t != nil {
fmt.Printf("%d ", t.Value)
t = t.Prev
}
fmt.Println()
}
func main() {
l := NewDoubleList()
l.Append(1)
l.Append(2)
l.Append(3)
l.Append(4)
l.Append(5)
l.Traverse()
gNode := l.Get(3)
l.InsertAfter(9, gNode)
l.Traverse()
l.Reverse()
}
>>>>>>>
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 9 5
5 9 4 3 2 1
应用:
LRU缓存淘汰
- LUR(Least Recently Used)最近最少使用【冷数据】
- 思路:缓存的key放到链表中,头部的元素表示最近刚使用
- 如果命中缓存,从链表中找到对应的key,移到链表头部
- 如果没有命中缓存:
- 如果缓存容量没超,放入缓存,并把key放到链表头部
- 如果超出缓存容量,删除链表尾部元素,再把key放到链表头部
示例代码:
模拟LRU缓存淘汰机制:
package main
import (
"container/list"
"fmt"
)
var cache map[int]string
var lst *list.List
const CAP = 10 //缓存容量上限
func init() {
cache = make(map[int]string, CAP)
lst = list.New()
}
func readFromDisk(key int) string {
return "china"
}
func read(key int) string {
if v, exists := cache[key]; exists { //命中缓存
head := lst.Front() //链表内第一个元素
notFound := false
for {
if head == nil {
notFound = true
break
}
if head.Value.(int) == key { //从链表内找到对应的key
lst.MoveToFront(head) //把key移到链表头部
break
} else {
head = head.Next()
}
}
if notFound { //正常情况下不会发生这种情况
lst.PushFront(key)
}
return v
} else { //没有命中缓存
v = readFromDisk(key) //从磁盘中读取数据
cache[key] = v //放入缓存
lst.PushFront(key) //放入链表头部
if len(cache) > CAP { //缓存已满
tail := lst.Back() //链表最后一个元素
delete(cache, tail.Value.(int)) //从缓存中移除很久不使用的元素
lst.Remove(tail) //从链表中删除最后一个元素
fmt.Printf("remove %d from cache\n", tail.Value.(int))
}
return v
}
}
func TraversList(lst *list.List) {
head := lst.Front()
for head.Next() != nil {
fmt.Printf("%v ", head.Value)
head = head.Next()
}
fmt.Println(head.Value)
}
func main() {
for i := 1; i <= 12; i++ {
_ = read(i)
}
for k, v := range cache {
fmt.Printf("%d:%s\n", k, v)
}
_ = read(1)
_ = read(5)
for k, v := range cache {
fmt.Printf("%d:%s\n", k, v)
}
fmt.Println("-------")
TraversList(lst)
}
>>>>>>
remove 1 from cache
remove 2 from cache
6:china
7:china
8:china
10:china
12:china
3:china
5:china
11:china
4:china
9:china
remove 3 from cache
6:china
7:china
8:china
10:china
12:china
1:china
5:china
11:china
4:china
9:china
-------
5 1 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 4
单双向循环链表
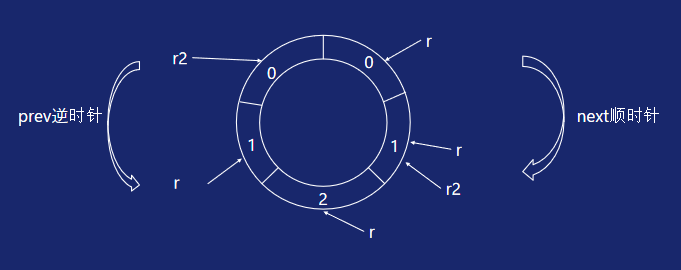
添加元素
package main
import (
"container/ring"
"fmt"
)
func TraverseRing(ring *ring.Ring) {
//通过Do()来遍历ring,内部实际上调用了Next()而非Prev()
ring.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Printf("%v ", i)
})
fmt.Println()
}
func main() {
//必须指定长度,各元素被初始化为nil
r := ring.New(5)
r2 := r.Prev()
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ {
r.Value = i
r = r.Next()
}
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ {
r2.Value = i
r2 = r2.Prev()
}
// r和r2当前所在的指针位置不同,所以遍历出来的顺序也不同
TraverseRing(r)
TraverseRing(r2)
}
>>>>
1 0 0 1 2
1 2 1 0 0
应用:
基于滑动窗口的统计:
- 最近100次接口调用的平均耗时
- 最近10笔订单的平均值
- 最近30个交易日股票的最高点
ring的容量即为滑动窗口的大小、把待观察变量按时间顺序不停地写入ring即可


