v4l2-ctl 库的编译和使用
如果要编写一个使用V4L2 的应用层app,最好的例子v4l2-util的应用程序
源码下载
https://git.linuxtv.org/v4l-utils.git/tree/
Example
•get/set/list video standard - v4l2-ctl-stds.cpp
•get/set/list video input - v4l2-ctl-io.cpp
•get/set/list video pixel format - v4l2-ctl-vidcap.cpp
•get/set/list video framesizes - v4l2-ctl-vidcap.cpp
•get/set/list video framerates - v4l2-ctl-vidcap.cpp
•video capture - v4l2-ctl-streaming.cpp v4l2-ctl-streaming.cpp
注意事项:按照流程在app中配置以下流程
•input (VIDIOC_S_INPUT)
•standard (VIDIOC_S_STD)
•format (VIDIOC_S_FMT) including width, height, pixel format, fields
•framerate (VIDIOC_S_PARM)
源码的教程编译
NOTE:交叉编译时,不要用apt-get的aarch64-linux-gnu交叉编译工具链,重新到linaro的官网去下载。
配置选项:
export PATH=your_path/aarch64-linux-gnu/bin:$PATH //设置交叉编译工具链
export PKG_CONFIG_LIBDIR=your_path/aarch64-linux-gnu/lib //设置交叉编译库
编译选项:
./configure --host=aarch64-linux-gnu --prefix=your_install_path //设置安装位置,生成makefile
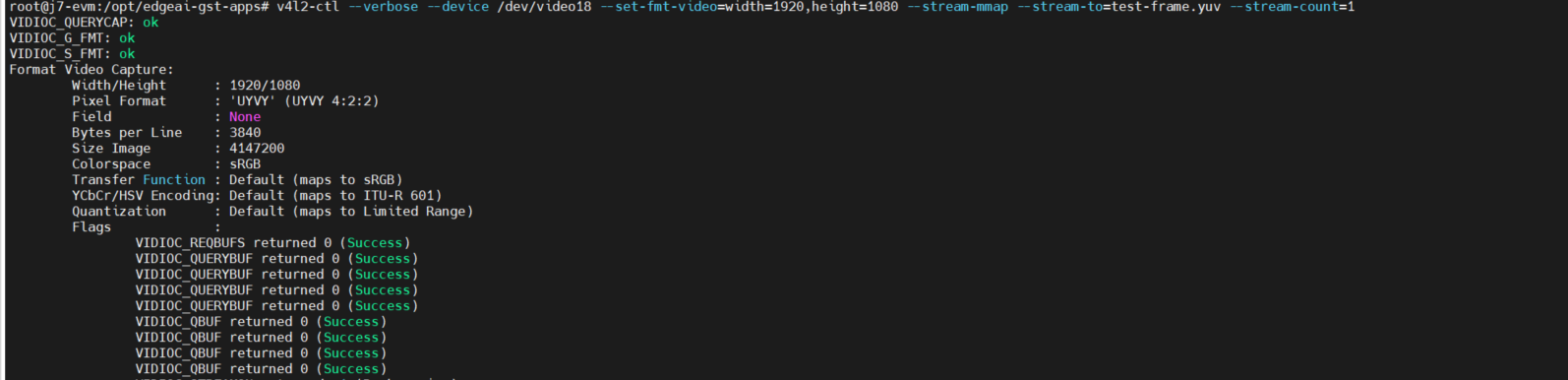
命令行的调试保存一张yuv的图(确定VIDIOC_S_FMT等可用)
v4l2-ctl --verbose --device /dev/video18 --set-fmt-video=width=1920,height=1080 --stream-mmap --stream-to=test-frame.yuv --stream-count=1
代码实现:
点击查看代码
/*
* V4L2 video capture example
*
* This program can be used and distributed without restrictions.
*
* This program is provided with the V4L2 API
* see http://linuxtv.org/docs.php for more information
*/
#include <byteswap.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <fcntl.h> /* low-level i/o */
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/videodev2.h>
#define CLEAR(x) memset(&(x), 0, sizeof(x))
struct buffer {
void *start;
size_t length;
};
static void errno_exit(const char *s)
{
fprintf(stderr, "%s error %d, %s\n", s, errno, strerror(errno));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
static int xioctl(int fh, int request, void *arg)
{
int r;
do {
r = ioctl(fh, request, arg);
} while (-1 == r && EINTR == errno);
return r;
}
/* 16bit/pixel interleaved YUV */
static void process_image(const void *_p, struct v4l2_pix_format *fmt)
{
const uint8_t *p = _p;
int8_t u;
uint8_t y1;
int8_t v;
uint8_t y2;
int r, g, b, c, d ,e;
int red, i, x, y;
int size = fmt->sizeimage;
printf("Processing Frame: %dx%d %c%c%c%c\n",
fmt->width, fmt->height,
(fmt->pixelformat >> 0) & 0xff,
(fmt->pixelformat >> 8) & 0xff,
(fmt->pixelformat >> 16) & 0xff,
(fmt->pixelformat >> 24) & 0xff);
red = 0;
for (i = 0; i < size; i += 4) {
u = p[i+0];
y1 = p[i+1];
v = p[i+2];
y2 = p[i+3];
u -= 128;
v -= 128;
r = y1 + v + (v>>2) + (v>>3) + (v>>5);
g = y1 - ((u>>2) + (u>>4) + (u>>5))
- ((v>>1) + (v>>3) + (v>>4) + (v>>5));
b = y1 + u + (u>>1) + (u>>2) + (u>>6);
if (r > 100 && g < 60 && b < 60) red++;
r = y2 + v + (v>>2) + (v>>3) + (v>>5);
g = y2 - ((u>>2) + (u>>4) + (u>>5))
- ((v>>1) + (v>>3) + (v>>4) + (v>>5));
b = y2 + u + (u>>1) + (u>>2) + (u>>6);
if (r > 100 && g < 60 && b < 60) red++;
/* describe pixels on first line every 250 pixels
* (colorbars)
*/
x = (i>>1) % fmt->width;
y = (i>>1) / fmt->height;
if (y == 0 && !(x % 250)) {
printf("[%4d,%4d] YUYV:0x%02x%02x%02x%02x ",
x,y,y1,(uint8_t)u,y2,(uint8_t)v);
printf("RGB:0x%02x%02x%02x\n", r,g,b);
}
}
printf("red pixel count=%d\n", red);
}
static void save_frame(const char *path, const void *p, int size)
{
int fd, rz;
fd = open(path, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0755);
if (fd < 0)
perror("open");
else {
rz = write(fd, p, size);
printf("Wrote %d of %d bytes to %s\n", rz, size, path);
close(fd);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
static char *dev_name;
int width, height;
static int fd = -1;
struct stat st;
struct buffer *buffers;
static unsigned int n_buffers;
enum v4l2_buf_type type;
struct v4l2_capability cap;
struct v4l2_format fmt;
struct v4l2_requestbuffers req;
struct v4l2_streamparm parm;
struct v4l2_input input;
v4l2_std_id std_id;
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
unsigned int count;
unsigned int i;
char filename[32];
/* parse args */
if (argc < 5) {
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <device> <width> <height> <count>\n",
argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
dev_name = argv[1];
width = atoi(argv[2]);
height = atoi(argv[3]);
count = atoi(argv[4]);
/* open device */
fd = open(dev_name, O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK, 0);
if (-1 == fd) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot open '%s': %d, %s\n",
dev_name, errno, strerror(errno));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* get standard (wait for it to be locked onto a signal) */
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_G_STD, &std_id))
perror("VIDIOC_G_STD");
for (i = 0; std_id == V4L2_STD_ALL && i < 10; i++) {
usleep(100000);
xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_G_STD, &std_id);
}
/* set the standard to the detected standard (this is critical for autodetect) */
if (std_id != V4L2_STD_UNKNOWN) {
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_STD, &std_id))
perror("VIDIOC_S_STD");
if (std_id & V4L2_STD_NTSC)
printf("found NTSC TV decoder\n");
if (std_id & V4L2_STD_SECAM)
printf("found SECAM TV decoder\n");
if (std_id & V4L2_STD_PAL)
printf("found PAL TV decoder\n");
}
/* ensure device has video capture capability */
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, &cap)) {
if (EINVAL == errno) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s is no V4L2 device\n",
dev_name);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else {
errno_exit("VIDIOC_QUERYCAP");
}
}
if (!(cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE)) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s is no video capture device\n",
dev_name);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (!(cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_STREAMING)) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s does not support streaming i/o\n",
dev_name);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* set video input */
CLEAR(input);
input.index = 1; /* IMX6 v4l2 driver: input1 is CSI<->MEM */
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_INPUT, &input))
perror("VIDIOC_S_INPUT");
/* set framerate */
CLEAR(parm);
parm.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_PARM, &parm))
perror("VIDIOC_S_PARM");
/* get framerate */
CLEAR(parm);
parm.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_G_PARM, &parm))
perror("VIDIOC_G_PARM");
/* set format */
CLEAR(fmt);
fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
fmt.fmt.pix.width = width;
fmt.fmt.pix.height = height;
fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = V4L2_PIX_FMT_UYVY;
fmt.fmt.pix.field = V4L2_FIELD_ANY;
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_S_FMT, &fmt))
errno_exit("VIDIOC_S_FMT");
/* get and display format */
CLEAR(fmt);
fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_G_FMT, &fmt))
errno_exit("VIDIOC_G_FMT");
printf("%s: %dx%d %c%c%c%c %2.2ffps\n", dev_name,
fmt.fmt.pix.width, fmt.fmt.pix.height,
(fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat >> 0) & 0xff,
(fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat >> 8) & 0xff,
(fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat >> 16) & 0xff,
(fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat >> 24) & 0xff,
(float)parm.parm.capture.timeperframe.denominator /
(float)parm.parm.capture.timeperframe.numerator
);
/* request buffers */
CLEAR(req);
req.count = 4;
req.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
req.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_REQBUFS, &req)) {
if (EINVAL == errno) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s does not support "
"memory mapping\n", dev_name);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else {
errno_exit("VIDIOC_REQBUFS");
}
}
if (req.count < 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "Insufficient buffer memory on %s\n",
dev_name);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* allocate buffers */
buffers = calloc(req.count, sizeof(*buffers));
if (!buffers) {
fprintf(stderr, "Out of memory\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* mmap buffers */
for (n_buffers = 0; n_buffers < req.count; ++n_buffers) {
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
CLEAR(buf);
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
buf.index = n_buffers;
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYBUF, &buf))
errno_exit("VIDIOC_QUERYBUF");
buffers[n_buffers].length = buf.length;
buffers[n_buffers].start =
mmap(NULL /* start anywhere */,
buf.length,
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE /* required */,
MAP_SHARED /* recommended */,
fd, buf.m.offset);
if (MAP_FAILED == buffers[n_buffers].start)
errno_exit("mmap");
}
/* queue buffers */
for (i = 0; i < n_buffers; ++i) {
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
CLEAR(buf);
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
buf.index = i;
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buf))
errno_exit("VIDIOC_QBUF");
}
/* start capture */
type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_STREAMON, &type))
errno_exit("VIDIOC_STREAMON");
/* capture frame(s) (we throw away first incomplete frame ) */
for (i = 0; i < count + 1; i++) {
for (;;) {
fd_set fds;
struct timeval tv;
int r;
FD_ZERO(&fds);
FD_SET(fd, &fds);
/* Timeout. */
tv.tv_sec = 2;
tv.tv_usec = 0;
r = select(fd + 1, &fds, NULL, NULL, &tv);
if (-1 == r) {
if (EINTR == errno)
continue;
errno_exit("select");
}
if (0 == r) {
fprintf(stderr, "select timeout\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* dequeue captured buffer */
CLEAR(buf);
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_DQBUF, &buf)) {
if (errno == EAGAIN)
continue;
errno_exit("VIDIOC_DQBUF");
}
assert(buf.index < n_buffers);
/* skip first image as it may not be sync'd */
if (i > 0) {
process_image(buffers[buf.index].start,
&fmt.fmt.pix);
sprintf(filename, "frame%d.raw", i);
save_frame(filename,
buffers[buf.index].start,
buf.bytesused);
}
/* queue buffer */
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buf))
errno_exit("VIDIOC_QBUF");
break;
}
}
/* stop capture */
type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
if (-1 == xioctl(fd, VIDIOC_STREAMOFF, &type))
errno_exit("VIDIOC_STREAMOFF");
/* unmap and free buffers */
for (i = 0; i < n_buffers; ++i)
if (-1 == munmap(buffers[i].start, buffers[i].length))
errno_exit("munmap");
free(buffers);
/* close device */
if (-1 == close(fd))
errno_exit("close");
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
return 0;
}
关于v4l2_field
enum v4l2_field {
V4L2_FIELD_ANY = 0, // driver can choose from none,
// top, bottom, interlaced
// depending on whatever it thinks
// is approximate ...
V4L2_FIELD_NONE = 1, // this device has no fields ...
V4L2_FIELD_TOP = 2, // top field only
V4L2_FIELD_BOTTOM = 3, // bottom field only
V4L2_FIELD_INTERLACED = 4, // both fields interlaced
V4L2_FIELD_SEQ_TB = 5, // both fields sequential into one buffer, top-bottom order
V4L2_FIELD_SEQ_BT = 6, // same as above + bottom-top order
V4L2_FIELD_ALTERNATE = 7, // both fields alternating into separate buffers
V4L2_FIELD_INTERLACED_TB = 8, // both fields interlaced, top field first and the top field is transmitted first
V4L2_FIELD_INTERLACED_BT = 9, // both fields interlaced, top field first and the bottom field is transmitted first
};
视频帧可以分为隔行和逐行,
逐行顺序的传输一帧所有的行,而隔行则把一帧划分成两个fields,分别保存帧的奇数行和偶数行,被称作奇场和偶场;在刷新率接近电影时,图片会消退的过快。使用奇偶场可以避免使用双倍的buffer以及额外的带宽需求。
首先要明确模拟camera(数字摄像头不在这个讨论之列。)并不是在同一时间曝光一帧,camera通过场来传输这些帧的,这些场是在不同瞬间拍摄的。屏幕上的一个运动对象因此会在两个field之间产生动画效果。这种情况下需要识别哪一帧更老一点,也称作“瞬间序“
当驱动通过fields 提供或者接收images,应用应该知道如何通过这些fields组合成帧,通过划分为top bottom field, “空间序”: top field的第一行是帧的第一行, bottom field的第一行是帧的第二行。
然而因为field是一个跟着一个拍的,争论帧是由top还是bottom开始的是没意义的,任何两个相邻的top bottom field, 或者 bottom top field都可以组成一个有效的帧。
与直觉相反top field不一定是older field, older filed是否包含top 或者bottom lines是由video标准决定的. 因此要区分瞬间序和空间序。下面的图会给出清晰的解释。
所有的video capture和out devices必须汇报当前的field顺序。 一些驱动可能允许选择不同的序,end应用可以在调用VIDIOC_S_FMT前初始化struct v4l2_pix_format的 field成员。否则可以使用V4L2_FIELD_ANY
所有的video capture和out devices必须汇报当前的field顺序。 一些驱动可能允许选择不同的序,终端应用可以在调用VIDIOC_S_FMT前初始化struct v4l2_pix_format的 field成员。否则可以使用V4L2_FIELD_ANY。下面列出了可能的field类型
参考文献:
https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/v4.8/media/uapi/v4l/field-order.html#v4l2-field https://www.linuxtv.org/downloads/v4l-dvb-apis-old/index.html
运行
$ ./capture /dev/video0 1920 1080 1
/dev/video0: 1920x1080 UYVY 60.00fps
Processing Frame: 1920x1080 UYVY
[ 0, 0] YUYV:0xeb00eb00 RGB:0xebebeb
[ 250, 0] YUYV:0x9dad9d0d RGB:0xaeb409
[ 500, 0] YUYV:0x801b80ae RGB:0x0bb6ae
[ 750, 0] YUYV:0x6dc96dbb RGB:0x0ab50b
[1000, 0] YUYV:0x52365244 RGB:0xb111b0
red pixel count=259200
Wrote 4147200 of 4147200 bytes to frame.raw
./convert -size 1920x1080 -depth 16 uyvy:frame.raw frame.png


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号