ASP.NET Core 2.2 基础知识(四) URL重写中间件
说到URL重写就不得不提URL重定向.
URL重定向
URL重定向是客户端操作,指示客户端访问另一个地址的资源.这需要往返服务器,并且当客户端对资源发出请求时,返回客户端的重定向URL会出现在浏览器的地址栏中.
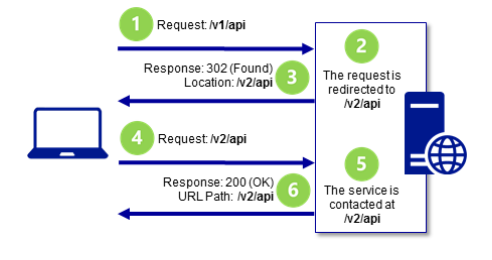
将请求重定向到不同的URL时,可指示重定向是永久的还是临时的.如果是永久的,则使用"301"状态码.收到"301"状态码时,客户端可能会缓存.如果是临时的,则使用"302"状态码,以使客户端将来不应存储和重用重定向URL.
示例:
新建一个WebAPI项目;新增一个 TestController 控制器;在 Startup 类的 Configure 方法中增加如下代码:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) { ...other codes var options = new RewriteOptions(); //options.AddRedirect("^redirect/(.*)", "api/test");//默认状态码为 302 options.AddRedirect("^redirect/(.*)", "api/test", 301); app.UseRewriter(options); app.Run(async context => { //注意重定向和重写URL两种情况下,浏览器地址栏和页面显示的 URL 的区别. await context.Response.WriteAsync($"URL:{context.Request.Path + context.Request.QueryString}"); }); app.UseMvc(); }
启动该项目,在浏览器地址栏输入 : https://localhost:44303/redirect/123 后,
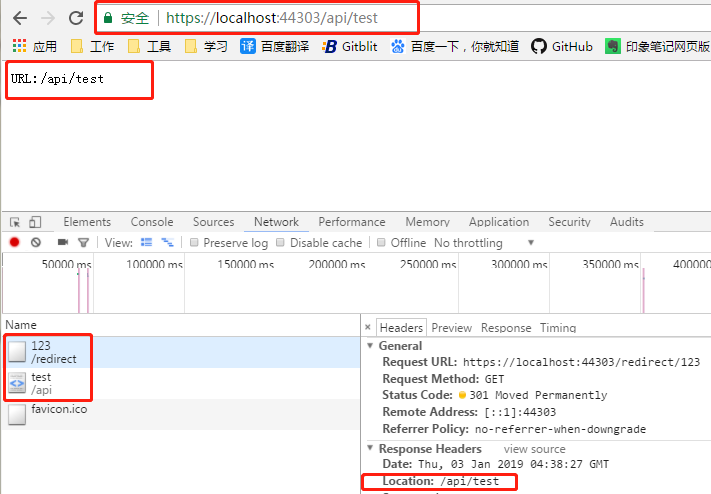
可以看出,客户端一共请求了两次,浏览器地址栏变成了重定向的URL.
URL重写
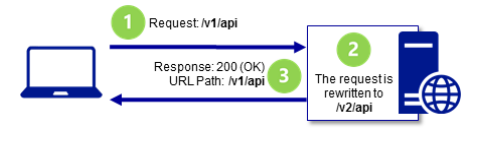
URL重写是服务器端操作.重写URL不需要往返服务器,重写的URL也不会返回客户端,也不会出现在浏览器地址栏.
示例:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) { ...other codes var options = new RewriteOptions(); options.AddRewrite("^rewrite/(.*)", "api/test", true);//重写URL,false/true 表示如果当前规则适用,是否跳过其他重写规则. app.UseRewriter(options); app.Run(async context => { //注意重定向和重写URL两种情况下,浏览器地址栏和页面显示的 URL 的区别. await context.Response.WriteAsync($"URL:{context.Request.Path + context.Request.QueryString}"); }); app.UseMvc(); } }
在浏览器地址栏输入 : https://localhost:44303/rewrite/1
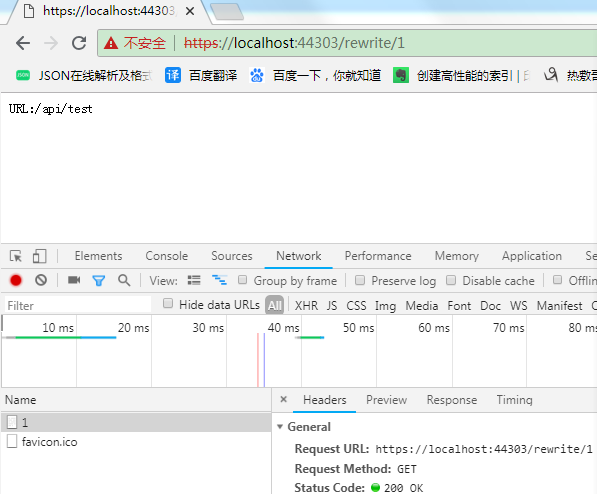
RewriteOptions 类型提供了很多重写和重定向的方法,除了上述的 AddRedirect , AddRewrite 外,还有两个比较好玩的方法.
1.Add(Action<RewriteContext> applyRule)
接收一个委托.当请求地址符合一个规则后,方法传递的委托便会执行.这里以修改 reContext.Result 的值为例.示例:
{ RewriteOptions options = new RewriteOptions(); options.AddRewrite("^rewrite*", "test", true).Add(reContext => { reContext.Result = RuleResult.EndResponse; }); app.UseRewriter(options); app.Run(async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync(context.Request.Path + context.Request.QueryString); }); }
只有请求地址符合规则时才会执行 app.Run(async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync(context.Request.Path + context.Request.QueryString); }) 这句代码.
测试图如下:
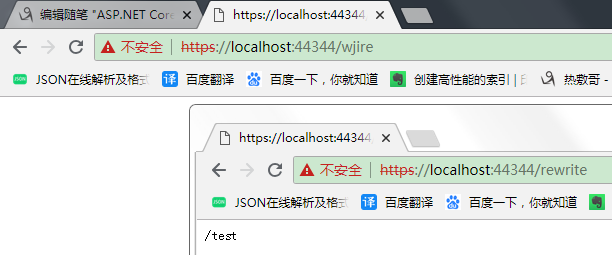
可以看到,上面的请求不符合规则,页面上什么都没显示;下面的请求符合规则,页面显示出了重写后的请求路径.
2.AddRedirectToHttps
该方法可以将 HTTP 请求重定向到采用 HTTPS 的相同主机和路径.
新建一个 WebAPI 项目,但是不勾选 "为HTTPS配置" 选项.
修改 Configure 方法.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } var options = new RewriteOptions(); options.AddRedirectToHttps(statusCode: 301, sslPort: 9527); app.UseRewriter(options); app.UseMvc(); }
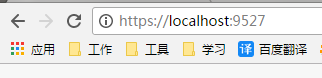
在浏览器地址栏输入该项目地址 : http://localhost:50588 ,会重定向到 https://localhost:9527 , 如图.
上面所有重写的示例中,重写的规则都是写在代码里面的,而ASP.NET Core 还提供了从文件中读取规则的方式.
新建一个文件夹 Rule ,添加一个 IISUrlRewrite.xml 文件,内容如下:
<rewrite> <rules> <rule name="MyIISUrlRewrite" stopProcessing="true"> <match url="^rewrite/(.*)"/> <!--还 没发现 appendQueryString = false 和 true 的区别--> <action type="Rewrite" url="api/values/{R:1}" appendQueryString="false"/> </rule> </rules> </rewrite>
修改 Configure 方法:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) { ...... var options = new RewriteOptions(); //方法一: //using (StreamReader sr = File.OpenText(Path.Combine(env.ContentRootPath, @"Rule\IISUrlRewrite.xml"))) //{ // options.AddIISUrlRewrite(sr); // app.UseRewriter(options); //} //方法二: var fileProvider = new PhysicalFileProvider(Path.Combine(env.ContentRootPath, "Rule")); options.AddIISUrlRewrite(fileProvider, "IISUrlRewrite.xml"); app.UseRewriter(options); app.Run(async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync(context.Request.Path + context.Request.QueryString); }); app.UseMvc(); }
图就不上了.
虽然还没用 ASP.NET Core 开发过任何项目,但是我觉得下面这种重写和重定向的方法或许会是用得最多的,因为它足够灵活.
public class MyRule : IRule { //可以自定义构造函数,做一些验证 //public MyRule(string extension, string newPath) //{ // if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(extension)) // { // throw new ArgumentException(nameof(extension)); // } // if (!Regex.IsMatch(extension, @"^rewrite*")) // { // throw new ArgumentException("Invalid extension", nameof(extension)); // } // if (!Regex.IsMatch(newPath, @"(/[A-Za-z0-9]+)+?")) // { // throw new ArgumentException("Invalid path", nameof(newPath)); // } // _extension = extension; // _newPath = new PathString(newPath); //} //private readonly string _extension; //private readonly PathString _newPath; private readonly string _extension; private readonly string _newPath; public MyRule(string extension, string newPath) { _extension = extension; _newPath = newPath; } public void ApplyRule(RewriteContext context) { HttpRequest request = context.HttpContext.Request; HttpResponse response = context.HttpContext.Response; //可以重写 request.Path = new PathString(_newPath); context.Result = RuleResult.SkipRemainingRules; //可以重定向 //if (request.Path.Value.EndsWith(_extension, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) //{ // response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status302Found; // context.Result = RuleResult.EndResponse; // response.Headers[HeaderNames.Location] = _newPath; //} } }
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } else { app.UseHsts(); } RewriteOptions options = new RewriteOptions(); options.Add(new MyRule("rewrite","/api/test")); app.UseRewriter(options); app.UseHttpsRedirection(); app.UseMvc(); } }
完



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号