Java Spring 中使用 @Valid 进行参数校验
下面示范一下如何在 Spring 中用 @Valid 进行校验,话不多说,直接上代码:
import com.demo.hello.common.TestDTO;
import com.demo.hello.common.TestRequest;
import com.demo.hello.service.TestService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.validation.Valid;
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private TestService service;
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String test(@Valid @RequestBody TestRequest request) {
TestDTO testDTO = new TestDTO();
testDTO.setName(request.getName());
testDTO.setAge(request.getAge());
return service.test(testDTO);
}
}
import com.demo.hello.common.TestDTO;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.validation.Valid;
@Service
public class TestService {
public String test(@Valid TestDTO testDTO) {
return testDTO.toString();
}
}
import lombok.Data;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
@Data
public class TestRequest {
@NotNull(message = "name不允许空")
private String name;
@Max(100)
private Integer age;
}
import lombok.Data;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
@Data
public class TestDTO {
@Size(max = 10)
private String name;
@Max(50)
private Integer age;
}
上述的 Controller 方法可以在 http 请求时正确地根据注解校验参数,如图所示:
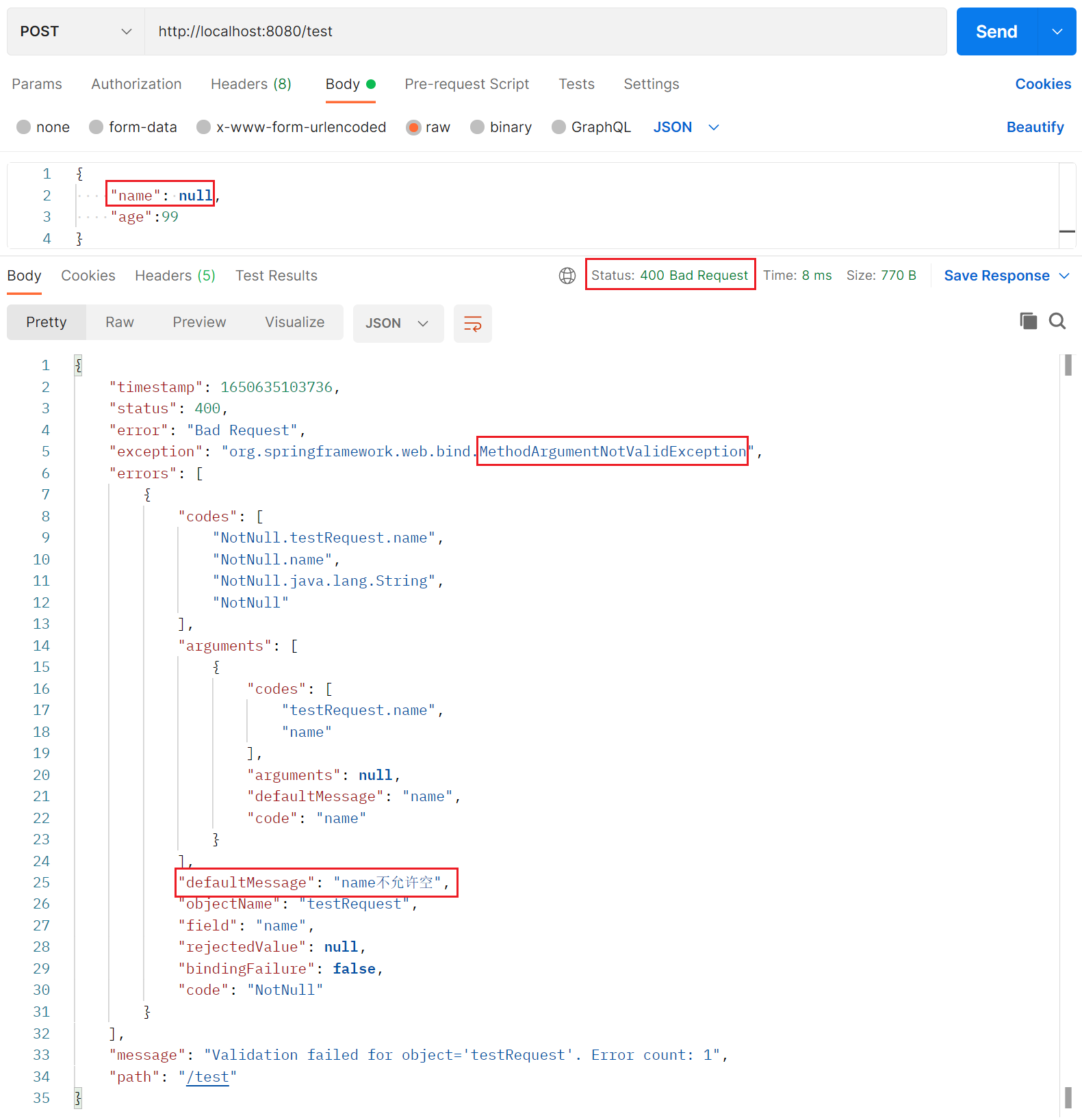
可以注意一下 校验不通过抛出的异常是MethodArgumentNotValidException,开发中经常会用一个 aop 来统一包装 http 返回前的各种异常:
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.FieldError;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ControllerAdvice
public class ControllerExceptionAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.OK)
@ResponseBody
public String handleArgumentValidationException(MethodArgumentNotValidException me) {
// 一些别的操作
FieldError fieldError = me.getBindingResult().getFieldError();
return fieldError.getDefaultMessage();
}
}
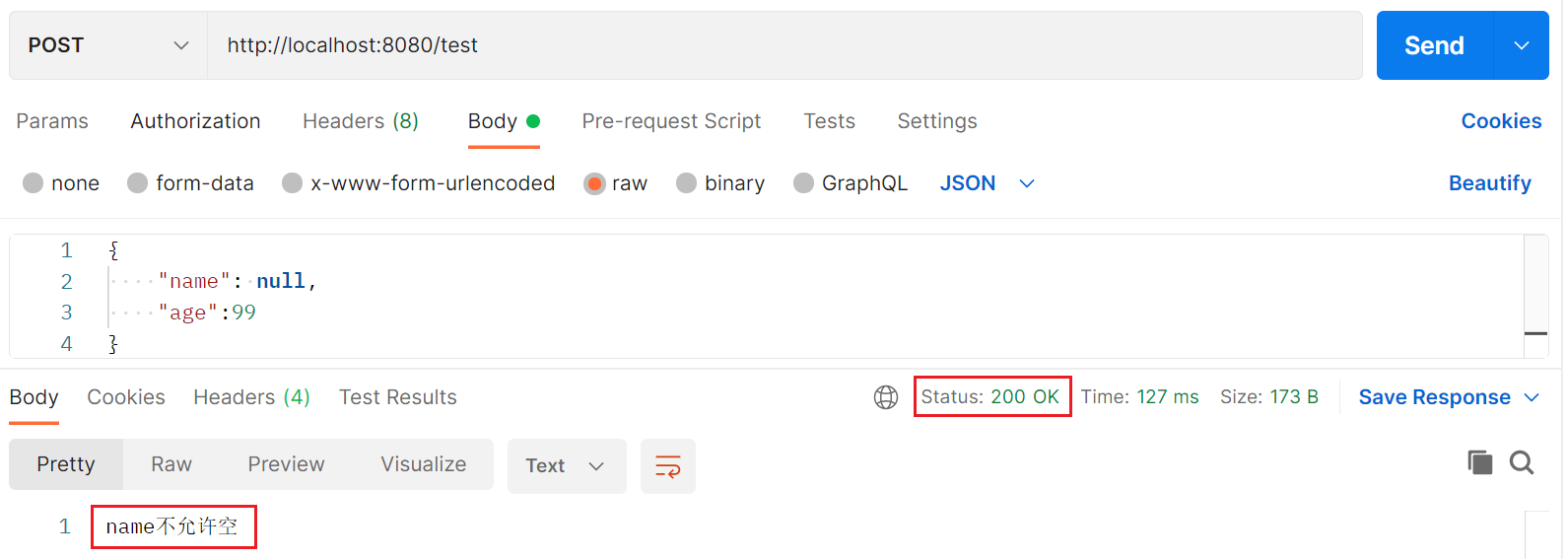
Spring Webflux 中 @Valid 校验失败会抛出
WebExchangeBindException。
以上是基本使用方法。再看下以下这个请求:
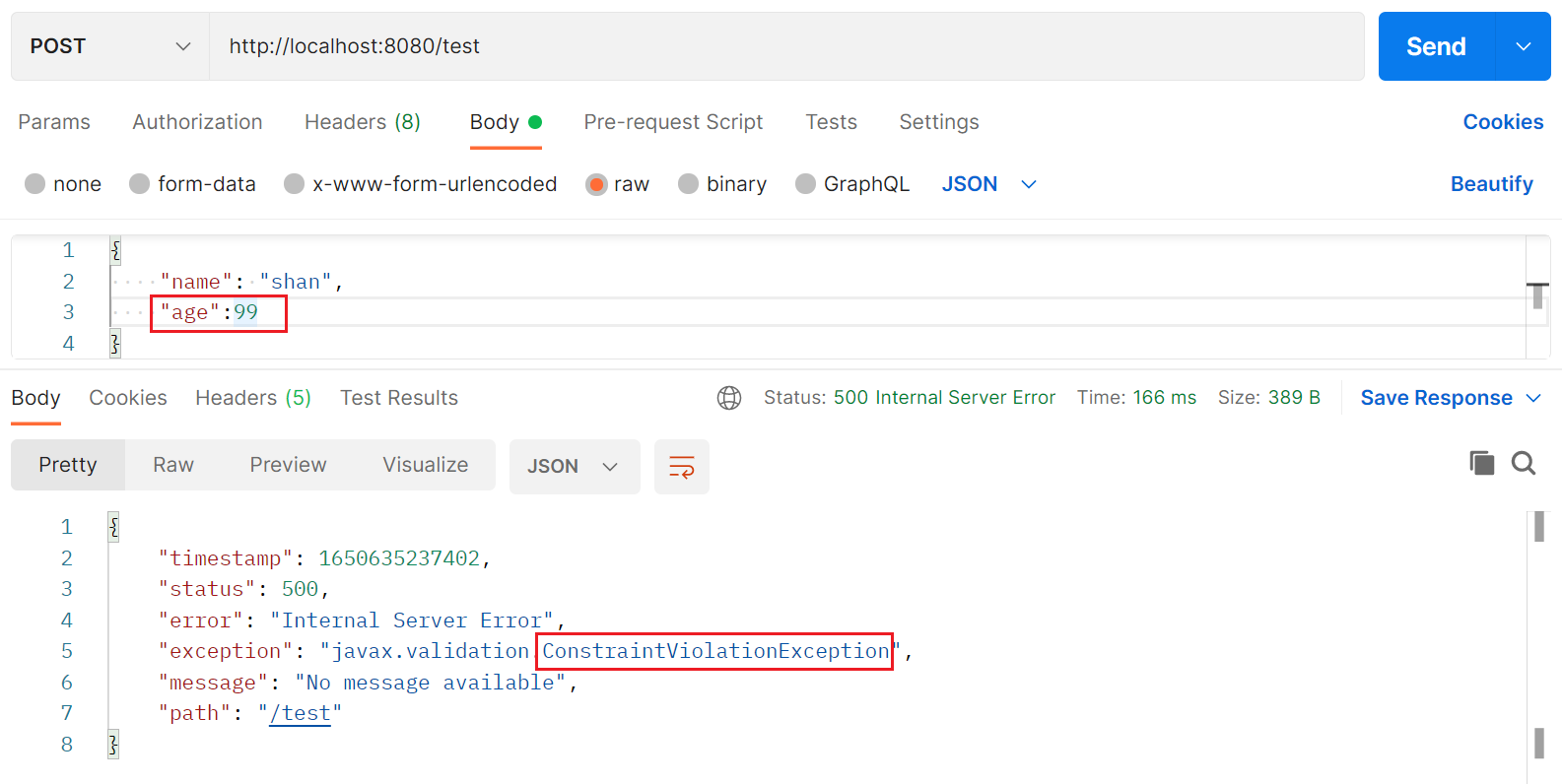
可以看到,age的值不满足TestDTO的注解校验,但是 Service 方法的校验却没有生效。如果需要 Service 层的方法也开启校验,则需要添加@Validated注解
import com.demo.hello.common.TestDTO;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import javax.validation.Valid;
@Validated
@Service
public class TestService {
public String test(@Valid TestDTO testDTO) {
return testDTO.toString();
}
}
如图所示:
参考:
https://www.baeldung.com/javax-validation
https://www.baeldung.com/javax-validation-method-constraints
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-valid-vs-validated
另,非空注解有非常多种,比较常见的是以下几种:
javax.annotation.Nonnull,似乎不起作用;javax.validation.constraints.NotNull,在上述代码中使用的是这种;lombok.NonNull,额外生成某些代码,提前抛出NPE;
Spring5 中也提供了两个注解:
org.springframework.lang.NonNullorg.springframework.lang.NonNullApi
详见 stackoverflow 上的这个提问:Which @NotNull Java annotation should I use?


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号