BasicDao、浅谈MVC架构
问题引出

基本说明

DAO: data access object ——用于访问数据库表的对象
代码实现
domain——Admin
package com.recorder.mvc.domain; /** * @author 紫英 * @version 1.0 * @discription admin表 javabean类 */ public class Admin { private String name; private String pwd; public Admin() { //一定要带一个无参构造器,方便底层反射 } @Override public String toString() { return "Admin{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", pwd='" + pwd + '\'' + '}'; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public Admin(String name, String pwd) { this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; } }
Dao——BasicDao
package com.recorder.mvc.dao; import com.recorder.mvc.utiils.JDBCUtilsByDruid; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.ScalarHandler; import javax.crypto.NullCipher; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.List; /** * @author 紫英 * @version 1.0 * @discription BasicDAO , 是其他 DAO 的父类, 使用到 apache-dbutils */ //使用泛型,等到子类继承时制定具体类型 public class BasicDao<T> { //使用 apache-dbutils QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner(); //开发通用的 dml 方法, 针对任意的表 public int dml(String sql, Object... params) { Connection connection = null; try { connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection(); int update = qr.update(connection, sql, params); return update; } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); //将编译异常->运行异常 ,抛出 } finally { JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection); } } //返回多个对象(即查询的结果是多行), 针对任意表 /** * @param sql 传入的sql语句 * @param clazz 对应的类的 Class 对象 比如 Admin.class * @param params 传入 ? 的具体的值,可以是多个 * @return 根据 Admin.class 返回对应的 ArrayList 集合 */ public List<T> selectMulti(String sql, Class<T> clazz, Object... params) { Connection connection = null; try { connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection(); return qr.query(connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<T>(clazz), params); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection); } } public T selectSingle(String sql,Class<T> clazz,Object...params){ Connection connection = null; try { connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection(); T query = qr.query(connection, sql, new BeanHandler<T>(clazz), params); return query; } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); }finally { JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null,connection); } } //查询单行单列的方法,即返回单值的方法 public Object selectScalar(String sql, Object... params) { Connection connection = null; try { connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection(); return qr.query(connection, sql, new ScalarHandler(), params); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection); } } }
Dao——AdminDao
package com.recorder.mvc.dao; import com.recorder.mvc.domain.Admin; /** * @author 紫英 * @version 1.0 * @discription AdminDao */ public class AdminDao extends BasicDao<Admin>{ //1. 原有 BasicDAO 的方法 // 2. 根据业务需求,可以编写特有的方法 }
utils——JDBCUtilsByDruid
package com.recorder.mvc.utiils; import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory; import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; import java.util.Properties; /** * @author 紫英 * @version 1.0 * @discription 基于 druid 数据库连接池的工具类 */ public class JDBCUtilsByDruid { private static DataSource ds; //在静态代码块完成 ds 初始化 static { Properties properties = new Properties(); try { properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\druid.properties")); ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //编写 getConnection 方法 public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return ds.getConnection(); } //关闭连接,这里注意: 在数据库连接池技术中,close 不是真的断掉连接 // 而是把使用的 Connection 对象放回连接池,因为这里的connection是上面的return ds.getConnection()得到的 public static void close(ResultSet set, Statement statement, Connection connection) { try { //判断是否为空 if (set != null) { set.close(); } if (statement != null) { statement.close(); } if (connection != null) { connection.close(); } } catch (SQLException e) { //将编译异常转成运行异常抛出 throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
测试类
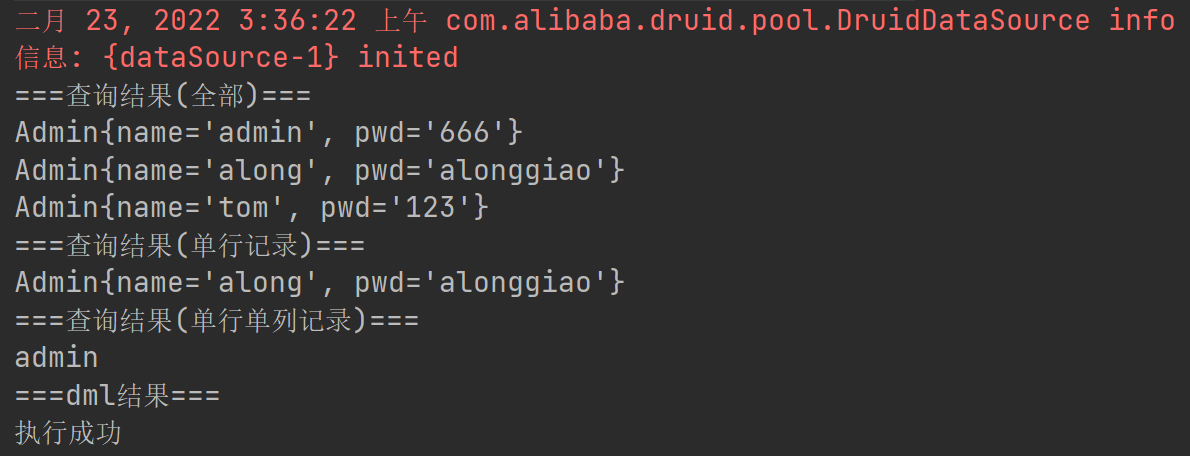
package com.recorder.mvc; import com.recorder.mvc.dao.AdminDao; import com.recorder.mvc.domain.Admin; import java.util.List; /** * @author 紫英 * @version 1.0 * @discription 测试类 */ public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { AdminDao adminDao = new AdminDao(); //1.查询 List<Admin> list = adminDao.selectMulti("select * from admin", Admin.class); System.out.println("===查询结果(全部)==="); for (Admin admin : list) { System.out.println(admin); } //2. 查询单行记录 System.out.println("===查询结果(单行记录)==="); //踩坑 AdminDao extends BasicDao<Admin> 之前继承的时候没有加泛型 //导致直编译报错 Admin admin = adminDao.selectSingle("select * from admin where name = ? ", Admin.class, "along"); System.out.println(admin); //3. 查询单行单列 System.out.println("===查询结果(单行单列记录)==="); Object o = adminDao.selectScalar("select name from admin where pwd = ?", "666"); System.out.println(o); //4. dml 操作 insert ,update, delete System.out.println("===dml结果==="); int dml = adminDao.dml("insert into admin values(?,?)", "root", "root"); System.out.println(dml > 0 ? "执行成功" : "执行没有影响表"); } }
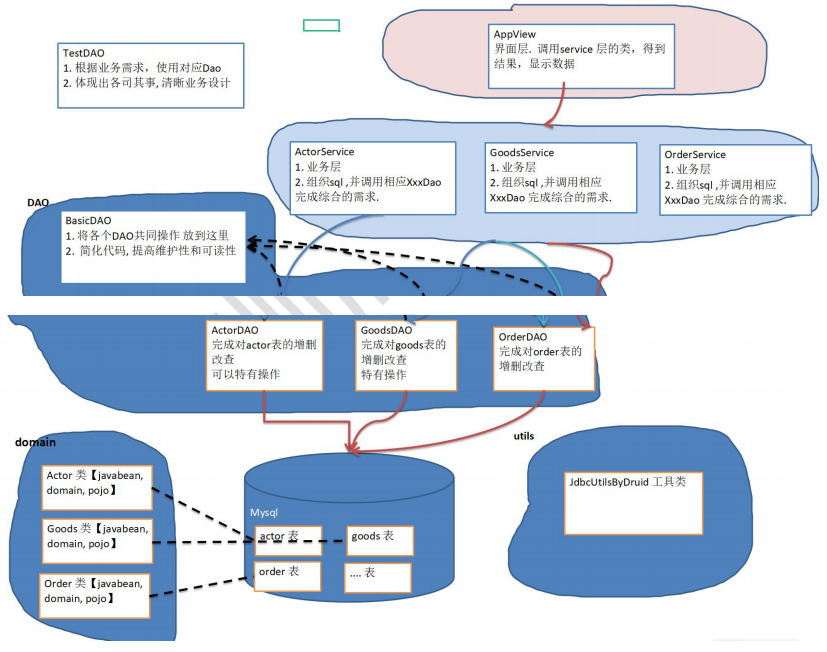
浅谈MVC架构
根据之前我们的一系列学习,逐渐摸索出了一套对数据库进行操作的程序架构。
- 首先,我们需要根据实际需求,来先设计我们所需要的数据库表——数据库层
- 之后我们需要将表结构英映射成对应的javabean类——domain层
- 在执行sql语句的时候,我们需要连接数据库,这时我们会用到数据库连接池、dbutils等,我们将对数据库惊醒的这些操作写成——DAO层
- 由于许多操作是重复的,例如连接数据库、DML、查询等,我们这时创建一个父类BasicDao,将这些操作封装到里面
- 之后不同的表的Dao再继承这个父类来实现一些自己特有的操作
- 我们还需要一个工具包——utils层
- 由于之前的Dao层每种Dao只能够操作一种类型的表,但是在实际需求中我们很可能会使用多张表
- 这时就需要引出service层,在每种表的service类中写上自己的业务逻辑,来实现多表操作
- 之后我们在view层来实现视图,并调用service层的业务
- 目前逻辑(各层之间调用关系): view - > service - > dao - > domain - > mysql表 utils工具人在其中穿插
分层的意义
1.软件分层是逻辑概念
2.可以使用不同的包来存放对应的类
3.体现了(各层之间)的调用关系
4.使类与类可以各司其职
本文来自博客园,作者:紫英626,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/recorderM/p/15925702.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号