JDBC02
封装 JDBCUtils
需求引出
因为操作数据库的步骤都相同,所以我们可以抽象出一个工具类,用来连接数据库和关闭连接
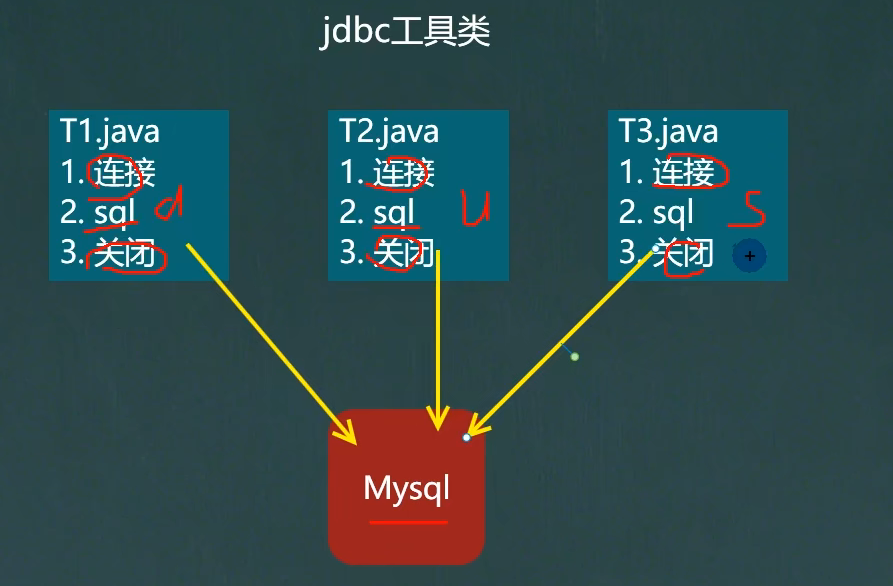

工具类
package com.recorder.jdbcutils; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.sql.*; import java.util.Properties; /** * @author 紫英 * @version 1.0 * @discription 数据库连接工具类 */ public class JdbcUtils { //定义相关的属性(4 个), 因为只需要一份,因此,我们做出 static private static String user; //用户名 private static String password; //密码 private static String url; //url private static String driver; //驱动名 //在 static 代码块初始化 static { try { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\jdbc.properties")); //读取相关的属性值 user = properties.getProperty("user"); password = properties.getProperty("password"); url = properties.getProperty("url"); driver = properties.getProperty("driver"); } catch (IOException e) { //在实际开发中,我们可以这样处理 //1. 将编译异常转成 运行异常 //2. 调用者,可以选择捕获该异常,也可以选择默认处理该异常,比较方便 throw new RuntimeException(e); } } //连接数据库, 返回 Connection public static Connection getConnection() { try { return DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); } catch (SQLException e) { //1. 将编译异常转成 运行异常 // 2. 调用者,可以选择捕获该异常,也可以选择默认处理该异常,比较方便 throw new RuntimeException(e); } } //关闭相关资源 /* 1. ResultSet 结果集 2. Statement 或者 PreparedStatement 3. Connection 4. 如果需要关闭资源,就传入对象,否则传入 null */ public static void close(ResultSet set, Statement statement, Connection connection) { try { //判断是否为空 if (set != null) { set.close(); } if (statement != null) { statement.close(); } if (connection != null) { connection.close(); } } catch (SQLException e) { //将编译异常转成运行异常抛出 throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
使用工具类执行DML语句
package com.recorder.jdbcutils; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * @author 紫英 * @version 1.0 * @discription DML语句 */ public class Test { @org.junit.jupiter.api.Test public void dmlTest(){ //1.得到链接 Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; //2.组织SQL String sql = "insert into admin values(?,?)"; try { connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //3.创建preparedstatement对象 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1, "along"); preparedStatement.setString(2, "666"); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); System.out.println("添加成功"); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭资源 //dml语句没有结果集所以写null JdbcUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection); } } }
事务
基本介绍

注意:4.5.也都是调用connection的对应方法
经典应用案例——转账业务

代码实现:
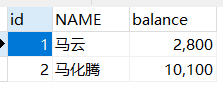
CREATE TABLE account ( id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment, NAME VARCHAR ( 32 ) NOT NULL DEFAULT '', balance double not null default 0) character set utf8; insert into account values(null, '马云',3000); insert into account values(null, '马化腾',10000);
package com.recorder.jdbc; import com.recorder.jdbcutils.JdbcUtils; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import java.sql.*; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * @author 紫英 * @version 1.0 * @discription JDBC中使用事务 */ public class Transaction_ { @Test //1.未使用事务 public void noTransaction() { //操作转账的业务 // 1. 得到连接 Connection connection = null; //2. 组织一个 sql(转钱) String sql = "update account set balance = balance - 100 where id = 1"; String sql2 = "update account set balance = balance + 100 where id = 2"; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; //3. 创建 PreparedStatement 对象 try { connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //执行第一条 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); int i = 1 / 0; //抛出异常 //执行第二条 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭资源 JdbcUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection); } } @Test //2.使用事务 public void useTransaction() { //操作转账的业务 // 1. 得到连接 Connection connection = null; //2. 组织一个 sql(转钱) String sql = "update account set balance = balance - 100 where id = 1"; String sql2 = "update account set balance = balance + 100 where id = 2"; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; //3. 创建 PreparedStatement 对象 try { connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //将 connection 设置为不自动提交 connection.setAutoCommit(false);//相当于开启事务 //执行第一条 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); int i = 1 / 0; //抛出异常 //执行第二条 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //两条sql都执行完过后进行提交 connection.commit(); } catch (SQLException e) { //这里我们可以进行回滚,即撤销执行的 SQL // 默认回滚到事务开始的状态. System.out.println("执行发生了异常,撤销执行的 sql"); try { connection.rollback(); } catch (SQLException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } finally { //关闭资源 JdbcUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection); } } }
数据查看:
1.初始状态
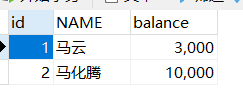
2.不使用事务,并在两条sql中间穿插异常,可以看到,业务出现了问题
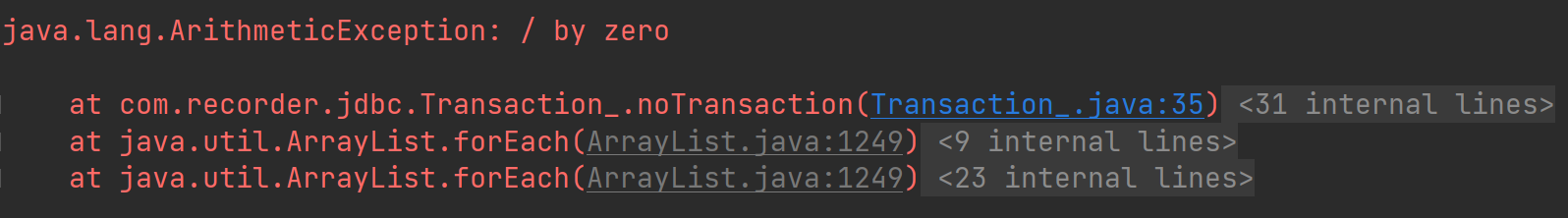
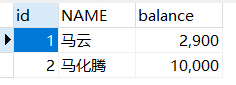
3.使用事务,并在两条sql中间穿插异常,由于catch语句中回滚无变化

4.使用事务正常操作,转账成功
批处理
基本介绍

url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db01?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
代码实现

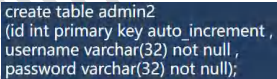
CREATE TABLE admin2 ( id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment, username VARCHAR ( 32 ) NOT NULL, `password` VARCHAR ( 32 ) NOT NULL );
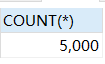
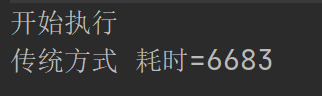
package com.recorder.batch; import com.recorder.jdbcutils.JdbcUtils; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; /** * @author 紫英 * @version 1.0 * @discription 批处理添加数据 */ public class Batch01 { //传统方法,添加 5000条数据到 admin2 @Test public void noBatch() throws Exception { Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into admin2 values(null, ?, ?)"; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); System.out.println("开始执行"); long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//开始时间 for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) { //5000 执行 preparedStatement.setString(1, "jack" + i); preparedStatement.setString(2, "666"); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("传统方式 耗时=" + (end - start));//传统方式耗时 //关闭连接 JdbcUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection); }
//使用批量操作方式添加5000条数据 到 admin2 @Test public void useBatch() throws Exception { Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into admin2 values(null, ?, ?)"; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); System.out.println("开始执行"); long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//开始时间 for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) { //5000 执行 preparedStatement.setString(1, "jack" + i); preparedStatement.setString(2, "666"); //将 sql 语句加入到批处理包中 -> 看源码 preparedStatement.addBatch(); if ((i + 1) % 1000 == 0) {//满 1000 条 sql preparedStatement.executeBatch(); // 清空一把 preparedStatement.clearBatch(); } } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("批处理方式 耗时=" + (end - start));//传统的方式 耗时 //关闭连接 JdbcUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection); }
速度快了大概1000倍
}
源码解读
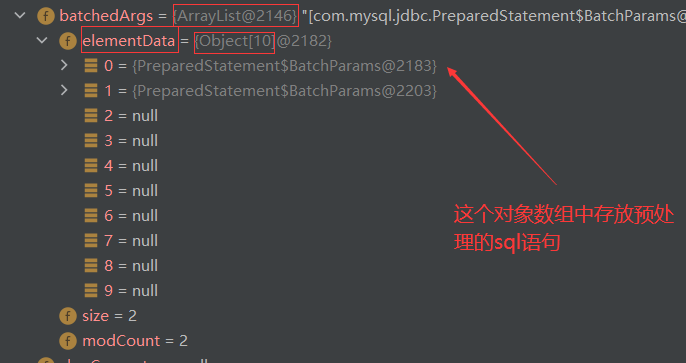
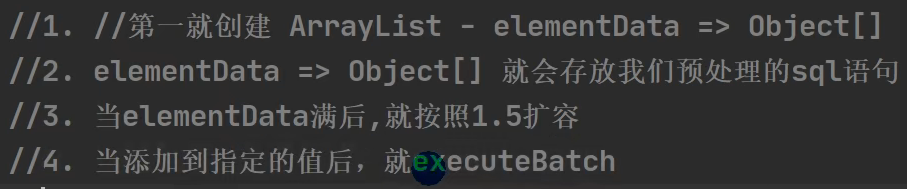
5.批处理语句可以帮助我们减少发送sql语句的网络开销,而且使用预编译也会减少编译次数,因此效率更高
(以下案例中5000条数据只需发送五次)
扩容就按照ArrayList的扩容机制,进行1.5倍扩容
public void addBatch() throws SQLException { synchronized(this.checkClosed().getConnectionMutex()) { if (this.batchedArgs == null) { this.batchedArgs = new ArrayList(); //第一次的时候创建一个ArrayList数组 } for(int i = 0; i < this.parameterValues.length; ++i) { this.checkAllParametersSet(this.parameterValues[i], this.parameterStreams[i], i); } this.batchedArgs.add(new PreparedStatement.BatchParams(this.parameterValues, this.parameterStreams, this.isStream, this.streamLengths, this.isNull)); } }
本文来自博客园,作者:紫英626,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/recorderM/p/15913706.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号