Business Model - Organizations And Organizations Theory
Organizations And Organizations Theory
| Current Challenges |
|---|
| Globalization |
| Intense Competition |
| Ethics and Social Responsibility |
| Speed of Responsiveness |
| The digital Workplace |
| Diversity |
Organization theory helps us explain what happened in the past, as well as what may happen in the future, so that we can manage organization more effectively.
what is Organization
- Social entities that are goal-directed
- Designed as deliberately structured and coordinated activity systems
- Linked to the external environment
- Includes large multinational corporations, family owned businesses as well as nonprofits.
Importance of Organization
- Organizations are a means to an end.
- The corporation has played a significant role in the last 100 years
- Produce goods and services efficiently
- Facilitate innovation
- Adapt to and influence a changing environment
- Create value for owners, customers, and employees
- Accommodate ongoing challenges of diversity, ethics, and the motivation and coordination of employees.
Dimension of Organization Design
| Structural Dimensions | Contigency Factors |
|---|---|
| Formalization | Size |
| Specialization | Organizational technology |
| Hierarchy of Authority | Environment |
| Centralization | Goal and strategy |
| Professionalism | Culture |
| Personnel Ratios |
Performance and Effectiveness Outcomes
Efficiency: amount of resources used to achieve the organization's goal
Effectiveness: the degree to which an organization achieves its goal
Stakeholder Approach: Balancing the needs of groups in and outside of the organization that has a stake in the organization's performance
Organic and Mechanistic Designs
| Mechanistic Design | Contigency Factors |
|---|---|
| Centralized structure | Rigid Culture |
| Specialized Tasks | Manufacturing Technology |
| Many Rules Formalized | Efficiency Strategy |
| Vertical Communication | Stable Environment |
| Strict Hierarchy of Authority | Large Size |
| Organic Design | Contigency Factors |
|---|---|
| Decentralized Structure | Adaptive Culture |
| Empowered Roles | Service Technology |
| Few Rules, informal | Innovation Strategy |
| Horizontal Communication | Changing Environment |
| Collaborative Teamwork | Small Size |
Devide and Coordinate
- Markets, hierarchies and conventions
Market Work division \(\rightarrow\) Specialization\(\rightarrow\) coordination\(\rightarrow\) conventions Hierarchy
Cordination
- Work division and coordination
- Thompson model
- Mintzberg model
Thompson coordination model
Born from workflow, Sharing of common resources
| Typology of Interdipendences |
|---|
| Generic |
| Sequential |
| Mutual |
| Coordination mode |
|---|
| Standardisation |
| Planning |
| Mutual Adjustment |
| Generic | Sequential | Mutual | |
| Standardisation | √ | ineffectiveness | NO(ineffectiveness) |
| Planning | inefficiency | √ | ineffectiveness |
| Mutual Adjustment | NO(inefficiency) | inefficiency | √ |
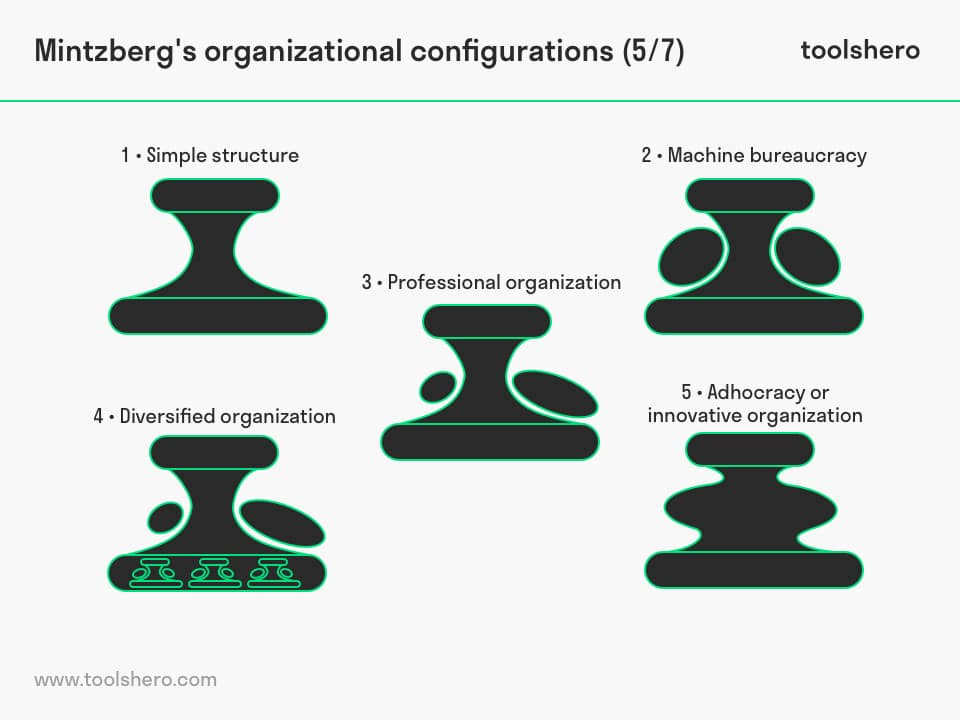
Mintzberg
| Five Components of the Organization |
|---|
| Top Management |
| Middle Management |
| Technical cores |
| Technical Support Staff |
| Administrative Support Staff |
| Five Coordination Mechanisms | |
|---|---|
| Direct Supervision | The organizational units to be coordinated have the same hierarchically superior unit(and therefore they have a homogeneity of supervision) which is therefore able to coordinate the two units. |
| Process Standardization | Standardization of cycles and working methods through codification of activities,equipment, employee methods. |
| Output Standardization | Standardization and codification of the result envisaged by an organizational unit. these results can be objectives set by a plan or products / services standardized in terms of design and operation. |
| Input Standardization | Standadization of incoming resources(raw materials, personnel, etc) with a consequent homogeneity and simplification of subsequent transformations. |
| Mutual Adjustment | The coordination is carried out through a frequent and easy connection system(for carrying out activities) between the organizational units, it provides communications and feedback systems between organzational units. It is necessary in cases where early or planned management is difficult. |
| Five Organization Models |
|---|
| Simple Structure |
| Mechanical Bureaucracy |
| Divisional Organisation |
| Professional Bureaucracy |
| Adhocracy(as-needed) |
Organization Structure
The Organization Variables
| The Organization Variable | Organization Structure | Operating Systems | Leadership Style |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Work division | Coordination | Leadership |
| 2. | Departmental Grouping Options | Control | Motivation |
| 3. | Hierarchical levels | Decision Making Process | Authority Management |
| 4. | Defination of tasks and roles | Communication/Information sharing | |
| 5. | Assessment |
| Departmental Grouping Options | Examples | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Functional Grouping | Production,Design,Marketing,Logistics,Sales,Management | best for one or few products | 1.Hierarchy overload 2.less innovation |
| Divisional Grouping | Product structure or strategic business units | By product, geographic area, customer | Divisional autonomy / self-sufficiency |
| Multifocused Grouping | 1.meet dual demands from customer,2.flexible sharing of human resources across products,3.best in medium-sized with multiple products | dual authority,frequent meetings,required great effort to maintain power banance | |
| Horizontal Grouping | 1.promotes flexibility response to changes in customer needs, promotes a focus on teamwork and collaboration | Determining core processes is difficult and time consuming,requires training | |
| Virtual Network Grouping |
Organization Structures
- Elementary Structure
- Functional Structure
- Division Structure
- By product
- By geographic area
- By customer
- Matrix Structure
- #
- Horizontal Structure
* - Virtual Structure


