shiro框架漏洞
Apache Shiro
Apache Shiro 是⼀个功能强⼤且易于使⽤的 Java 安全框架,它⽤于处理身份验证,授权,加密和会话
管理
在默认情况下 , Apache Shiro 使⽤ CookieRememberMeManager 对⽤户身份进⾏序列化/反序列化 , 加
密/解密和编码/解码 , 以供以后检索 .
因此 , 当 Apache Shiro 接收到未经身份验证的⽤户请求时 , 会执⾏以下操作来寻找他们被记住的身份.
从请求数据包中提取 Cookie 中 rememberMe 字段的值,对提取的 Cookie 值进⾏ Base64 解码,对
Base64 解码后的值进⾏ AES 解密,对解密后的字节数组调⽤ ObjectInputStream.readObject() ⽅法来
反序列化.
但是默认AES加密密钥是 “硬编码” 在代码中的 . 因此 , 如果服务端采⽤默认加密密钥 , 那么攻击者就可以
构造⼀个恶意对象 , 并对其进⾏序列化 , AES加密 , Base64编码 , 将其作为 Cookie 中 rememberMe 字段
值发送 . Apache Shiro 在接收到请求时会反序列化恶意对象 , 从⽽执⾏攻击者指定的任意代码 .
Shiro 550 反序列化漏洞存在版本:shiro <1.2.4,产⽣原因是因为shiro接受了Cookie⾥⾯rememberMe
的值,然后去进⾏Base64解密后,再使⽤aes密钥解密后的数据,进⾏反序列化。
构造该值为⼀个利⽤链序列化后的值进⾏该密钥aes加密后进⾏base64加密,反序列化payload内容后就
可以命令执⾏。
shiro550 shiro <1.2.4漏洞复现
环境搭建
shiro下载 https://codeload.github.com/apache/shiro/zip/shiro-root-1.2.4
环境 tomcat 8.5
jdk版本 1.8.0.65
idea 2021
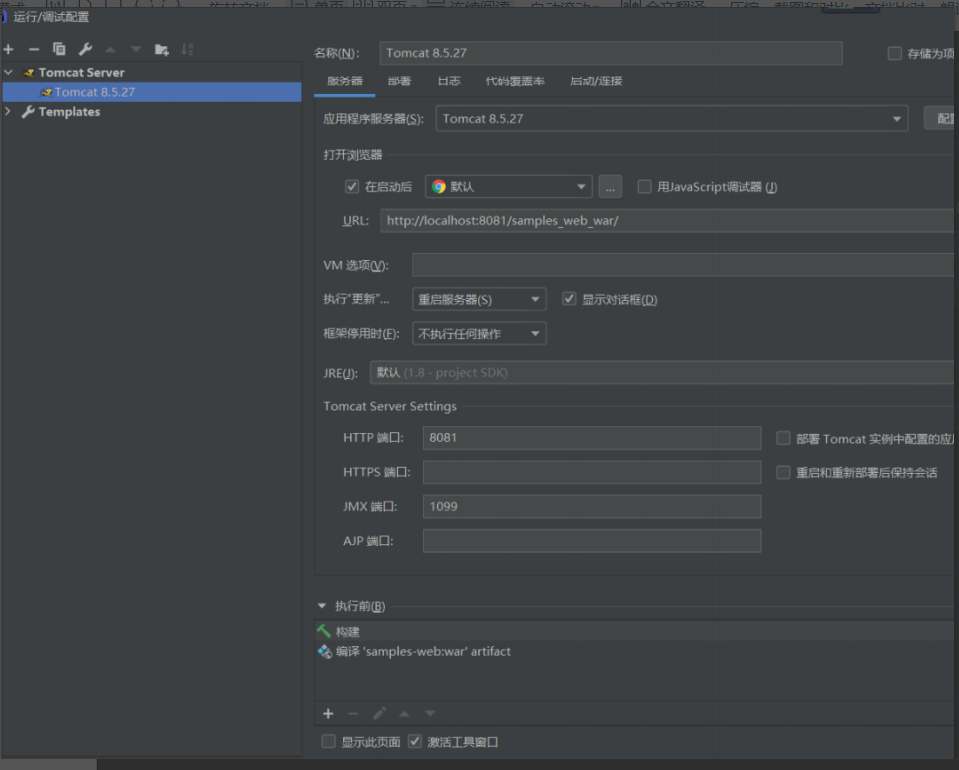
⽤idea开 shiro-shiro-root-1.2.4\samples 设置⼀下pox.xml maven更新包
修改pom.xml 修改⼀下版本
如果测试cc3依赖可以添加
如果测试cc4
当前测试测试环境pom.xml
接着添加tomcat
1.漏洞分析
shiro默认使⽤了CookieRememberMeManager,其处理cookie的流程是:
得到rememberMe的cookie值 --> Base64解码 --> AES解密 --> 反序列化
然⽽AES的密钥是硬编码的,就导致了攻击者可以构造恶意数据造成反序列化的RCE漏洞。
payload 构造的顺序则就是相对的反着来:
恶意命令-->序列化-->AES加密-->base64编码-->发送cookie
在整个漏洞利⽤过程中,⽐较重要的是AES加密的密钥,该秘钥默认是默认硬编码的,所以如果没有修
改默认的密钥,就⾃⼰可以⽣成恶意构造的cookie了。
shiro特征:
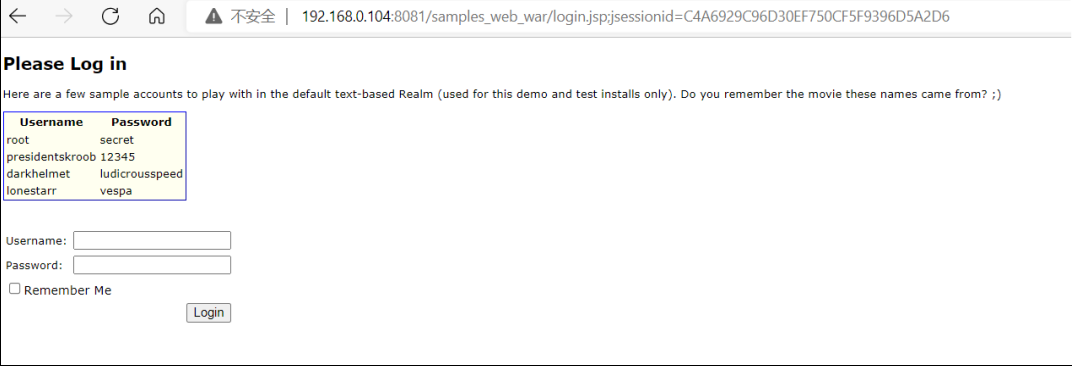
未登陆的情况下,请求包的cookie中没有rememberMe字段,返回包set-Cookie⾥也没有deleteMe字段
登陆失败的话,不管勾选RememberMe字段没有,返回包都会有rememberMe=deleteMe字段
不勾选RememberMe字段,登陆成功的话,返回包set-Cookie会有rememberMe=deleteMe字段。但是
之后的所有请求中Cookie都不会有rememberMe字段
勾选RememberMe字段,登陆成功的话,返回包set-Cookie会有rememberMe=deleteMe字段,还会
有rememberMe字段,之后的所有请求中Cookie都会有rememberMe字段
2.代码分析
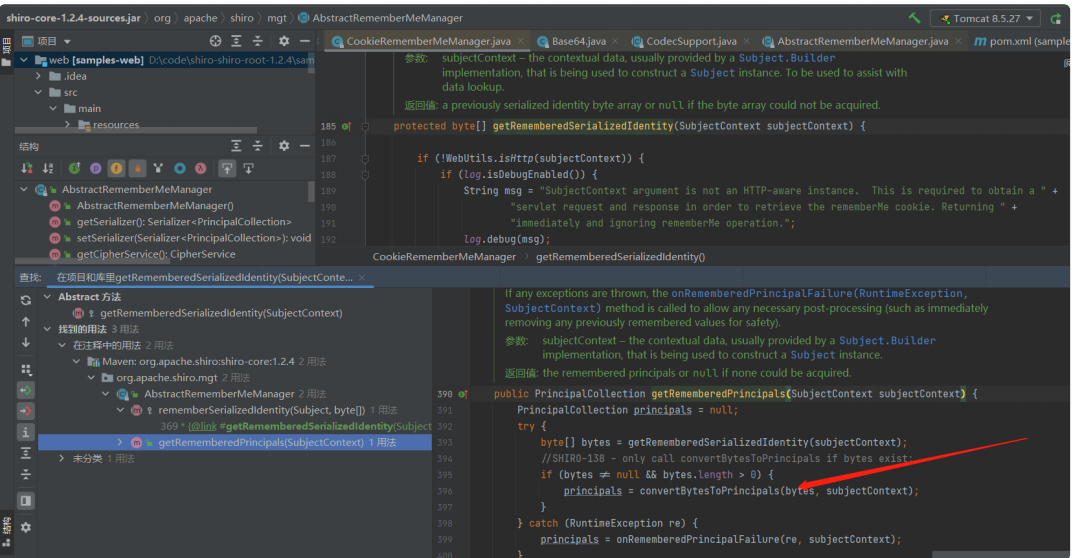
代码分析 ⾸先找到 org/apache/shiro/web/mgt/CookieRememberMeManager.java
找到 getRememberedSerializedIdentity⽅法
从代码上看到返回的是 base64解码之后的内容 接着寻找调⽤处
org/apache/shiro/mgt/AbstractRememberMeManager.java
convertBytesToPrincipals
bytes = decrypt(bytes)的内容等会再看 现在 进⼊ deserialize
进⼊ deserialize 发现是⼀个接⼝ 接着寻找实现接⼝的类
org/apache/shiro/io/DefaultSerializer.java
发现调⽤原⽣的 T deserialized = (T) ois.readObject(); 导致存在反序列化漏洞
既然是硬编码反序列化漏洞 继续寻找 跟进 decrypt
getCipherService() 这⾥是获取密钥服务 加密⽅法是aes 跟进 decrypt getDecryptionCipherKey()
点击跟进 decryptionCipherKey 是⼀个私有字段 寻找赋值的地⽅
private byte[] encryptionCipherKey;
org/apache/shiro/mgt/AbstractRememberMeManager.java
寻找 setEncryptionCipherKey调⽤
org/apache/shiro/mgt/AbstractRememberMeManager.java
接着setCipherKey调⽤
发现 DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES是⼀个常量
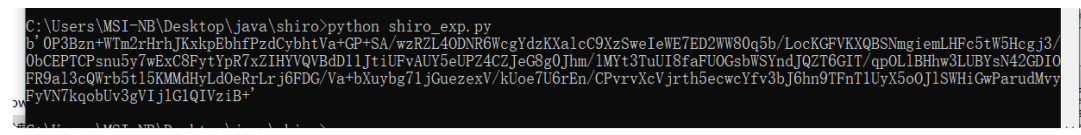
kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA== 这个值就是shiro加密的硬编码
3.漏洞测试
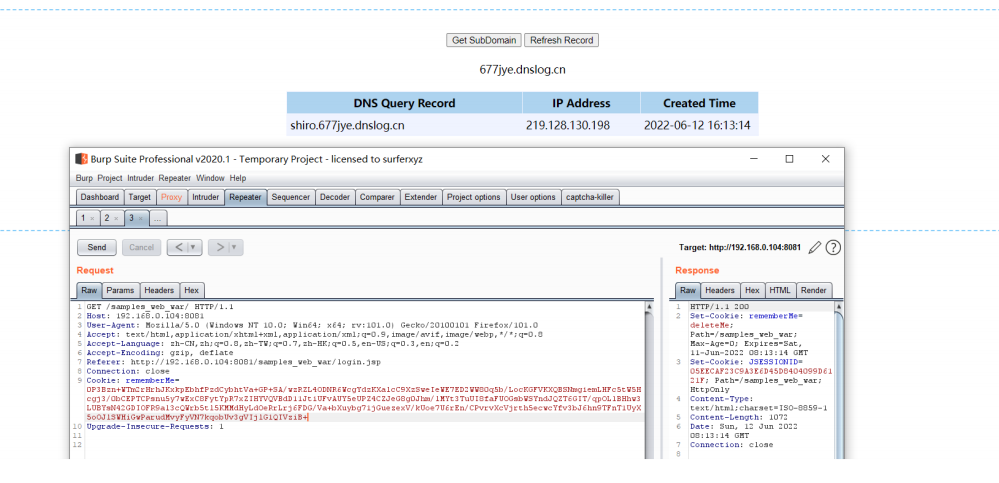
⼀般测试都是⽤jdk原⽣态的URLDNS链
接着⽤脚本进⾏加密 kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==这个编码⼀定对应。
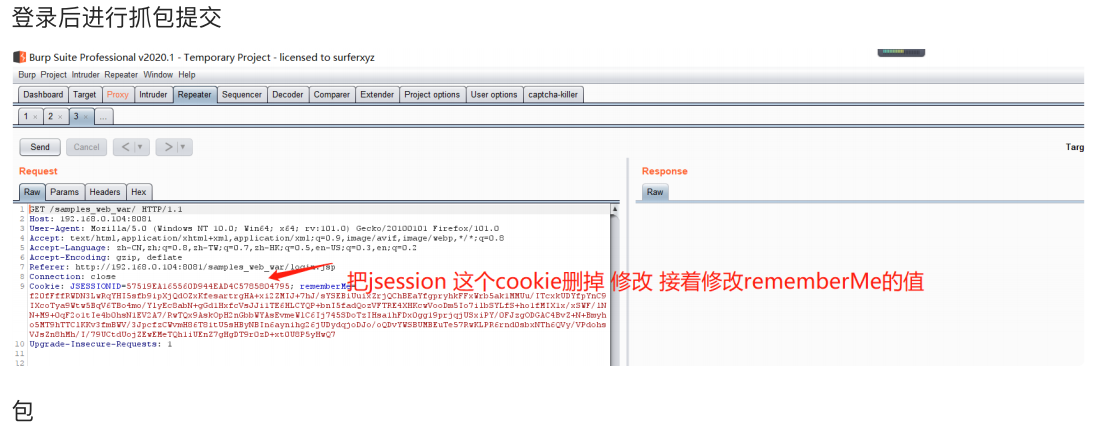
登录⽬标上勾上 Remember Me
4.深⼊利⽤
由于Shrio对resolveClass进⾏了修改,导致数组类⽆法加载,因此原⽣的cc链是⽆法直接使⽤的
cc链
commons-beanutils cb 链⽆依赖利⽤链
shiro721 CVE-2019-12422 漏洞详细
这两个漏洞主要区别在于Shiro550使⽤已知密钥碰撞,后者Shiro721是使⽤ 登录
后rememberMe= {value}去爆破正确的key值 进⽽反序列化,对⽐Shiro550条件只
要有 ⾜够密钥库 (条件⽐较低)、Shiro721需要登录(要求⽐较⾼鸡肋 )。
Apache Shiro < 1.4.2 默认使⽤ AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding 模式
1.漏洞详细
shiro721⽤到的加密⽅式是AES-CBC,⽽且其中的ase加密的key基本猜不到了,是系统随机⽣成的。⽽
cookie解析过程跟cookie的解析过程⼀样,也就意味着如果能伪造恶意的rememberMe字段的值且⽬标
含有可利⽤的攻击链的话,还是能够进⾏RCE的。
通过Padding Oracle Attack攻击可以实现破解AES-CBC加密过程进⽽实现rememberMe的内容伪造。
下⾯会有单独的篇幅讲Padding Oracle Attack。
影响版本:
详细 说明 参考 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41874930/article/details/121314926 这个⾯试的时候经常
也是考点。
2.漏洞测试
⼀次成功的Shiro Padding Oracle需要⼀直向服务器不断发包,判断服务器返回,攻击时间通常需要⼏个
⼩时。由于此漏洞利⽤起来耗时时间特别⻓,很容易被waf封禁,因此在真实的红队项⽬中,极少有此漏
洞的攻击成功案例
这⾥测试的时候cb这条利⽤链 如果在⽬标上最好测试urldns链。。
__EOF__

本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/rayob1/p/16816124.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具