HBase 2、HBase安装与初试牛刀
官方帮助文档:http://hbase.apache.org/book.html PDF:http://hbase.apache.org/apache_hbase_reference_guide.pdf
1、安装前准备
– Hadoop集群要启动正常
– Zookeeper集群启动正常
HBase 分布式存储的运行依托于Zookeeper和HDFS所以必须有一个完整的Hadoop分布式运行环境和Zookeeper运行环境;
Hadoop高可用安装参见:http://www.cnblogs.com/raphael5200/p/5154325.html
2、安装HBase
1)、配置hbase-env.sh
进入HBase 的conf目录下,编辑hbase-env.sh 添加如下配置:
# 指定HBase是否使用HBase本身自带的Zookeeper export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=false # 指定Jdk目录 export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.7.0_79 # 指定Hadoop配置文件目录 export HBASE_CLASSPATH=/usr/local/hadoop-2.5.1/etc/hadoop
2)、配置hbase-site.xml
编辑conf目录下的hbase-site.xml,配置内容如下:
# 指定HDFS的根目录,在这个地方,如果想使用HBase高可用的话,必须配置成dfs.nameservices 不能配置节点名称 <property> <name>hbase.rootdir</name> <value>hdfs://raphael/hbase</value> </property> <property> <name>hbase.cluster.distributed</name> <value>true</value> </property> # 配置Zookeeper节点,配置可不加端口 <property> <name>hbase.zookeeper.quorum</name> <value>node5,node6,node7</value> </property>
3)、配置reginservers,数据节点
编辑conf下的regionservers,在该文件中配置HBase的节点,每台节点占一行:
node5
node6
node7
4)、配置HBase环境变量
编辑/root/.bash_profile 在该文件中配置HBase的环境变量:
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.7.0_79 PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin export JAVA_HOME HADOOP_HOME=/usr/local/hadoop-2.5.1 export HADOOP_HOME HIVE_HOME=/usr/local/apache-hive-1.2.1 export HIVE_HOME HBASE_HOME=/usr/local/hbase-1.1.3 export HBASE_HOME PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/zookeeper-3.4.6/bin/:$HADOOP_HOME/bin/:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin/:$HIVE_HOME/bin/:$HBASE_HOME/bin export PATH
配置完成以后,将HBase分发到其他的HBase节点上:
scp -r /usr/local/hbase root@node6:/usr/local/hbase
5)、启用HBase
#首先启动Zookeeper的节点 $ zkServer.sh start #再启动Hadoop $ start-all.sh #最后启动HBase $ start-hbase.sh
启动完成以后就可以访问 http://节点:16010 来查看了
在关闭节点之前必须先关闭HBase,否则下次启动HBase有可以会出错;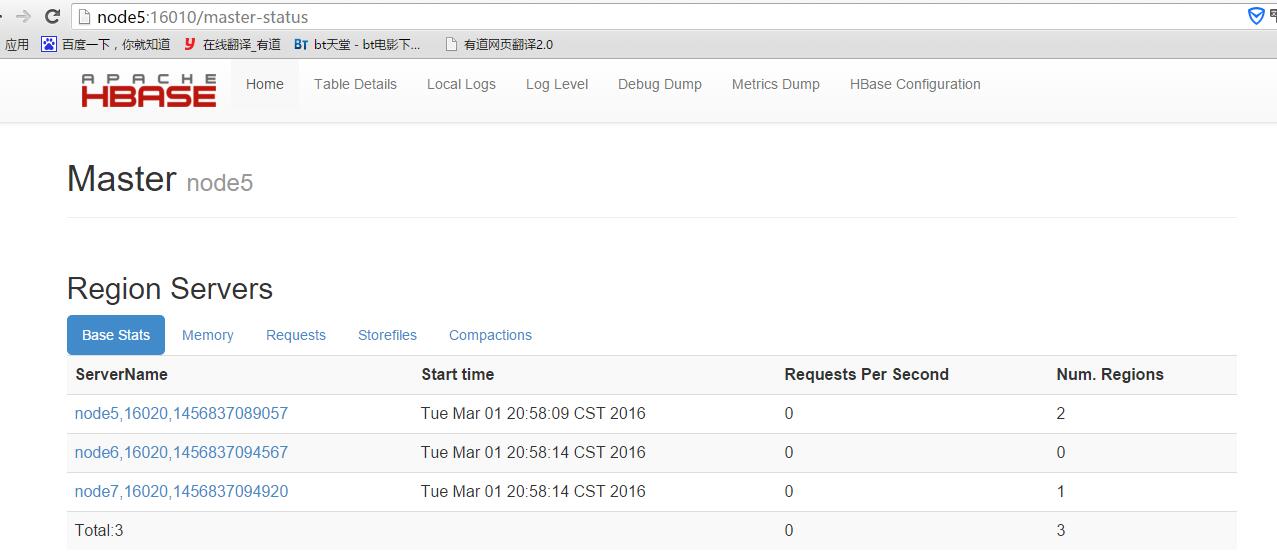
3、使用HBase 和 Hbase使用帮助
1)、进入HBase
#使用命令进入HBase Shell $ hbase shell The HBase shell is the (J)Ruby IRB with the above HBase-specific commands added. For more on the HBase Shell, see http://hbase.apache.org/book.html hbase(main):003:0>
2)、使用HBase帮助
HBase 提供了大量的帮助文档,只要在HBase 下使用命令help就能够查看HBase所有关键字的帮助
hbase(main):003:0> help HBase Shell, version 1.1.3, r72bc50f5fafeb105b2139e42bbee3d61ca724989, Sat Jan 16 18:29:00 PST 2016 Type 'help "COMMAND"', (e.g. 'help "get"' -- the quotes are necessary) for help on a specific command. Commands are grouped. Type 'help "COMMAND_GROUP"', (e.g. 'help "general"') for help on a command group. COMMAND GROUPS: Group name: general Commands: status, table_help, version, whoami Group name: ddl Commands: alter, alter_async, alter_status, create, describe, disable, disable_all, drop, drop_all, enable, enable_all, exists, get_table, is_disabled, is_enabled, list, show_filters Group name: namespace Commands: alter_namespace, create_namespace, describe_namespace, drop_namespace, list_namespace, list_namespace_tables Group name: dml Commands: append, count, delete, deleteall, get, get_counter, get_splits, incr, put, scan, truncate, truncate_preserve ...
如果不知道某个关键字如何使用的话,只需要在Hbase下直接建入该关键字即可:
hbase(main):004:0> put ERROR: wrong number of arguments (0 for 4) Here is some help for this command: Put a cell 'value' at specified table/row/column and optionally timestamp coordinates. To put a cell value into table 'ns1:t1' or 't1' at row 'r1' under column 'c1' marked with the time 'ts1', do: hbase> put 'ns1:t1', 'r1', 'c1', 'value' hbase> put 't1', 'r1', 'c1', 'value' hbase> put 't1', 'r1', 'c1', 'value', ts1 hbase> put 't1', 'r1', 'c1', 'value', {ATTRIBUTES=>{'mykey'=>'myvalue'}} hbase> put 't1', 'r1', 'c1', 'value', ts1, {ATTRIBUTES=>{'mykey'=>'myvalue'}} hbase> put 't1', 'r1', 'c1', 'value', ts1, {VISIBILITY=>'PRIVATE|SECRET'} The same commands also can be run on a table reference. Suppose you had a reference t to table 't1', the corresponding command would be: hbase> t.put 'r1', 'c1', 'value', ts1, {ATTRIBUTES=>{'mykey'=>'myvalue'}}
在HBase 下,如果输入内容错了,使用回退键是不管用的,必须使用Ctrl+回退键才行。
3)、创建表、插入数据、查询数据
进入hbase shell console $HBASE_HOME/bin/hbase shell 如果有kerberos认证,需要事先使用相应的keytab进行一下认证(使用kinit命令),认证成功之后再使用hbase shell进入可以使用whoami命令可查看当前用户 hbase(main)> whoami 表的管理 1)查看有哪些表 hbase(main)> list 2)创建表 # 语法:create <table>, {NAME => <family>, VERSIONS => <VERSIONS>} # 例如:创建表t1,有两个family name:f1,f2,且版本数均为2 hbase(main)> create 't1',{NAME => 'f1', VERSIONS => 2},{NAME => 'f2', VERSIONS => 2} 3)删除表 分两步:首先disable,然后drop 例如:删除表t1 hbase(main)> disable 't1' hbase(main)> drop 't1' 4)查看表的结构 # 语法:describe <table> # 例如:查看表t1的结构 hbase(main)> describe 't1' 5)修改表结构 修改表结构必须先disable # 语法:alter 't1', {NAME => 'f1'}, {NAME => 'f2', METHOD => 'delete'} # 例如:修改表test1的cf的TTL为180天 hbase(main)> disable 'test1' hbase(main)> alter 'test1',{NAME=>'body',TTL=>'15552000'},{NAME=>'meta', TTL=>'15552000'} hbase(main)> enable 'test1' 权限管理 1)分配权限 # 语法 : grant <user> <permissions> <table> <column family> <column qualifier> 参数后面用逗号分隔 # 权限用五个字母表示: "RWXCA". # READ('R'), WRITE('W'), EXEC('X'), CREATE('C'), ADMIN('A') # 例如,给用户‘test'分配对表t1有读写的权限, hbase(main)> grant 'test','RW','t1' 2)查看权限 # 语法:user_permission <table> # 例如,查看表t1的权限列表 hbase(main)> user_permission 't1' 3)收回权限 # 与分配权限类似,语法:revoke <user> <table> <column family> <column qualifier> # 例如,收回test用户在表t1上的权限 hbase(main)> revoke 'test','t1' 表数据的增删改查 1)添加数据 # 语法:put <table>,<rowkey>,<family:column>,<value>,<timestamp> # 例如:给表t1的添加一行记录:rowkey是rowkey001,family name:f1,column name:col1,value:value01,timestamp:系统默认 hbase(main)> put 't1','rowkey001','f1:col1','value01' 用法比较单一。 2)查询数据 a)查询某行记录 # 语法:get <table>,<rowkey>,[<family:column>,....] # 例如:查询表t1,rowkey001中的f1下的col1的值 hbase(main)> get 't1','rowkey001', 'f1:col1' # 或者: hbase(main)> get 't1','rowkey001', {COLUMN=>'f1:col1'} # 查询表t1,rowke002中的f1下的所有列值 hbase(main)> get 't1','rowkey001' b)扫描表 # 语法:scan <table>, {COLUMNS => [ <family:column>,.... ], LIMIT => num} # 另外,还可以添加STARTROW、TIMERANGE和FITLER等高级功能 # 例如:扫描表t1的前5条数据 hbase(main)> scan 't1',{LIMIT=>5} c)查询表中的数据行数 # 语法:count <table>, {INTERVAL => intervalNum, CACHE => cacheNum} # INTERVAL设置多少行显示一次及对应的rowkey,默认1000;CACHE每次去取的缓存区大小,默认是10,调整该参数可提高查询速度 # 例如,查询表t1中的行数,每100条显示一次,缓存区为500 hbase(main)> count 't1', {INTERVAL => 100, CACHE => 500} 3)删除数据 a )删除行中的某个列值 # 语法:delete <table>, <rowkey>, <family:column> , <timestamp>,必须指定列名 # 例如:删除表t1,rowkey001中的f1:col1的数据 hbase(main)> delete 't1','rowkey001','f1:col1' 注:将删除改行f1:col1列所有版本的数据 b )删除行 # 语法:deleteall <table>, <rowkey>, <family:column> , <timestamp>,可以不指定列名,删除整行数据 # 例如:删除表t1,rowk001的数据 hbase(main)> deleteall 't1','rowkey001' c)删除表中的所有数据 # 语法: truncate <table> # 其具体过程是:disable table -> drop table -> create table # 例如:删除表t1的所有数据 hbase(main)> truncate 't1' Region管理 1)移动region # 语法:move 'encodeRegionName', 'ServerName' # encodeRegionName指的regioName后面的编码,ServerName指的是master-status的Region Servers列表 # 示例 hbase(main)>move '4343995a58be8e5bbc739af1e91cd72d', 'db-41.xxx.xxx.org,60020,1390274516739' 2)开启/关闭region # 语法:balance_switch true|false hbase(main)> balance_switch 3)手动split # 语法:split 'regionName', 'splitKey' 4)手动触发major compaction #语法: #Compact all regions in a table: #hbase> major_compact 't1' #Compact an entire region: #hbase> major_compact 'r1' #Compact a single column family within a region: #hbase> major_compact 'r1', 'c1' #Compact a single column family within a table: #hbase> major_compact 't1', 'c1' 配置管理及节点重启 1)修改hdfs配置 hdfs配置位置:/etc/hadoop/conf # 同步hdfs配置 cat /home/hadoop/slaves|xargs -i -t scp /etc/hadoop/conf/hdfs-site.xml hadoop@{}:/etc/hadoop/conf/hdfs-site.xml #关闭: cat /home/hadoop/slaves|xargs -i -t ssh hadoop@{} "sudo /home/hadoop/cdh4/hadoop-2.0.0-cdh4.2.1/sbin/hadoop-daemon.sh --config /etc/hadoop/conf stop datanode" #启动: cat /home/hadoop/slaves|xargs -i -t ssh hadoop@{} "sudo /home/hadoop/cdh4/hadoop-2.0.0-cdh4.2.1/sbin/hadoop-daemon.sh --config /etc/hadoop/conf start datanode" 2)修改hbase配置 hbase配置位置: # 同步hbase配置 cat /home/hadoop/hbase/conf/regionservers|xargs -i -t scp /home/hadoop/hbase/conf/hbase-site.xml hadoop@{}:/home/hadoop/hbase/conf/hbase-site.xml # graceful重启 cd ~/hbase bin/graceful_stop.sh --restart --reload --debug inspurXXX.xxx.xxx.org




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号