python的deque(双向)队列详解
首先 python的队列有很多种
Python标准库中包含了四种队列,分别是queue.Queue / asyncio.Queue / multiprocessing.Queue / collections.deque
可见deque是标准库collections中的
这其中最好用的是deque
以下是deque的基本操作:
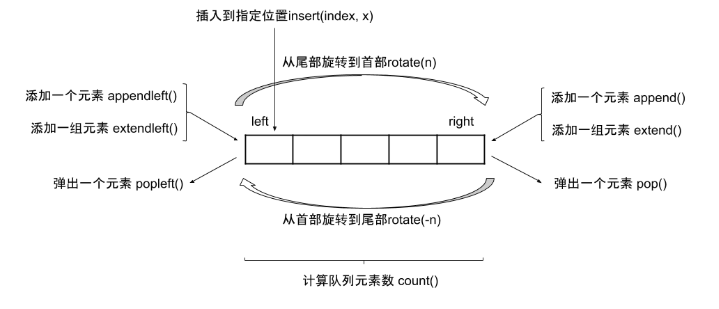
它的操作很像list 同时
相比于list实现的队列,deque实现拥有更低的时间和空间复杂度。list实现在出队(pop)和插入(insert)时的空间复杂度大约为O(n),deque在出队(pop)和入队(append)时的时间复杂度是O(1)。
所以deque更有优越性 而且deque既可以表示队列 又可以表示栈 实在是太方便了
下面再介绍几个黑科技:
deque支持in操作符(真没想到这都支持)
1 q = collections.deque([1, 2, 3, 4]) 2 print(5 in q) # False 3 print(1 in q) # True
还可以顺逆时针旋转...
# 顺时针 q = collections.deque([1, 2, 3, 4]) q.rotate(1) print(q) # [4, 1, 2, 3] q.rotate(1) print(q) # [3, 4, 1, 2] # 逆时针 q = collections.deque([1, 2, 3, 4]) q.rotate(-1) print(q) # [2, 3, 4, 1] q.rotate(-1) print(q) # [3, 4, 1, 2]
还可以复制一个新队列:
>>> d.append(1) >>> d.append(2) >>> d deque([1, 2]) >>> d1 = d.copy() >>> d1 deque([1, 2])
值得注意的是 deque里边的形式是列表形式
所以 试试extend呢?
>>> d.clear() >>> d.append(1) >>> d.extend([3,4,5]) >>> d deque([1, 3, 4, 5])
能不能从左边extend呢:
>>> d.clear() >>> d.append(1) >>> d.extendleft([3,4,5]) >>> d deque([5, 4, 3, 1])
还有index:查找索引位置
>>> d.extend(["a","b","c","d","e","f"]) >>> d deque(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e','f']) >>> d.index("c",0,4) #指定查找的区间 2 >>> d.index("c",0,2) error...
其他的一些基本操作 还有
d.insert(位置,元素) 在指定位置插入元素
d.remove(元素) 删除指定元素
d.reverse 队列翻转
接下来我们做一道面试题:
题目
请定义一个队列并实现函数 max_value 得到队列里的最大值,要求函数max_value、push_back 和 pop_front 的均摊时间复杂度都是O(1)。
若队列为空,pop_front 和 max_value 需要返回 -1
输入:
["MaxQueue","push_back","push_back","max_value","pop_front","max_value"]
[[],[1],[2],[],[],[]]
输出: [null,null,null,2,1,2]
既然时间复杂度是O(1)
我们用deque就好
代码:
from collections import deque class MaxQueue: def __init__(self): self.d = deque() def max_value(self) -> int: return max(self.d) if self.d else -1 def push_back(self, value: int) -> None: self.d.append(value) def pop_front(self) -> int: return self.d.popleft() if self.d else -1




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端