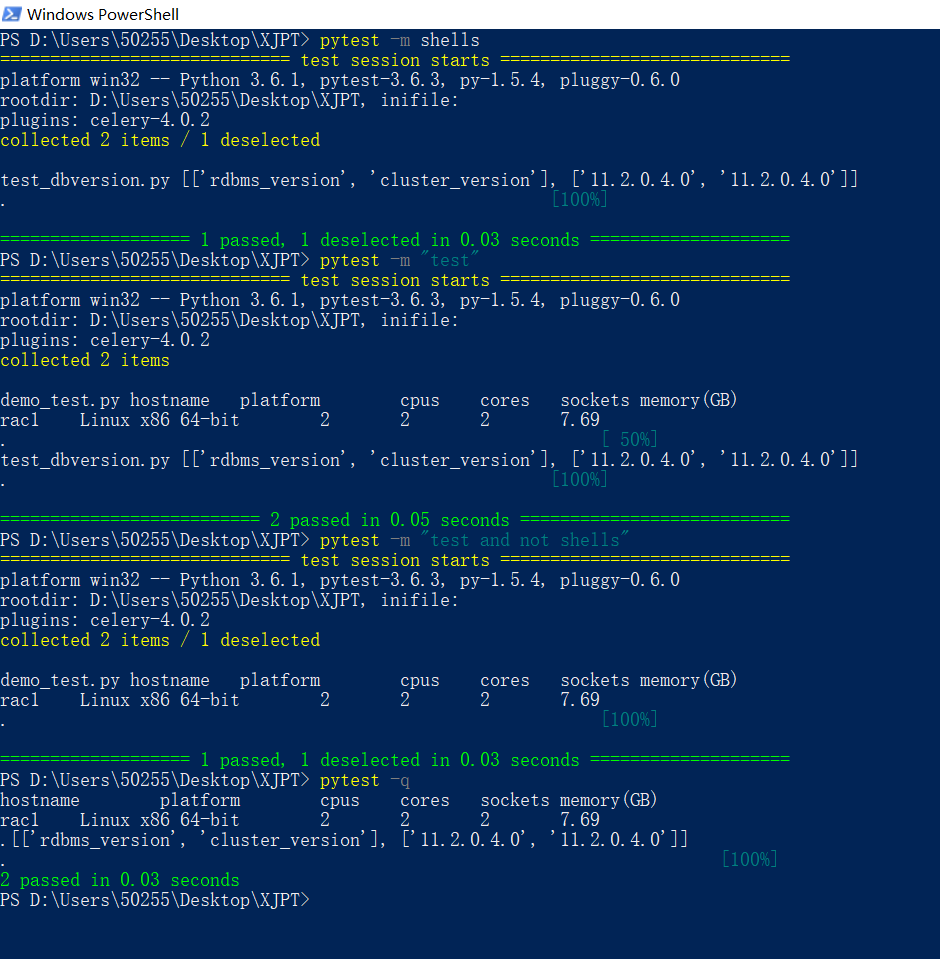
代码示例: pytest的简单用法
demo文件目录结构:
demo_project/
|----------- __init__.py
|----------- demo_test.py
|----------- test_dbversion.py
|----------- serialize.py
|----------- readme.txt
说明:
执行结果中包含print输出。需要注意的是,在pytest中,print输出不能直接使用print("xxx")的方式,因为会被pytest模块归入capsys中。
因为对于pytest而言,print属于sys.stdout,即输出结果的类型。类似的,assert属于sys.stderr的类型
具体的捕获方式参考: https://docs.pytest.org/en/latest/capture.html#capturing-of-the-stdout-stderr-output
简单贴一下官方示例代码:
1 def test_myoutput(capsys): # or use "capfd" for fd-level 2 print("hello") 3 sys.stderr.write("world\n") 4 captured = capsys.readouterr() 5 assert captured.out == "hello\n" 6 assert captured.err == "world\n" 7 print("next") 8 captured = capsys.readouterr() 9 assert captured.out == "next\n"
因此,在我的示例代码中,使用with通过上下文管理,临时关闭capsys,使得print的结果能被打印出来,具体效果参见最后的执行结果示例
各文件代码如下:
__init__.py
1 #
demo_test.py
1 import pytest 2 3 4 @pytest.mark.test 5 def test_demo(capsys): 6 with capsys.disabled(): 7 print(host_info_call_data()) 8 assert host_info_call_data() == '''hostname\tplatform\tcpus cores\tsockets\tmemory(GB) 9 rac1 Linux x86 64-bit 2 2 2 7.69 ''' 10 return 1 11 12 13 def host_info_call_data(): 14 data = '''hostname platform cpus cores sockets memory(GB) 15 rac1 Linux x86 64-bit 2 2 2 7.69 ''' 16 return data
test_dbversion.py
1 import pytest 2 3 from .serialize import serialize 4 5 6 def script_data(num): 7 data = { 8 1: '''rdbms_version\tcluster_version 9 11.2.0.4.0\t11.2.0.4.0 10 ''', 11 2: '''rdbms_version\tcluster_version 12 11.2.0.4.0 - 13 ''' 14 } 15 return data[num] 16 17 18 @pytest.mark.test 19 @pytest.mark.shells 20 def test_all_version_exist(capsys): 21 data = script_data(1) 22 row, column, data = serialize(data) 23 with capsys.disabled(): 24 print(data) 25 assert data == [['rdbms_version', 'cluster_version'], 26 ['11.2.0.4.0', '11.2.0.4.0']]
serialize.py
1 def serialize(data): 2 if isinstance(data, list): 3 data = str(data) 4 data = data.split('\n') 5 if data[-1] == '': 6 data = data[:-1] 7 data = [i.split('\t') for i in data if isinstance(i, str)] 8 row = len(data) 9 column = len(data[0]) 10 return row, column, data
执行结果示例: