11-散列1 电话聊天狂人
题目
- 给定大量手机用户通话记录,找出其中通话次数最多的聊天狂人。
输入格式:
- 输入首先给出正整数N(≤10^5),为通话记录条数。随后N行,每行给出一条通话记录。简单起见,这里只列出拨出方和接收方的11位数字构成的手机号码,其中以空格分隔。
输出格式:
- 在一行中给出聊天狂人的手机号码及其通话次数,其间以空格分隔。如果这样的人不唯一,则输出狂人中最小的号码及其通话次数,并且附加给出并列狂人的人数。
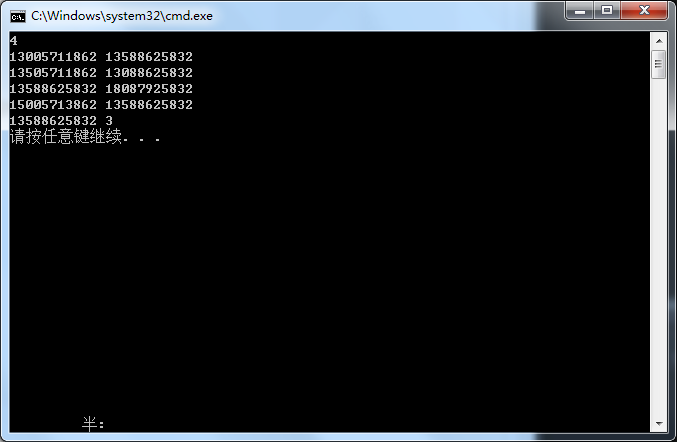
输入样例:
4
13005711862 13588625832
13505711862 13088625832
13588625832 18087925832
15005713862 13588625832
输出样例:
13588625832 3
思路分析


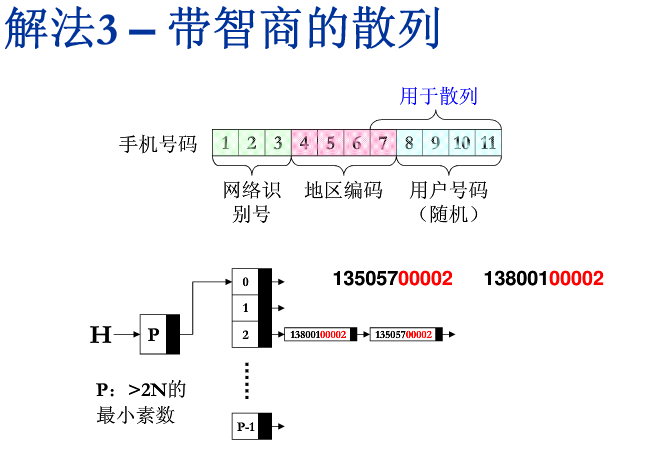
AC代码
- 散列表实现
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAXTABLESIZE 100000 /*允许开辟的最大散列表长度*/
#define KEYLENGTH 11 /*关键词字符串的最大长度*/
#define MAXD 5 /*参与散列映射计算的字符数*/
typedef char ElementType[KEYLENGTH + 1]; /*关键词类型用字符串*/
typedef int Index; /*散列地址类型
/******单链表的定义*************/
typedef struct LNode *PtrToLNode;
struct LNode
{
ElementType Data;
PtrToLNode Next;
int Count;
};
typedef PtrToLNode Position;
typedef PtrToLNode List;
/*******************************/
typedef struct TblNode *HashTable; //散列表类型
struct TblNode //散列表结点定义
{
int TabSize; //表的最大长度
List Heads; //指向链表头节点的数组
};
int NextPrime(int N)
{
/*返回大于N且不超过MAXTABLESIZE的最小素数*/
int i=0;
int p = (N % 2) ? (N + 2) : (N + 1); //从大于N的下一个奇数开始
while (p <= MAXTABLESIZE)
{
for (i = (int)sqrt(p); i > 2; i--)
{
if (!(p%i))
{
break; //有被整数的元素,p不是素数
}
}
if (i == 2)
{
break; //for正常结束,说明p是素数
}
else
{
p += 2; //否则试探下一个奇数
}
}
return p;
}
HashTable CreateTable(int TabSize)
{
HashTable H;
H = (HashTable)malloc(sizeof(struct TblNode));
H->TabSize = NextPrime(TabSize); /* 保证散列表最大长度是素数 */
H->Heads = (List)malloc(H->TabSize*sizeof(struct LNode)); /* 以下分配链表头结点数组 */
//初始话表头结点
for (int i = 0; i < H->TabSize; ++i)
{
H->Heads[i].Data[0] = '\0';
H->Heads[i].Next = NULL;
H->Heads[i].Count = 0;
}
return H;
}
Index Hash(int Key, int TabSize)
{
return Key%TabSize;
}
Position Find(HashTable H, ElementType Key) //散列表的查找
{
Position p;
Index Pos;
Pos = Hash(atoi(Key + KEYLENGTH - MAXD), H->TabSize); //将电话号码的后5位作为转为数字作为键值
p = H->Heads[Pos].Next;//从链表的第1个结点开始
//当未到表尾,并且Key未找到时
while (p&&strcmp(p->Data, Key))
p = p->Next;
return p; //此时P或者指向找到的结点。或者为NULL
}
bool Insert(HashTable H, ElementType Key)
{
Position p, NewCell;
Index Pos;
p = Find(H, Key);
if (!p) //关键词未找到,可以插入
{
NewCell = (Position)malloc(sizeof(struct LNode));
strcpy(NewCell->Data, Key);
NewCell->Count = 1;
Pos = Hash(atoi(Key + KEYLENGTH - MAXD), H->TabSize);
//将NewCell插入为H->Heads[Pos]链表的第1个结点,插入表头
NewCell->Next = H->Heads[Pos].Next;
H->Heads[Pos].Next = NewCell;
return true;
}
else
{
p->Count++; //关键词已经存在
return false;
}
}
void DestroyTable(HashTable H)
{
Position p, temp;
//释放每个链表的结点
for (int i = 0; i < H->TabSize; ++i)
{
p = H->Heads[i].Next;
while (p)
{
temp = p->Next;
free(p);
p = temp;
}
}
free(H->Heads); //释放头结点数组
free(H); //释放散列表结点
}
void ScanAndOutput(HashTable H)
{
int MaxCnt = 0, Pcnt = 0; //MaxCnt最大通话次数
ElementType MinPhone;
List Ptr;
MinPhone[0] = '\0';
for (int i = 0; i < H->TabSize; ++i) //扫描链表
{
Ptr = H->Heads[i].Next;
while (Ptr)
{
if (Ptr->Count > MaxCnt) //更新最大通话次数
{
MaxCnt = Ptr->Count;
strcpy(MinPhone, Ptr->Data);
Pcnt = 1;
}
else if (Ptr->Count == MaxCnt)
{
Pcnt++; //狂人计数
if (strcmp(MinPhone, Ptr->Data) > 0)
{
strcpy(MinPhone, Ptr->Data); /* 更新狂人的最小手机号码*/
}
}
Ptr = Ptr->Next;
}
}
cout << MinPhone << " " << MaxCnt;
if (Pcnt > 1)
{
cout << " " << Pcnt;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
HashTable hash;
ElementType Key;
int N;
cin >> N;
hash = CreateTable(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
cin >> Key;
Insert(hash, Key);
cin >> Key;
Insert(hash, Key);
}
ScanAndOutput(hash);
DestroyTable(hash);
return 0;
}
-
运行超时
-
在遍历unordered_map,进行处理
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
int n;
cin >> n;
unordered_map<string, int> myMap;
myMap.reserve(n);
char s[12];
for (int i(0); i < 2 * n; ++i) {
scanf("%s", s);
++myMap[s];
}
auto it = myMap.cbegin();
int num = 1; //人数
string minStr = it->first; //最小号码
int callCnt = it->second; //呼叫次数
for (++it; it != myMap.cend(); ++it) {
if (it->second == callCnt) {
++num;
if (it->first < minStr) minStr = it->first;
}
else if (it->second > callCnt) {
num = 1;
minStr = it->first;
callCnt = it->second;
}
}
cout << minStr << " " << callCnt;
if (num > 1) cout << " " << num;
return 0;
}
- 认识unordered_map的rehash,reserve方法
std::unordered_map::reserve
void reserve ( size_type n );
Request a capacity change
Sets the number of buckets in the container (bucket_count) to the most appropriate to contain at least n elements.
If n is greater than the current bucket_count multiplied by the max_load_factor, the container's bucket_count is increased and a rehash is forced.
If n is lower than that, the function may have no effect.
std::unordered_map::rehash
void rehash( size_type n );
Set number of buckets
Sets the number of buckets in the container to n or more.
If n is greater than the current number of buckets in the container (bucket_count), a rehash is forced. The new bucket count can either be equal or greater than n.
If n is lower than the current number of buckets in the container (bucket_count), the function may have no effect on the bucket count and may not force a rehash.
A rehash is the reconstruction of the hash table: All the elements in the container are rearranged according to their hash value into the new set of buckets. This may alter the order of iteration of elements within the container.
Rehashes are automatically performed by the container whenever its load factor is going to surpass its max_load_factor in an operation.
Notice that this function expects the number of buckets as argument. A similar function exists, unordered_map::reserve, that expects the number of elements in the container as argument.
Reference
C/C++基本语法学习
STL
C++ primer





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号