numpy实现多层感知机,完成手写数字识别任务
所需的库有:
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from tqdm import tqdm
1. 模型模板#
class Module(object):
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.training = True
def __call__(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
return self.forward(x)
def forward(self, x: np.ndarray):
...
def backward(self, dy: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
return dy
def train(self):
if 'training' in vars(self):
self.training = True
for attr in vars(self).values():
if isinstance(attr, Module):
Module.train()
"""递归调用train函数"""
def eval(self):
if 'training' in vars(self):
self.training = False
for attr in vars(self).values():
if isinstance(attr, Module):
Module.eval()
2. tensor#
import numpy as np
class Tensor(np.ndarray): # 基于np.ndarray 添加新属性grad,并且可以添加自定义其他属性
"""Derived Class of np.ndarray."""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.grad = None
def tensor(shape):
"""Return a tensor with a normal Gaussian distribution."""
return random(shape)
def from_array(arr):
"""Convert the input array-like to a tensor."""
t = arr.view(Tensor)
t.grad = None
return t
def zeros(shape):
"""Return a new tensor of given shape, filled with zeros."""
t = Tensor(shape)
t.fill(0)
return t
def ones(shape):
"""Return a new tensor of given shape, filled with ones."""
t = Tensor(shape)
t.fill(1)
return t
def ones_like(tensor):
"""Return a new tensor with the same shape as the given tensor,
filled with ones."""
return ones(tensor.shape)
def random(shape, loc=0.0, scale=1):
"""Return a new tensor of given shape, from normal distribution."""
return from_array(np.random.normal(loc=loc, scale=scale, size=shape))
3. 基于Module的线性层#
class Linear(Module):
def __init__(self, in_length: int, out_length: int):
self.w = tensor((in_length+1, out_length))
def forward(self, x):
self.x = x
return np.dot(x, self.w[1:]) + self.w[0]
def backward(self, dy):
self.w.grad = np.vstack((np.sum(dy, axis=0), np.dot(self.x.T, dy)))
# 反向传播,先计算参数的本地grad然后再与后层传过来的dy相乘得到向后传播的新的grad
return np.dot(dy, self.w[1:].T)
4. BatchNorm1d层#
class BatchNorm1d(Module):
def __init__(self, length: int, momentum: float=0.9):
super(BatchNorm1d, self).__init__()
self.running_mean = np.zeros((length,))
self.running_var = np.zeros((length,))
self.gamma = ones((length,))
self.beta = zeros((length,))
self.momentum = momentum
self.eps = 1e-5
def forward(self, x):
if self.training:
self.mean = np.mean(x, axis=0)
self.var = np.var(x, axis=0)
self.running_mean = self.momentum * self.running_mean + \
(1 - self.momentum) * self.mean
self.running_var = self.momentum * self.running_var + \
(1 - self.momentum) * self.var
self.x = (x - self.mean) / np.sqrt(self.var + self.eps)
else:
self.x = (x - self.running_mean) / np.sqrt(
self.running_var + self.eps)
return self.gamma * self.x + self.beta
def backward(self, dy):
self.gamma.grad = np.sum(dy * self.x, axis = 0)
self.beta.grad = np.sum(dy, axis = 0)
N = dy.shape[0]
dx = N * dy - np.sum(dy, axis=0) - self.x * np.sum(dy * self.x, axis=0)
return dx / N / np.sqrt(self.var + self.eps)
5. ReLU层和Softmax层(激活函数层)#
class ReLU(Module):
def forward(self, x):
self.x = x
return np.maximum(x, 0)
def backward(self, dy):
return np.where(self.x>0, dy, 0)
class Softmax(Module):
def forward(self, x):
exps = np.exp(x)
self.probs = exps/np.sum(exps, axis=1, keepdims=True)
return self.probs
def backward(self, dy):
ret = []
for i in range(dy.shape[0]): # 将一个batch一个个处理,然后拼接
dout = np.dot(dy[i], np.diag(self.probs[i]) - np.outer(self.probs[i], self.probs[i]))
ret.append(dout)
return np.array(ret)
6. 损失函数#
class Loss(object): # 先定义一个分类器的损失函数的基类
def __init__(self, n_classes):
self.n_classes = n_classes
def __call__(self, probs, targets):
self.probs = probs
self.targets = targets
return self
def backward(self): # 需要重写
...
class CrossEntropyLoss(Loss):
def __call__(self, probs, targets):
super(CrossEntropyLoss, self).__call__(probs, targets)
self.value = np.sum(-np.eye(self.n_classes)[targets] * np.log(probs))
return self
def backward(self):
return self.probs - np.eye(self.n_classes)[self.targets]
7. 优化器Optimizer#
class Optim(object): # 定义优化器的基类, 用来操作更新模型的。
def __init__(self, module, lr): # 传入学习率以及要优化的对象
self.module = module
self.lr = lr
def step(self):
self._step_module(self.module) # 传入模型进行优化
def _step_module(self, module):
for attr in vars(module).values():
if isinstance(attr, Tensor):
if hasattr(attr, 'grad'):
self._update_weight(attr)
if isinstance(attr, Module):
self._step_module(attr)
if isinstance(attr, list):
for item in attr:
self._step_module(item)
def _update_weight(self, tensor):
tensor -= self.lr * tensor.grad
class SGD(Optim):
def __init__(self, module, lr, momentum: float = 0):
super(SGD, self).__init__(module, lr)
self.momentum = momentum
def _update_weight(self, tensor):
tensor.v = self.momentum * tensor.v + self.lr * tensor.grad \
if 'v' in vars(tensor) else self.lr * tensor.grad
tensor -= tensor.v
8. 数据加载器DataLoader#
# 自定义数据加载器, 输入data,解析后输出batch个(X, y), 分批次输出
class DataLoader(object):
def __init__(self, data, batch_size = None):
self.X, self.y = data # data是一个元组(X, y)
self.batch = batch_size
def __iter__(self): # 可遍历
if self.batch is None:
yield self.X, self.y # 直接输出所有的(X, y)
else:
n = 0
while n + self.batch <= self.X.shape[0]:
yield self.X[n:n+self.batch], self.y[n:n+self.batch]
n += self.batch
# 每次输出batch个
def __len__(self):
return (self.X.shape[0]/self.batch) if self.batch is not None else 1
9. 加载数据#
def load_mnist(mode="train", n_samples = None, flatten = True):
"""n_samples 用来取样,这里取前面n_samples个数据输出"""
data_path = './data/'
images = data_path + ('train-images-idx3-ubyte' if mode == 'train' else 't10k-images-idx3-ubyte')
labels = data_path + ('train-labels-idx1-ubyte' if mode == 'train' else 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte')
length = 60000 if mode == 'train' else 10000
X = np.fromfile(open(images), np.uint8)[16:].reshape(
(length, 28, 28)).astype(np.int32)
if flatten:
X = X.reshape(length, -1)
y = np.fromfile(open(labels), np.uint8)[8:].reshape(
(length)).astype(np.int32)
return (X[:n_samples] if n_samples is not None else X,
y[:n_samples] if n_samples is not None else y)
10. 模型搭建#
class Model(Module):
def __init__(self, lengths: list) -> None:
self.layers = []
for i in range(len(lengths)-1):
self.layers.append(Linear(lengths[i], lengths[i+1]))
self.layers.append(BatchNorm1d(lengths[i+1], lengths[i+1]))
self.layers.append(ReLU() if i != len(lengths)-2 else Softmax())
def forward(self, x):
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x)
return x
def backward(self, delta):
for layer in reversed(self.layers):
delta = layer.backward(delta)
11. 结果可视化#
def vis_demo(model):
X, y = load_mnist('test', 20)
probs = model.forward(X)
preds = np.argmax(probs, axis=1)
fig = plt.subplots(nrows=4, ncols=5, sharex='all',
sharey='all')[1].flatten()
for i in range(20):
img = X[i].reshape(28, 28)
fig[i].set_title(preds[i])
fig[i].imshow(img, cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
fig[0].set_xticks([])
fig[0].set_yticks([])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("vis.png")
plt.show()
# 结果可视化
12. 开始训练#
n_features = 28*28
n_classes = 10
n_epochs = 20
bs = 1000
lr = 1e-3
lengths = (n_features, 512, n_classes)
np.random.seed(0)
trainloader = DataLoader(load_mnist('train'), batch_size=bs) # bs = 1000
testloader = DataLoader(load_mnist('test'))
model = Model(lengths) # 初始化模型
optimizer = SGD(model, lr=lr, momentum=0.9) # 使用SGD优化器
criterion = CrossEntropyLoss(n_classes=n_classes) # 通过CrossEntropyLoss来作为评价函数
train_acc, test_acc, loss_val= 0, 0, 0
result={'train_acc':[], 'test_acc':[], 'loss_val':[]}
for i in range(n_epochs):
bar = tqdm(trainloader, total=6e4 / bs) # 总共有6e4/bs个batch,每次加载一个batch,tqdm是一个很好用的进度条工具,其会自动调用加载器
# 每个epoch都要重新装载数据,每个epoch都会有一个进度条
bar.set_description(f'epoch {i:2}') # 进度条描述设置
for X, y in bar: # 加载X, y,并显示进度条
probs = model.forward(X) # 模型训练得到结果
loss = criterion(probs, y) # 计算损失函数
model.backward(loss.backward()) # 利用损失函数的梯度反向传播更新参数的grad
optimizer.step() # 利用参数的grad以及lr、momentum更新参数
preds = np.argmax(probs, axis=1) # 输出结果是概率,转为预测结果,axis=1 说明安第二维遍历取最大值的第二维度的index
train_acc = np.sum(preds == y) / len(y) * 100
loss_val = loss.value
bar.set_postfix_str(f'train acc={train_acc:.1f} loss={loss_val:.3f}') # 输出这个epoch的训练集的正确率
for X, y in testloader: # 每个epoch训练集上训练完后,会在测试集上进行测试,此时不用更新参数
probs = model.forward(X)
preds = np.argmax(probs, axis=1)
test_acc = np.sum(preds == y) / len(y) * 100
print(f' test acc: {test_acc:.1f}') # 输出训练集上的正确率
result['train_acc'].append(train_acc)
result['test_acc'].append(test_acc)
result['loss_val'].append(loss_val)
vis_demo(model)
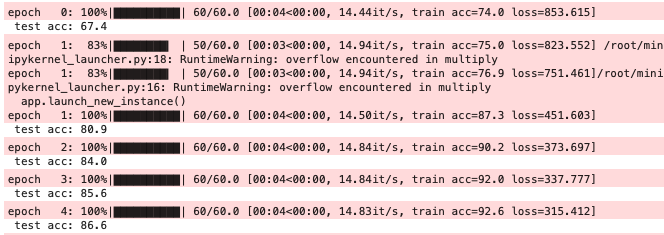
13. 训练结果#
部分截图:其中第二个epoch发生了溢出,不知道问题出在哪,猜测应该出现在BatchNorm1d层。
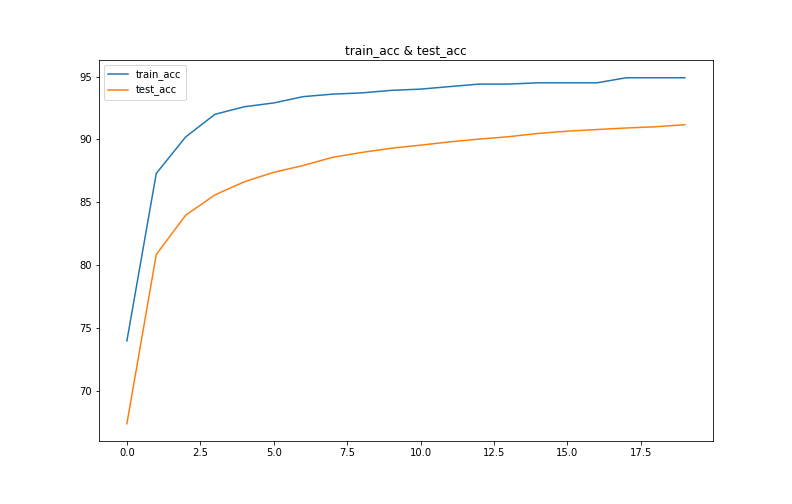
# 使用训练得到的result绘制图像
plt.figure(figsize=(11,7))
plt.plot(result['train_acc'],label='train_acc')
plt.plot(result['test_acc'],label='test_acc')
plt.title('train_acc & test_acc')
plt.legend()
plt.savefig("train_test_acc.png")
plt.show()
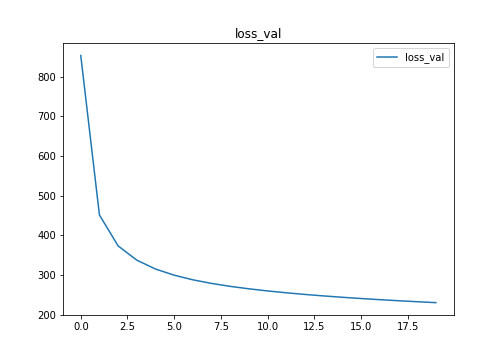
plt.figure(figsize=(7,5))
plt.plot(result['loss_val'],label='loss_val')
plt.title('loss_val')
plt.legend()
plt.savefig("loss_val.png")
plt.show()
训练数据在这里




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理