利用graphviz 绘制树状图
digraph action { node [shape = record,height=.1]; node0 [label = "<head> head|<body> body|<foot> foot", height=.5] node2 [shape = box label="mind"] node0:head:n -> node2:n [label = "n"] //node0的头结点的n方位指向node2的n方位 node0:head:ne -> node2:ne [label = "ne"] node0:head:e -> node2:e [label = "e"] node0:head:se -> node2:se [label = "se"] node0:head:s -> node2:s [label = "s"] node0:head:sw -> node2:sw [label = "sw"] node0:head:w -> node2:w [label = "w"] node0:head:nw -> node2:nw [label = "nw"] node0:head:c -> node2:c [label = "c"] //center node0:head:_ -> node2:_ [label = "_"] //_表示任意位置 node0:body[style=filled color=lightblue] }

digraph { rankdir = LR splines = false A -> B -> C -> D -> F [color = green] E -> F -> B -> D [color = blue] B -> E -> H[color = red] }
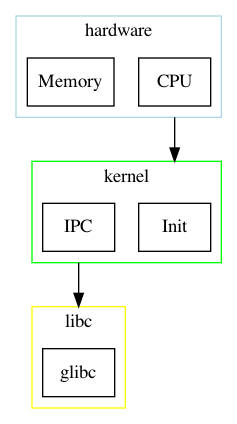
digraph G { compound = true // 允许子图间存在边 ranksep = 1 node [shape = record] subgraph cluster_hardware { label = "hardware" color = lightblue CPU Memory //两小图CPU,Memory从右向左添加 } subgraph cluster_kernel { label = "kernel" color = green Init IPC } subgraph cluster_libc { label = "libc" color = yellow glibc } CPU -> Init [lhead = cluster_kernel ltail = cluster_hardware] IPC -> glibc [lhead = cluster_libc ltail = cluster_kernel] }
输出.dot文件然后通过终端输入“dot x.dot -T png -o x.png”输出图形。
所以可以利用Tree root先根遍历,从而输出为.dot文本。
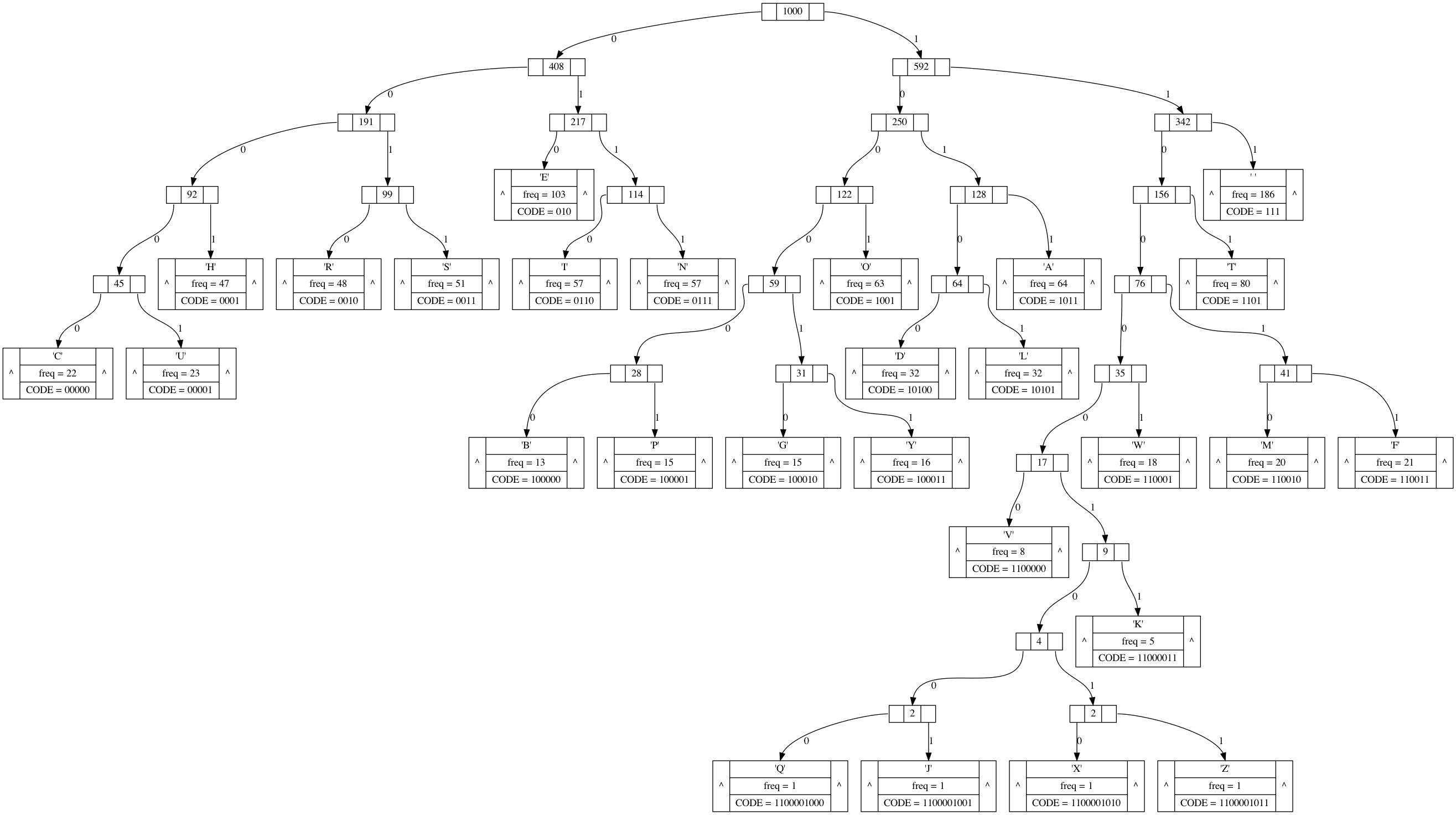
void process_null_node(int index, int nullcount, FILE* stream) { fprintf(stream, " null%d [shape=hexagon, width = .2,height = .2, style = filled, color = \"#636e72\", fontcolor = white]\n", nullcount); fprintf(stream, " node%d -> null%d\n",index, nullcount); } void __tree2dot(Huffman root,FILE* stream) { static int null_node_cnt = 0; if(root) { if(root->ch!=0) fprintf( stream, "node%d [ label = \"<f0>^|{<head>\'%c\'|freq = %d|CODE = %s}|<f2>^\"]\n", root->index, root->ch, root->freq, root->code); else fprintf( stream, "node%d [label = \"<f0>|<f1>%d|<f2>\"]\n", root->index, root->freq); } if(root->left) { fprintf(stream," node%d:f0 -> node%d:n [ label = \"0\"]\n",root->index,root->left->index); __tree2dot(root->left,stream); } else { //process_null_node(root->index,null_node_cnt++,stream); } if(root->right) { fprintf(stream," node%d:f2 -> node%d:n [ label = \"1\"]\n",root->index,root->right->index); __tree2dot(root->right,stream); } else { //process_null_node(root->index,null_node_cnt++,stream); } } void tree2index(Huffman root){ if(root==NULL) return; queue<Node *> s; s.push(root); int i = 0; while(!s.empty()){ s.front()->index = i++; Node *temp = s.front(); s.pop(); if(temp->left) s.push(temp->left); if(temp->right) s.push(temp->right); } } int tree2dot(Huffman tree,char* filename) { assert(tree != NULL && filename != NULL); Tree_array T_array[100]={}; FILE* stream = fopen(filename,"w+"); if(stream == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "open failed \n"); return -1; } tree2index(tree); fprintf(stream,"digraph {\n"); fprintf(stream,"node [shape=\"record\", height=.1]\n"); __tree2dot(tree,stream); fprintf(stream,"}\n"); fclose(stream); return 0; }
输出树状图(此图为哈夫曼树),如下:






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理