CentOS7下systemctl添加自定义服务
CentOS7下systemctl添加自定义服务
一、服务文件位置
CentOS7的服务systemctl脚本存放在/usr/lib/systemd/下,有系统和用户之分
需要开机不登陆就能运行的程序,存在系统服务里,路径:/usr/lib/systemd/system
登陆后才可以运行的程序,存在用户服务里,路径:/usr/lib/systemd/user
二、服务的基础组成
服务以.service结尾,一般会分为3部分:[Unit]、[Service]和[Install],每个部分有自己的配置。
1、[Unit]
Description : 服务的简单描述
Documentation : 服务文档
Before:代表本服务在xxx.service启动之前启动。
After:代表本服务在xxx.service之后启动。
Requires:这个服务启动了,它需要的服务也会被启动;它需要的服务被停止了,这个服务也停止了。
Wants:这个服务启动了,它需要的服务也会被启动;它需要的服务被停止了,对本服务没有影响。
2、[Service]
Type:定义服务的启动方式,有下面的值可以选
| 取值 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Type=oneshot | 这一选项适用于只执行一项任务、随后立即退出的服务。可能需要同时设置 RemainAfterExit=yes 使得 systemd 在服务进程退出之后仍然认为服务处于激活状态。 |
| Type=notify | 与 Type=simple 相同,但约定服务会在就绪后向 systemd 发送一个信号。这一通知的实现由 libsystemd-daemon.so 提供。 |
| Type=dbus | 若以此方式启动,当指定的 BusName 出现在DBus系统总线上时,systemd认为服务就绪。 |
| Type=idle | systemd会等待所有任务处理完成后,才开始执行 idle 类型的单元。其他行为与 Type=simple 类似。 |
| Type=forking | systemd认为当该服务进程fork,且父进程退出后服务启动成功。对于常规的守护进程(daemon),除非你确定此启动方式无法满足需求,使用此类型启动即可。使用此启动类型应同时指定 PIDFile=,以便 systemd 能够跟踪服务的主进程 |
| Type=simple | (默认值) systemd认为该服务将立即启动。服务进程不会 fork 。如果该服务要启动其他服务,不要使用此类型启动,除非该服务是socket 激活型。 |
PIDFile:pid文件路径
ExecStart:启动服务的命令或者脚本,
ExecStartPre:在ExecStart之前用户自定义执行的脚本
ExecStartPost:在ExecStart之后用户自定义执行的脚本。Type=oneshot允许指定多个希望顺序执行的用户自定义命令。
ExecReload:指定服务停止时执行的命令或者脚本。
ExecStop:指定服务停止时执行的命令或者脚本。
PrivateTmp:True表示给服务分配独立的临时空间
Restart:这个选项如果被允许,服务重启的时候进程会退出,会通过systemctl命令执行清除并重启的操作。
RemainAfterExit:如果设置这个选择为真,服务会被认为是在激活状态,即使所以的进程已经退出,默认的为假,这个选项只有在Type=oneshot时需要被配置。
Restart:退出后的重启方式,有下面的值可以选
| 取值 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| no(默认值) | 退出后不会重启 |
| on-success | 只有正常退出时(退出状态码为0),才会重启 |
| on-failure | 非正常退出时(退出状态码非0),包括被信号终止和超时,才会重启 |
| on-abnormal | 只有被信号终止和超时,才会重启 |
| on-abort | 只有在收到没有捕捉到的信号终止时,才会重启 |
| on-watchdog | 超时退出,才会重启 |
| always | 不管是什么退出原因,总是重启 |
3、[Install]
Alias:为单元提供一个空间分离的附加名字。
RequiredBy:单元被允许运行需要的一系列依赖单元,RequiredBy列表从Require获得依赖信息。
WantBy:单元被允许运行需要的弱依赖性单元,Wantby从Want列表获得依赖信息。
Also:指出和单元一起安装或者被协助的单元。
DefaultInstance:实例单元的限制,这个选项指定如果单元被允许运行默认的实例。
三、服务文件实例
可以看看原始的服务都是怎么写的cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/某某服务.service
nginx服务
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
[Unit]
Description=The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server
After=network-online.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
Wants=network-online.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/run/nginx.pid
# Nginx will fail to start if /run/nginx.pid already exists but has the wrong
# SELinux context. This might happen when running `nginx -t` from the cmdline.
# https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1268621
ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/rm -f /run/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx
ExecReload=/usr/sbin/nginx -s reload
KillSignal=SIGQUIT
TimeoutStopSec=5
KillMode=process
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[root@localhost ~]#
sshd服务
[root@localhost ~]# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service
[Unit]
Description=OpenSSH server daemon
Documentation=man:sshd(8) man:sshd_config(5)
After=network.target sshd-keygen.service
Wants=sshd-keygen.service
[Service]
Type=notify
EnvironmentFile=/etc/sysconfig/sshd
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/sshd -D $OPTIONS
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
KillMode=process
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=42s
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[root@localhost ~]#
四、自定义服务
使用go编写了一个web服务
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", func(writer http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
n, err := fmt.Fprintln(writer, "我启动成功了")
if err != nil {
return
} else {
fmt.Println(n)
}
})
err := http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
if err != nil {
return
}
}
编译后放在了/home/tmp下,名字就叫s
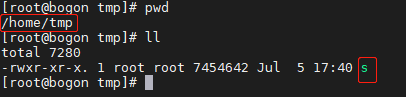
部署为服务
①创建并编辑服务文件
vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/mygoweb.service
输入以下内容
[Unit]
Description=MY-GO-WEB-SERVER
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/home/tmp/s
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
③加载配置
systemctl daemon-reload
④启动服务
systemctl start mygoweb.service
重启服务
systemctl restart mygoweb.service
停止服务
systemctl stop mygoweb.service
查看服务
systemctl status mygoweb.service
五、遇到的错误
1、执行systemctl start 某某服务,然后卡住了,一般是Type设置错误(应该设置Type=simple但设置成了Type=forking),可参考:centos7编写自己的服务,运行systemctl后卡住了(即shell阻塞了)
2、上面提及到:
Type=forking systemd认为当该服务进程fork,且父进程退出后服务启动成功。对于常规的守护进程(daemon),除非你确定此启动方式无法满足需求,使用此类型启动即可。使用此启动类型应同时指定 PIDFile=,以便 systemd 能够跟踪服务的主进程
但是我遇到使用Type=forking 然后指定PIDFile,然后systemctl start 某某服务,也是卡住了,解决办法是不写PIDFile
卡住现象:
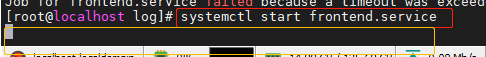
错误的配置(PIDFile文件写错了)
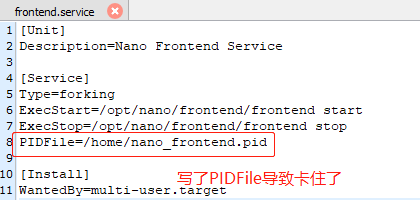
正确的配置(去掉了PIDFile)

正确的配置2(写你的程序输出的PID文件,如果没有,那就不写PIDFile)
六、常用的命令
查看开机自启动的服务
systemctl list-unit-files --type service | grep enabled
查看某个服务是否是开机自启动
例如查看防火墙服务是否开启自启动,enabled就是自启动 disabled就是非自启动
systemctl list-unit-files --type service | grep firewalld

设置开机自启动
systemctl enable service_name
禁止开机自启动
systemctl disable service_name
七、日志重定向到文件
如果服务的日志是控制台输出,当我们需要重定向日志到文件时,可以这么做。
①在自定义 xxx.service 文件中 [Service] 增加
StandardOutput=syslog
StandardError=syslog
SyslogIdentifier=identifier_for-me
identifier_for-me是随意写的字符串,表示唯一标识日志,可以理解是唯一ID
②创建 /etc/rsyslog.d/<new_file>.conf 文件,其内容为
if $programname == 'identifier_for-me' then /home/log/mylog.log
& stop
③重启 rsyslog
重新启动 rsyslog (sudo systemctl restart rsyslog)
④重新启动服务 systemctl restart xxx
参考:https://www.codenong.com/37585758/ 和 https://my.oschina.net/u/3625745/blog/4693099



