Linux设备树
基本概念
介绍
在不使用设备树的时候(Linux 3.x版本)都是通过 arch/arm/match-xxx 和 arch/arm/plat-xxx 文件夹内的文件来描述板级信息。每个芯片的板子都会有自己的板级信息,而这些文件都会被编译进Linux内核中,大量无用和冗余的板级信息文件导致Linux内核十分臃肿。
设备树(Flattened Device Tree),将描述板级硬件信息的内容从Linux内核中分离出来,其文件扩展名为 .dts(Device Tree Source)。
- dts文件一般描述板级信息(外设)
- dtsi文件描述SOC级信息(CPU、主频、控制器)
DTC工具
DTC(Device Tree Compiler)设备树编译工具将 .dts 文件编译成 .dtb(Device Tree Blob)二进制文件。
引用dtsi头文件
#include <xxx.h>
#include "xxx.dtsi"
设备节点
节点命名
label: node-name@unit-address
通过label访问节点:
&label
属性
-
字符串
compatible = "arm,cortex-a7"; compatible = "fsl,imx6ull-gpmi-nand", "fsl, imx6ul-gpmi-nand"; -
32位无符号整数
reg = <0>; reg = <0 0x123456 100>;
compatible
compatible属性的值是一个字符串列表,用于将设备和驱动绑定起来。
compatible属性值格式一般为:
compatible = "manufacturer, module" // 厂商, 模块对应的驱动名
compatible = "omnivision,ov13850-v4l2-i2c-subdev","omnivision,ov13850";
驱动程序内,定义struct of_device_id 驱动匹配表,并赋值给 .of_match_table,就可通过compatible进行设备树和驱动的匹配。
static const struct of_device_id ov13850_of_match[] = {
{.compatible = "omnivision,ov13850-v4l2-i2c-subdev"},
{},
};
static struct i2c_driver ov13850_i2c_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = ov13850_DRIVER_NAME,
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.of_match_table = ov13850_of_match
},
.probe = ov13850_probe,
.remove = ov13850_remove,
};
module
model属性用于描述设备模块信息,属性值为字符串。
status
status用于描述设备状态,属性值为字符串
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| "okay" | 设备是可操作的 |
| "disabled" | 设备当前是不可操作的,但未来可变为可操作,如热插拔设备插入后。disable的具体含义需看设备绑定的文档 |
| "fail" | 设备不可操作,设备检测到了一些错误,设备不太可能变为可操作 |
| "fail-sss" | 与"fail"相同,sss部分为检测到的错误内容 |
#address-cells & #size-cells
#address-cells & #size-cells用于描述子节点的地址信息,属性值为32位无符号整型。
#address-cells决定子节点reg属性中地址信息所占用的字长(32bit)。
#size-cells决定了子节点reg属性中长度信息所占的字长(32bit)。
spi4 {
compatible = "spi-gpio";
#address-cells = <1>; // 起始地址所占用的长度为32bit
#size-cells = <0>; // 地址长度所占长度为0
gpio_spi: gpio_spi@0 {
compatible = "fairchild,74hc595";
reg = <0>;
};
};
/ {
compatible = "rockchip,rk3399";
interrupt-parent = <&gic>;
#address-cells = <2>; // 起始地址所占用的长度为64bit
#size-cells = <2>; // 地址长度所占长度为64bit
led-test { //GPIO0_B5
compatible = "user-led";
status = "okay";
reg = < 0x0 0xff320004 0x0 0x04 /* PMUGRF_GPIOB_IOMUX */
0x0 0xff720000 0x0 0x04 /* GPIO_SWPORTA_DR */
0x0 0xff720004 0x0 0x04 >; /* GPIO_SWPORTA_DDR */
};
};
reg
reg属性用来描述地址空间资源信息:起始地址、地址长度。
格式如下:
reg = < address1 length1
address2 length2
... ...>;
address为起始地址length为地址长度
ranges
ranges是一个地址映射表,属性值为数字矩阵:
ranges = <child-bus-address parent-bus-address length>
child-bus-address:子总线地址空间的物理地址,由父节点的#address-cells指定此物理地址所占用的字长。parent-bus-address:父总线地址空间的物理地址,由父节点的#address-cells指定此物理地址所占用的字长。length:子地址空间的长度,由父节点的#size-cells指定此地址长度所占用的字长。
若ranges为空值,说明子地址空间和父地址空间完全相同,无需地址转换。
例如:
soc {
compatible = "simple-bus";
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
ranges = <0x0 0xe0000000 0x00100000>;
serial {
device_type = "serial";
compatible = "ns16550";
reg = <0x4600 0x100>;
clock-frequency = <0>;
interrupts = <0xA 0x8>;
interrupt-parent = <&ipic>;
};
};
表示节点soc子地址空间的物理起始地址为0x0,父地址空间的物理起始地址为0xe0000000,地址范围为0x00100000(1024KB)。
serial节点的起始地址为0x4600,长度为0x100。经地址转换serial的起始地址为:\(\text{0xe0000000+0x4600=0xe0004600}\)。
name(弃用)
name属性用于记录节点名字,属性值为字符串。
device_type(弃用)
device_type用于描述设备的FCode,但设备数无Fcode,故已被弃用。属性值为字符串。
此属性只能用于cpu节点或memory节点。
bindings文档
/Documentation/devicetree/bindings文件夹下有设备树相关的说明文档,添加节点时可参考这些文档。
在系统中查看设备树信息
Linux内核解析的设备树的各节点信息在 /proc/device-tree目录下:
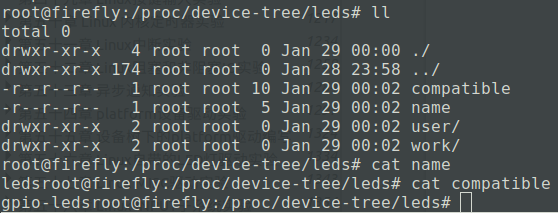
chosen子节点
chosen不是一个真实的设备,该节点是uboot向Linux内核传递的数据:

uboot会在设备树中寻找chosen节点,如果没有的话会自己创建。然后将bootargs环境变量的内容添加到chosen节点的bootargs属性。这一系列动作是uboot通过fdt_chosen函数实现的。
驱动中获取设备树信息
device_node结构体
Linux内核使用device_node结构体来描述一个节点:
include/linux/of.h
struct device_node {
const char *name; // 节点名字
const char *type; // 设备类型
phandle phandle;
const char *full_name; // 节点全名
struct fwnode_handle fwnode;
struct property *properties; // 属性
struct property *deadprops; // removed属性
struct device_node *parent; // 父节点
struct device_node *child; // 子节点
struct device_node *sibling;
struct kobject kobj;
unsigned long _flags;
void *data;
#if defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
const char *path_component_name;
unsigned int unique_id;
struct of_irq_controller *irq_trans;
#endif
};
property结构体
节点的属性信息保存在property结构体中:
include/linux/of.h
struct property {
char *name; // 属性名
int length; // 属性长度
void *value; // 属性值
struct property *next; // 下一个属性
unsigned long _flags;
unsigned int unique_id;
struct bin_attribute attr;
};
resource结构体
Linux内核使用resource结构体来描述内存空间(如IIC、SPI、GPIO等对应的寄存器也是一组内存空间),resource结构体表示的是设备的资源信息:
include/linux/ioport.h
struct resource {
resource_size_t start;
resource_size_t end;
const char *name;
unsigned long flags;
struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child;
};
resource_size_t为u32类型的值。
start:开始地址end:结束地址name:资源名字flag:资源标志位,用来表示资源类型
资源类型 IORESOURCE
include/linux/ioport.h
#define IORESOURCE_BITS 0x000000ff /* Bus-specific bits */
#define IORESOURCE_TYPE_BITS 0x00001f00 /* Resource type */
#define IORESOURCE_IO 0x00000100 /* PCI/ISA I/O ports */
#define IORESOURCE_MEM 0x00000200
#define IORESOURCE_REG 0x00000300 /* Register offsets */
#define IORESOURCE_IRQ 0x00000400
#define IORESOURCE_DMA 0x00000800
#define IORESOURCE_BUS 0x00001000
#define IORESOURCE_PREFETCH 0x00002000 /* No side effects */
#define IORESOURCE_READONLY 0x00004000
#define IORESOURCE_CACHEABLE 0x00008000
#define IORESOURCE_RANGELENGTH 0x00010000
#define IORESOURCE_SHADOWABLE 0x00020000
#define IORESOURCE_SIZEALIGN 0x00040000 /* size indicates alignment */
#define IORESOURCE_STARTALIGN 0x00080000 /* start field is alignment */
#define IORESOURCE_MEM_64 0x00100000
#define IORESOURCE_WINDOW 0x00200000 /* forwarded by bridge */
#define IORESOURCE_MUXED 0x00400000 /* Resource is software muxed */
#define IORESOURCE_EXCLUSIVE 0x08000000 /* Userland may not map this resource */
#define IORESOURCE_DISABLED 0x10000000
#define IORESOURCE_UNSET 0x20000000 /* No address assigned yet */
#define IORESOURCE_AUTO 0x40000000
#define IORESOURCE_BUSY 0x80000000 /* Driver has marked this resource busy */
查找节点
of_find_node_by_name
通过节点名字查找指定节点:
include/linux/of.h
drivers/of/base.c
struct device_node *of_find_node_by_name(struct device_node *from, const char *name)
from:开始查找的节点,NULL表示从根节点查找。name:要查找的节点名字return:找到的节点,若为NULL则查找失败
of_find_node_by_type
通过device_type属性查找指定节点:
include/linux/of.h
drivers/of/base.c
struct device_node *of_find_node_by_type(struct device_node *from, const char *type)
from:开始查找的节点,NULL表示从根节点查找。type:要查找的节点对应的type字符串,也就是device_type属性值return:找到的节点,若为NULL则查找失败
of_find_compatible_node
根据 device_type 和 compatible 属性查找指定的节点:
include/linux/of.h
drivers/of/base.c
struct device_node *of_find_compatible_node(struct device_node *from,
const char *type,
const char *compat)
from:开始查找的节点,NULL表示从根节点查找。type:要查找的节点对应的type字符串,也就是device_type属性值,NULL表示忽略device_type属性compatible:要查找的节点所对应的compatible属性列表return:找到的节点,若为NULL表示查找失败
of_find_matching_node_and_match
通过of_device_id匹配表来查找指定的节点:
include/linux/of.h
drivers/of/base.c
struct device_node *of_find_matching_node_and_match(
struct device_node *from,
const struct of_device_id *matches,
const struct of_device_id **match)
from:开始查找的节点,NULL表示从根节点查找。matches:of_device_id匹配表match:找到的匹配的of_device_idreturn:找到的节点,若为NULL表示查找失败
of_find_node_by_path
通过路径查找指定节点:
include/linux/of.h
drivers/of/base.c
static inline struct device_node *of_find_node_by_path(const char *path)
path:带有全路径的节点名,可以使用节点别名return:找到的节点,若为NULL表示查找失败
查找父/子节点
of_get_parent
获取指定节点的父节点:
include/linux/of.h
drivers/of/base.c
struct device_node *of_get_parent(const struct device_node *node)
node:要查找父节点的节点return:找到父节点
of_get_next_child
递归地查找子节点:
include/linux/of.h
drivers/of/base.c
struct device_node *of_get_next_child(const struct device_node *node,
struct device_node *prev)
node:父节点prev:从哪个子节点开始查找,若为NULL表示从第一个子节点开始查找return:找到的子节点
提取属性值
of_find_property
查找指定的属性:
include/linux/of.h
drivers/of/base.c
struct property *of_find_property(const struct device_node *np,
const char *name,
int *lenp)
np:设备节点name:属性名lenp:属性值的字节数return:找到的属性
of_property_count_elems_of_size
获取属性中元素的数量,如reg属性值是一个数组,则此函数可获取这个数组的大小:
include/linux/of
drivers/of/property.c
int of_property_count_elems_of_size(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname, int elem_size)
np:设备节点proname:属性名elem_size:元素长度return:返回值
of_property_read_u32_index
从属性中通过index获取的u32类型数值:
include/linux/of
drivers/of/property.c
int of_property_read_u32_index(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u32 index, u32 *out_value)
np:设备节点proname:属性名index:索引号out_value:读取到的值return:0->成功;负值->失败;-EINVAL->属性不存在,-ENODATA->没有数据,-EOVERFLOW->越界
of_property_read_u??_array
of_property_read_u8_array、of_property_read_u16_array、of_property_read_u32_array、of_property_read_u64_array用于读取属性中u8、u16、u32、u64类型的数组数据:
include/linux/of
static inline int of_property_read_u??_array(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u?? *out_values, size_t sz)
np:设备节点proname:属性名out_value:读取到数组sz:要读取的数组元素数量return:0->成功,负值->失败;-EINVAl->属性不存在,-ENODATA->没有数据,-EOVERFLOW->越界
of_property_read_u??
有些属性只有一个整型值,可用of_property_read_u8、of_property_read_u16、of_property_read_u32、of_property_read_u64读取属性中u8、u16、u32、u64类型的数据:
include/linux/of
static inline int of_property_read_u??_array(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u?? *out_values, size_t sz)
np:设备节点proname:属性名out_value:读到的值return:return:0->成功,负值->失败;-EINVAl->属性不存在,-ENODATA->没有数据
of_property_read_string
读取属性中的字符串值:
include/linux/of
drivers/of/property.c
int of_property_read_string(struct device_node *np, const char *propname,
const char **out_string)
np:设备节点proname:属性名out_string:读到字符串值return:0->成功,负值->失败
of_n_addr_cells
获取address-cells属性值:
include/linux/of.h
drivers/of/base.c
int of_n_addr_cells(struct device_node *np)
np:设备节点return:获取的#address-cells属性值
of_n_size_cell
获取size-cells属性值:
include/linux/of.h
drivers/of/base.c
int of_n_size_cell(struct device_node *np)
np:设备节点return:获取的#size-cells属性值
其他
of_device_is_compatible
查看节点的compatible属性是否包含指定字符串:
include/linux/of.h
drivers/of/base.c
int of_device_is_compatible(const struct device_node *device,
const char *)
device:设备节点compat:要查找的字符串return:0->不包含,正值->包含
of_get_address
获取地址相关属性,主要是reg或assigned-addresses属性:
include/linux/of_address.h
drivers/of/address.c
const __be32 *of_get_address(struct device_node *dev, int index,
u64 *size, unsigned int *flags)
dev:设备节点index:要读取的地址标号size:地址长度flags:资源类型,如IORESOURCE_IO、IORESOURCE_MEN等return:读取到的地址数据的首地址,NULL表示读取失败
of_translate_address
将从设备树读取到的地址转换为物理地址:
include/linux/of_address.h
drivers/of/address.c
u64 of_translate_address(struct device_node *dev, const __be32 *in_addr)
dev:设备节点in_addr:要转换的地址return:得到的物理地址,OF_BAD_ADDR表示转换失败
of_address_to_resource
从设备树提取资源信息,将reg属性值转换为resource结构体类型:
include/linux/of_address.h
drivers/of/address.c
int of_address_to_resource(struct device_node *dev, int index,
struct resource *r)
dev:设备节点index:地址资源标号r:得到的resource结构体return:0->成功,负值->失败
of_iomap
用于直接内存映射,将reg属性中指定的地址信息转换为虚拟地址。使用设备树后,of_iomap将替代原先的ioremap函数来完成物理地址到虚拟地址的映射。
include/linux/of_address.h
drivers/of/address.c
void __iomem *of_iomap(struct device_node *np, int index)
np:设备节点index:reg属性中要内存映射的段(从0开始)return:经过内存映射后的虚拟内存首地址,NULL表示内存映射失败



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号