Spring-Lesson2
使用注解配置spring
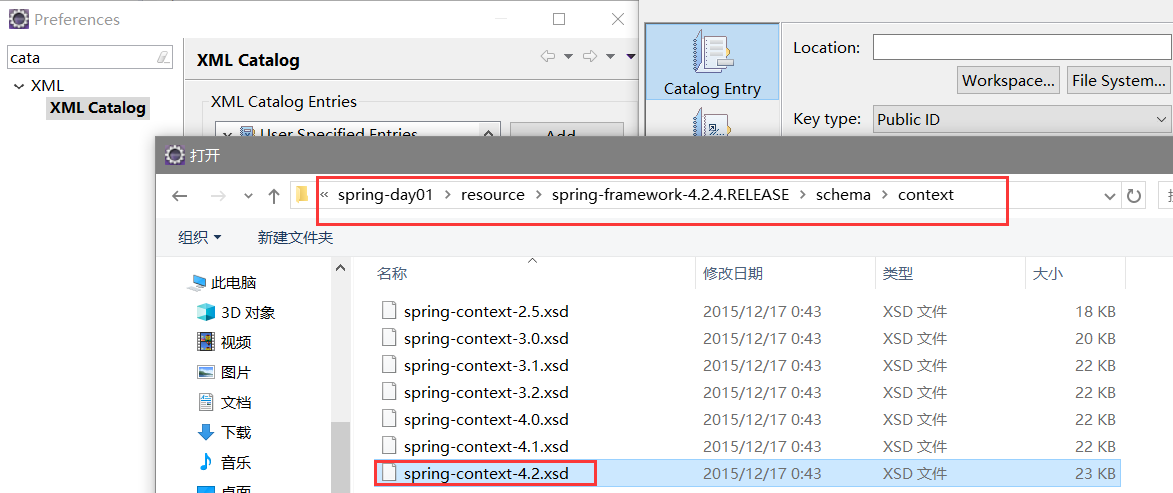
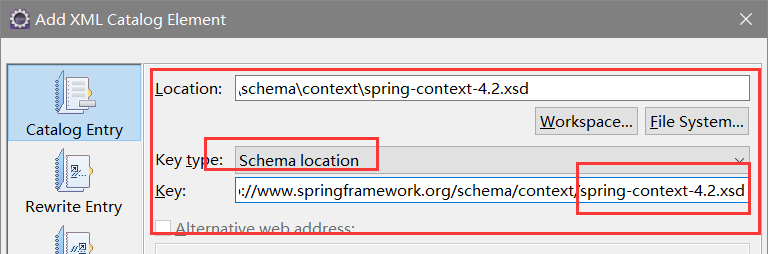
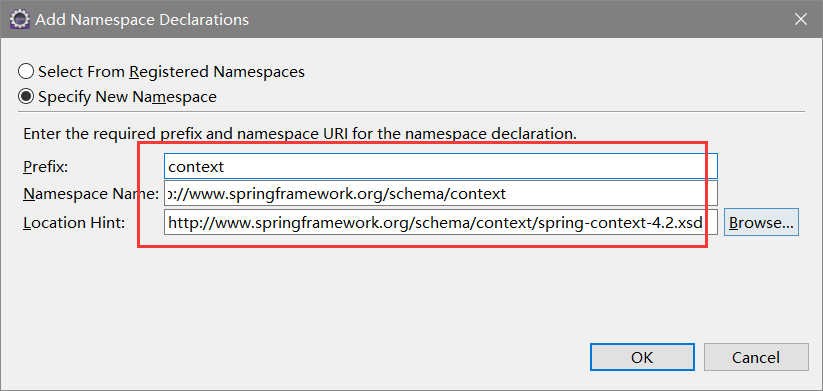
1.为主配置文件引入新的命名空间(约束)
(拷贝一个xml,清空,重复上一课导beans约束的操作,另外增加导入context约束,完了再重命名)
2.开启使用注解代理配置文件
<!-- 指定扫描cn.itcast.bean包下的所有类中的注解. 注意:扫描包时.会扫描指定包下的所有子孙包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.itcast.bean"></context:component-scan>
用注解将对象注册到容器
//代替spring配置文件中的<bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" /> @Component("user")//早期研制出来使用的,后来搞了下面三个来将对象注册到不同的容器 // @Service("user") // service层 // @Controller("user") // web层 // @Repository("user")// dao层 public class User { }
使用上面4个注解的任意一个,皆可从ClassPathXmlApplicationContext中取到对象
//1 创建容器对象 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //2 向容器"要"user对象 User u1 = (User) ac.getBean("user");
指定对象得作用范围
@Scope(scopeName="prototype")//不写的话默认是singleton(意思是每次从容器中取得其实是同一个实例对象)
@Scope(scopeName="prototype")//singleton prototype public class User { }
通过注解给属性赋值
public class User { //方式一 通过反射的Field赋值,破坏了封装性 @Value("tom") private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
public class User { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } //方式二 通过set方法赋值,推荐使用. @Value("tom") public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
默认value属性
public class User { @Value("18")//实际是@Value(value="18") private Integer age; public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } }
给User中得对象属性Car赋值:两步
@Component("car")//将Car放到容器中
public class Car {
@Value("玛莎拉蒂")
private String name;
@Value("呕吐绿")
private String color;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [name=" + name + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
}
@Component("user")
public class User {
//@Autowired //方式1 自动装配 spring从它的容器中去找 如果当心重复,可以增加 @Qualifier("car2") 不过@Resource更方便
@Resource(name="car")//手动注入,指定注入哪个名称的对象
private Car car;
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
}
初始话和销毁对象时增强方法
@Component("user")
@Scope(scopeName="singleton")//singleton prototype
public class User {
@PostConstruct //在对象被创建后调用.init-method
public void init(){
System.out.println("我是初始化方法!");
}
@PreDestroy //在销毁之前调用.destory-method
public void destory(){
System.out.println("我是销毁方法!");
}
}
Eclipse安装STS插件
在线安装,好像还没有完全安装成功,睡觉之前开vpn再更新一下
安装完成后配置文件可以spring方式编辑,且提示方便
spring与junit整合测试
需要导包spring-test-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
//帮我们创建容器 @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) //指定创建容器时使用哪个配置文件 @ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml") public class Demo { //将名为user的对象注入到u变量中 @Resource(name="user") private User u; @Test public void fun1(){ System.out.println(u); } }
spring中的aop
横向重复,纵向抽取
(filter解决乱码问题;动态代理;拦截器)
spring中的aop概念
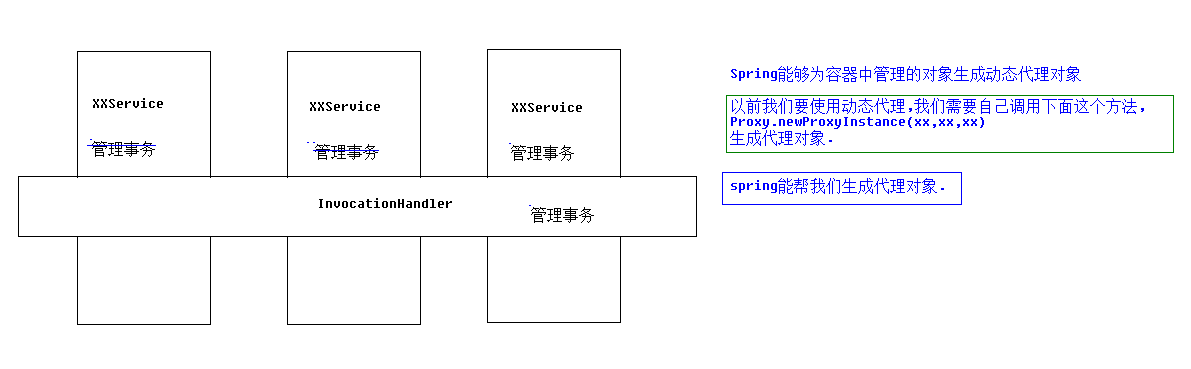
spring实现aop的原理
动态代理(优先)
被代理对象必须要实现接口,才能产生代理对象.如果没有接口将不能使用动态代理技术
cglib代理(没有接口)
第三方代理技术,cglib代理.可以对任何类生成代理.代理的原理是对目标对象进行继承代理. 如果目标对象被final修饰.那么该类无法被cglib代理.
动态代理实例
package cn.itcast.service; public interface UserService { void save(); void delete(); void update(); void find(); }
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Override public void save() { System.out.println("保存用户!"); //int i = 1/0; } @Override public void delete() { System.out.println("删除用户!"); } @Override public void update() { System.out.println("更新用户!"); } @Override public void find() { System.out.println("查找用户!"); } }
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import cn.itcast.service.UserService; import cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl; //观光代码=>动态代理 public class UserServiceProxyFactory implements InvocationHandler { public UserServiceProxyFactory(UserService us) { super(); this.us = us; } private UserService us; public UserService getUserServiceProxy(){ //生成动态代理 UseService这个服务被代理了,被这个this对象代理了,通过这个get方法 UserService usProxy = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(UserServiceProxyFactory.class.getClassLoader(), UserServiceImpl.class.getInterfaces(), this); //返回 return usProxy; } @Override public Object invoke(Object arg0, Method method, Object[] arg2) throws Throwable { System.out.println("打开事务!"); Object invoke = method.invoke(us, arg2); System.out.println("提交事务!"); return invoke; } }
import org.junit.Test; import cn.itcast.service.UserService; import cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl; public class Demo { @Test //动态代理 “代理牌工厂”代理了某项服务,想要拿到这个服务,则通过这个代理工厂,对用户来讲只是多了个步骤,多绕了个路;工厂是通过Proxy.newProxyInstance这个野路子取得的服务对象(比如技师) public void fun1(){ UserService us = new UserServiceImpl(); UserServiceProxyFactory factory = new UserServiceProxyFactory(us); UserService usProxy = factory.getUserServiceProxy(); usProxy.save(); //代理对象与被代理对象实现了相同的接口 //代理对象 与 被代理对象没有继承关系 System.out.println(usProxy instanceof UserServiceImpl );//false } }
cglib代理(基于上面的服务)
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Callback; import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer; import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor; import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy; import cn.itcast.service.UserService; import cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl; //观光代码=>cglib代理 public class UserServiceProxyFactory2 implements MethodInterceptor { public UserService getUserServiceProxy(){ Enhancer en = new Enhancer();//帮我们生成代理对象 en.setSuperclass(UserServiceImpl.class);//设置对谁进行代理 en.setCallback(this);//代理要做什么 UserService us = (UserService) en.create();//创建代理对象 return us; } @Override public Object intercept(Object prxoyobj, Method method, Object[] arg, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { //打开事务 System.out.println("打开事务!"); //调用原有方法 Object returnValue = methodProxy.invokeSuper(prxoyobj, arg); //提交事务 System.out.println("提交事务!"); return returnValue; } }
@Test public void fun2(){ UserServiceProxyFactory2 factory = new UserServiceProxyFactory2(); UserService usProxy = factory.getUserServiceProxy(); usProxy.save(); //判断代理对象是否属于被代理对象类型 //代理对象继承了被代理对象=>true System.out.println(usProxy instanceof UserServiceImpl );//true }
继承方式的代理,利用它的干儿子!
aop名词学习

spring中的aop演示
(玩aop就是让spring帮忙生成代理对象)
1.导包
spring的aop包
spring-aspects-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
spring-aop-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
spring需要第三方aop包
com.springsource.org.aopalliance-1.0.0.jar
com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver-1.6.8.RELEASE.jar
2.准备目标对象
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Override public void save() { System.out.println("保存用户!"); //int i = 1/0; } @Override public void delete() { System.out.println("删除用户!"); } @Override public void update() { System.out.println("更新用户!"); } @Override public void find() { System.out.println("查找用户!"); } }
3.准备通知
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; //通知类 public class MyAdvice { //前置通知 // |-目标方法运行之前调用 //后置通知(如果出现异常不会调用) // |-在目标方法运行之后调用 //环绕通知 // |-在目标方法之前和之后都调用 //异常拦截通知 // |-如果出现异常,就会调用 //后置通知(无论是否出现 异常都会调用) // |-在目标方法运行之后调用 //---------------------------------------------------------------- //前置通知 public void before(){ System.out.println("这是前置通知!!"); } //后置通知 public void afterReturning(){ System.out.println("这是后置通知(如果出现异常不会调用)!!"); } //环绕通知 public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("这是环绕通知之前的部分!!"); Object proceed = pjp.proceed();//调用目标方法 System.out.println("这是环绕通知之后的部分!!"); return proceed; } //异常通知 public void afterException(){ System.out.println("出事啦!出现异常了!!"); } //后置通知 public void after(){ System.out.println("这是后置通知(出现异常也会调用)!!"); } }
4.配置进行织入,将通知织入目标对象中
(新的配置文件中进行aop约束配置)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd "> <!-- 准备工作: 导入aop(约束)命名空间 --> <!-- 1.配置目标对象 --> <bean name="userService" class="cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl" ></bean> <!-- 2.配置通知对象 --> <bean name="myAdvice" class="cn.itcast.d_springaop.MyAdvice" ></bean> <!-- 3.配置将通知织入目标对象 --> <aop:config> <!-- 配置切入点 public void cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl.save() void cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl.save() * cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl.save() * cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl.*() * cn.itcast.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..) * cn.itcast.service..*ServiceImpl.*(..) --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="pc"/> <aop:aspect ref="myAdvice" > <!-- 指定名为before方法作为前置通知 --> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pc" /> <!-- 后置 --> <aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="pc" /> <!-- 环绕通知 --> <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pc" /> <!-- 异常拦截通知 --> <aop:after-throwing method="afterException" pointcut-ref="pc"/> <!-- 后置 --> <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pc"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
测试方法
import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import cn.itcast.bean.User; import cn.itcast.service.UserService; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:cn/itcast/d_springaop/applicationContext.xml") public class Demo { @Resource(name="userService") private UserService us; @Test public void fun1(){ us.save(); } }
以上为xml配置,下面介绍注解配置
(注解本身就是用于代替配置文件)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.2.xsd "> <!-- 准备工作: 导入aop(约束)命名空间 --> <!-- 1.配置目标对象 --> <bean name="userService" class="cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <!-- 2.配置通知对象 --> <bean name="myAdvice" class="cn.itcast.e_annotationaop.MyAdvice"></bean> <!-- 3.开启使用注解完成织入 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> </beans>
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; //通知类 @Aspect //表示该类是一个通知类 public class MyAdvice { @Pointcut("execution(* cn.itcast.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))") public void pc(){} //前置通知 //指定该方法是前置通知,并制定切入点 @Before("MyAdvice.pc()") public void before(){ System.out.println("这是前置通知!!"); } //后置通知 @AfterReturning("execution(* cn.itcast.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))") public void afterReturning(){ System.out.println("这是后置通知(如果出现异常不会调用)!!"); } //环绕通知 @Around("execution(* cn.itcast.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("这是环绕通知之前的部分!!"); Object proceed = pjp.proceed();//调用目标方法 System.out.println("这是环绕通知之后的部分!!"); return proceed; } //异常通知 @AfterThrowing("execution(* cn.itcast.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))") public void afterException(){ System.out.println("出事啦!出现异常了!!"); } //后置通知 @After("execution(* cn.itcast.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))") public void after(){ System.out.println("这是后置通知(出现异常也会调用)!!"); } }
import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import cn.itcast.bean.User; import cn.itcast.service.UserService; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:cn/itcast/e_annotationaop/applicationContext.xml") public class Demo { @Resource(name="userService") private UserService us; @Test public void fun1(){ us.save(); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号