字符串, 多级指针
可以用字符指针表示字符串,也可以用字符数组表示,但是本质上是不一样的
1:用字符指针表示字符串: const char *str = "I love China!"; (可以没有这个const,不过有的编译器会出现警告),反正是不能修改
2:用字符数组表示字符串,char str[] = "You are a student!";
初始化指针所创建的字符串常量被定义为只读,如果出现试图用指针修改这个字符串的行为,编译器会出现警告,说常量怎么着……
用字符数组定义字符串得到的字符数组倒是可以修改
在主函数中用这两种定义方法定义的字符串作为参数传进子函数中的时候,不管你是否修改字符串,参数可以是char str[], 也可以是char *s
(ps:传进来的参数是const类型的时候子函数要对应的加上),因为它能否修改这个性质在主函数中定义的时候已经明确了,也就是说能否修改不看子函数传参的时候用的字符指针还是字符数组,要看主函数中传进来的参数定义的时候是用的字符数组还是字符指针
代码1:
#include <stdio.h> void copyString(const char *from, char *to); int main() { const char *str1 = "I love China!"; char b[] = "You are a student!"; printf("string_a = %s string_b = %s\n", str1, b); copyString(str1, b); printf("string_a = %s string_b = %s\n", str1, b); return 0; } void copyString(const char from[], char to[]) { for (; *from != '\0'; from++, to++) { *to = *from; } *to = '\0'; }
代码2:
#include <stdio.h> void copyString(const char *from, char *to); int main() { const char *str1 = "I love China!"; char b[] = "You are a student!"; printf("string_a = %s string_b = %s\n", str1, b); copyString(str1, b); printf("string_a = %s string_b = %s\n", str1, b); return 0; } void copyString(const char from[], char *to) { int i = 0; while(from[i] != '\0') { to[i]= from[i]; i++; } to[i] = '\0'; }
1:字符串表示形式,用字符数组实现
#include <stdio.h> int main() { char str[] = "I love China!"; printf("%s\n", str); printf("%s\n", str + 7); return 0; }
2:字符串表示形式,用字符指针实现
#include <stdio.h> int main() { char *str = "I love China!"; printf("%s\n", str); str += 7; while (*str) { putchar(str[0]); str++; } return 0; }
3:可以这样定义:

易混淆的地方:
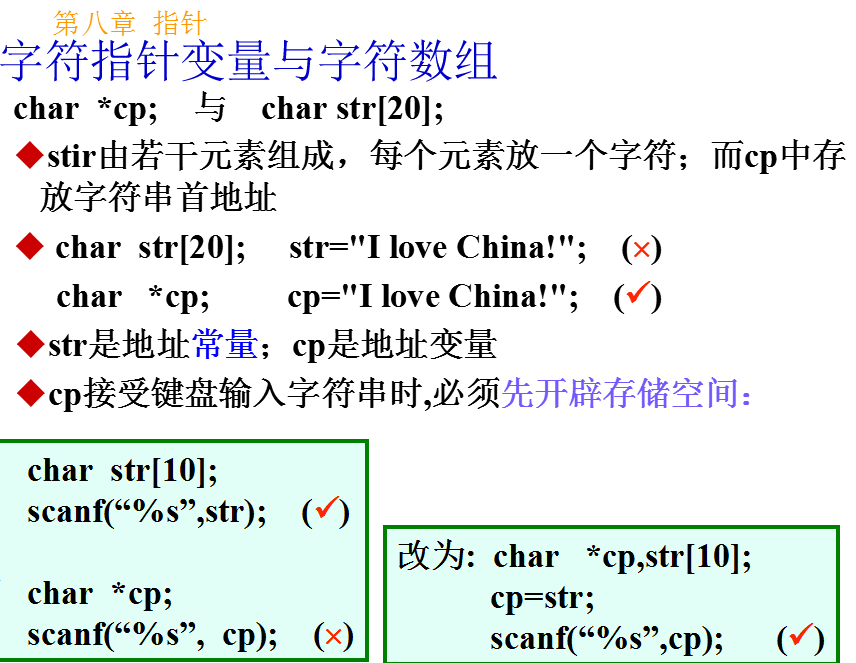
定义方法:



指针数组的使用!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!这其实也是容易错的地方char *name[],子函数写参数的时候忘了加方括号了,哭笑不得……
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { void sort(const char *name[], int n); void prin(const char *name[], int n); const char *name[] = {"Follow me", "BASIC", "Great Wall", "FORTRAN", "Computer"}; int n = 5; sort(name, n); prin(name, n); return 0; } void sort(const char *name[], int n) { int i, j, k; const char *t; for(i = 0; i < n-1; i++) { k = i; for(j = i+1; j < n; j++) { if(strcmp(name[k], name[j]) > 0) k = j; } if(k != i) { t = name[k]; name[k] = name[i]; name[i] = t; } } } void prin(const char *name[], int n) { for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%s ", name[i]); }
多级指针的使用,上代码:
/*对于二级指针,指针变量中存放的是一级指针变量的地址 比如int **p1, *p2, i = 3;` p2 = &i; p1 = &p2; 那么**p1 = 3; 区分int (*p)[4]这个定义的是指向包含四个元素的一维数组的指针p, 区分int *p[4]这个定义的是指向int型数据的四个指针,p[0],p[1], p[2], p[3] */ #include <stdio.h> #include <iostream> using namespace std; void swap(int **p, int **q) { int *t; t = *p; *p = *q; *q = t; } int main() { int a = 1, b = 2, *p, *q; p = &a; q = &b; cout << "*p:" << *p << "\t*q:" << *q << endl; cout << "a:" << a << "\tb:" << b << endl; swap(&p, &q); cout << "*p:" << *p << "\t*q:" << *q << endl; cout << "a:" << a << "\tb:" << b << endl; return 0; }

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号