JDBC
1.数据库驱动
附录 我是附录内容啦啦啦啦啦……
 我们的程序会通过 数据库驱动 和数据库打交道
我们的程序会通过 数据库驱动 和数据库打交道
2.JDBC
sun 公司为了简化开发 人员的(对数据库的统一)操作,提供一个(Java操作数据库的)规范,俗称JDBC这些规范的实现由具体的厂商去做~
没有什么是加一层解决不了的
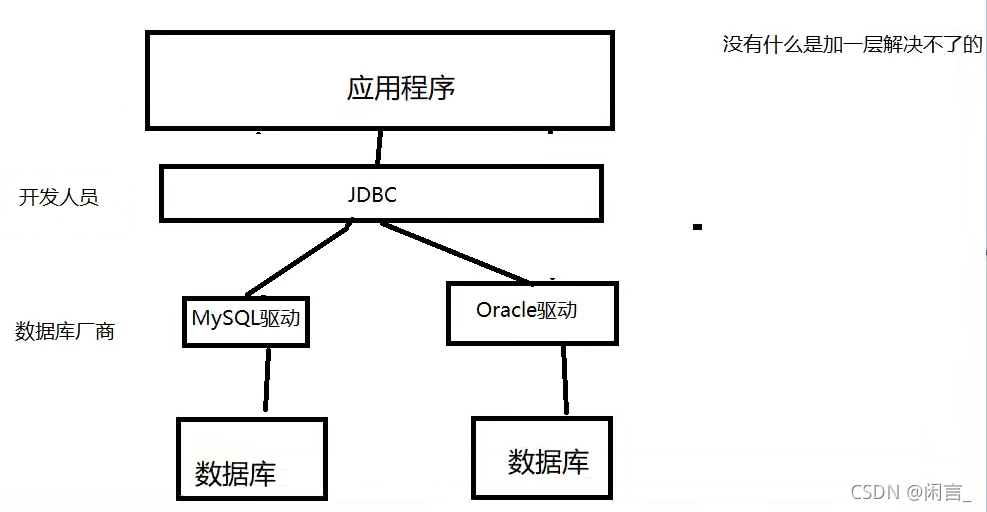
java.sql
javax.sql
还需要导入一个数据库驱动包 mysql-connector-java-x.x.xx.jar
3.第一个JDBC程序
步骤总结
- 加载驱动
- 创建连接 DriverManager
- 获取数据库对象 Statement
- 执行SQL
- [获取结果集]
- 释放连接
3.1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
3.2.用户信息和url
/*jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jabcstudy这样就可以链接了
?:连接字符
useUnicode=true 支持中文编码
characterEncoding=utf8 编码格式utf-8
useSSL=true 采用一个安全的链接*/
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jabcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";
String username = "root";
String passsword = "root";
3.3.链接成功,返回数据库对象
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
3.4.执行SQL的对象 Statement (不安全的)
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
3.5.执行SQL的对象 去 执行SQL,可能存在结果,查看返回结果
String sql = "select * from users";
//返回的结果集,其中封装了我们查询到的全部结果
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
//利用循环从结果集中获取内容,从对应列名获取
while(resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("id=" + resultSet.getObject(id));
}
3.6.释放连接
resuletSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
4.Java中JDBC对象的解释
DriverManager
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//固定写法,加载驱动
URL
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy";
//mysql --3306
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy
协议://主机名:端口号/数据库名?参数1&参数2&参数3
//oracle --1521
jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:sid
Connection
//Connection 代表数据库,可设置自动提交,事务回滚,事务提交等
connection.commit(); //设置提交事务
connection.isReadOnly();//是否只读
connection.setAutoCommit(true);//设置事务自动提交
Statement(执行SQL的对象) prepareStatement()(执行SQL的对象)
statement.executeQuery(sql);//执行查询,返回一个结果集
statement.execute();//执行任何SQL,因为存在判断过程,所以效率低
statement.executeUpdate();//执行更新操作:插入、修改、删除,返回受影响的行数
ResultSet 查询的结果集:封装了程序结果
// 在不知道类型的情况下使用getObject类型
resultSet.getObject();
// 在知道类型的情况下使用对应类型
resultSet.getString();
resultSet.getFloat();
resultSet.getDate();
resultSet.getDouble();
resultSet.getInt();
resultSet.getLong();
//查询数据表中number类型的代表金额的字段时,推荐使用 getBigDecimal()
resultSet.getBigDecimal();
遍历,指针
resultSet.next();//移动到下一个
resultSet.beforeFirst();//移动到第一个
resultSet.afterLast();//移动到最后面
resultSet.previous();//移动到前一行
resultSet.absolute(row);//移动到指定行
释放资源
resultSet.close();
statement.cancel();
connection.close();
5.Statement 对象详解
jdbc中的statement 用于向数据库发送SQL语句,想要完成对数据库的增、删、改、查,只需要通过这个对象向数据库发送增删改查语句即可。
Statement 对象的 executeUpdate( )方法,用于向数据库 发送增、删、改的SQL语句,executeUpdate执行完后,将会返回一个整数(即增删改语句导致数据库几行数据发生了变化)。
Statement. executeQuery( )方法用于向数据库发送查询语句,executeQuery( )方法返回代表查询结果的ResultSet对象。
CRUD是指在做计算处理时的增加(Create)、读取查询(Retrieve)、更新(Update)和删除(Delete)几个单词的首字母简写。主要被用在描述软件系统中DataBase或者持久层的基本操作功能。
5.1.CRUD操作–insert
使用statement.executeUpdate(String sql)方法完成数据添加操作
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "insert into user(...) values(...)"
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num > 0){
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
5.2.CRUD操作–delete
使用statement.executeUpdate(String sql)方法完成数据删除操作
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "delete from user where id = 1"
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num > 0){
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
5.3.CRUD操作–update
使用statement.executeUpdate(String sql)方法完成数据修改操作
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "update user set name='' where id = 1"
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if(num > 0){
System.out.println("修改成功");
}
5.4.CRUD操作–select
使用**statement.executeQuery(String sql) **完成查询操作
[rs相应方法详情](#ResultSet 查询的结果集:封装了程序结果)
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from user";
ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){
//根据获取列的数据类型,分别调用rs的相应方法映射到java对象中
}
5.5.抽取工具类实现CRUD操作
1.通过加载配置文件实现连接数据库与断开连接
public class JdbcUtils {
private static String driver;
private static String url;
private static String username;
private static String password;
static {
try {
InputStream in = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
//驱动只加载一次
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
//释放连接资源
public static void release(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.增
package cn.bloghut.lesson02;
import cn.bloghut.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestInsert {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//2.创建SQL的执行对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//3.执行SQL
String sql = "insert into users(id,name,password,email,birthday) values(4,'闲言','123','123@qq.com',null) ";
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if (num > 0) {
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
}
}
3.删
package cn.bloghut.lesson02;
import cn.bloghut.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestDelete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//2.创建SQL的执行对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//3.执行SQL
String sql = "delete from users where id = 4";
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if (num > 0) {
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
}
}
4.改
package cn.bloghut.lesson02;
import cn.bloghut.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestUpdate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//2.创建SQL的执行对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//3.执行SQL
String sql = "update users set name='update闲言' where id = 2";
int num = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if (num > 0) {
System.out.println("修改成功");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
}
}
5.查
package cn.bloghut.lesson02;
import cn.bloghut.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class TestQuery {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//2.创建SQL的执行对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//3.执行SQL
String sql = "select * from users";
//4.遍历结果集
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println(resultSet.getString(2));
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
}
}
6.PreparedStatement 对象
SQL注入问题
sql 存在漏洞,会被攻击,导致数据泄漏。SQL会被拼接
preparedStatement 可以防止SQL 注入,效率更好!
6.1、新增
package cn.bloghut.lesson03;
import cn.bloghut.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class TestInsert {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pst = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别
//使用 ? 占位符代替参数
String sql = "insert into users(id,name,password,email,birthday) values(?,?,?,?,?)";
pst = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //预编译sql,先写sql 然后不执行
//手动给参数赋值
pst.setInt(1, 4);
pst.setString(2, "闲言");
pst.setString(3, "123");
pst.setString(4, "123@qq.com");
// 注意点: sql.Date 数据库
// util.Date java new java.util.Date().getTime() 获得时间戳
pst.setDate(5, new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime()));
//执行sql
int num = pst.executeUpdate();
if (num > 0) {
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection, pst, null);
}
}
}
6.2、删除
package cn.bloghut.lesson03;
import cn.bloghut.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class TestDelete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pst = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别
//使用 ? 占位符代替参数
String sql = "delete from users where id = ?";
pst = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //预编译sql,先写sql 然后不执行
//手动给参数赋值
pst.setInt(1, 4);
//执行sql
int num = pst.executeUpdate();
if (num > 0) {
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection, pst, null);
}
}
}
5.3、修改
package cn.bloghut.lesson03;
import cn.bloghut.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class TestUpdate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pst = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别
//使用 ? 占位符代替参数
String sql = "update users set name=? where id = ?";
pst = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //预编译sql,先写sql 然后不执行
//手动给参数赋值
pst.setString(1, "闲言碎语");
pst.setInt(2, 1);
//执行sql
int num = pst.executeUpdate();
if (num > 0) {
System.out.println("修改成功!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection, pst, null);
}
}
}
5.4、查询
package cn.bloghut.lesson03;
import cn.bloghut.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TestExecuteQuery {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pst = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//获取连接
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//编写sql
String sql = "select * from users where id = ?";
//预编译
pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setInt(1, 1);
rs = pst.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString("name"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("password"));
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(conn, pst, rs);
}
}
}
5.5、防止SQL注入
package cn.bloghut.lesson03;
import cn.bloghut.lesson02.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class SqlIn {
public static void main(String[] args) {
login("闲言碎语", "123");
// login("'or' 1=1","12133 'or'1=1");
}
//登录业务
public static void login(String username, String password) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pst = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//preparedStatement 防止sql注入的本质,把传递进来的参数当做字符
//假设其中出现转义字符,就直接忽略了
String sql = "select * from users where name = ? and password = ?";
pst = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setString(1,username);
pst.setString(2,password);
resultSet = pst.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("name"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("password"));
System.out.println("===================");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JdbcUtils.release(connection, pst, resultSet);
}
}
}
7、使用IDEA 连接数据库


连接
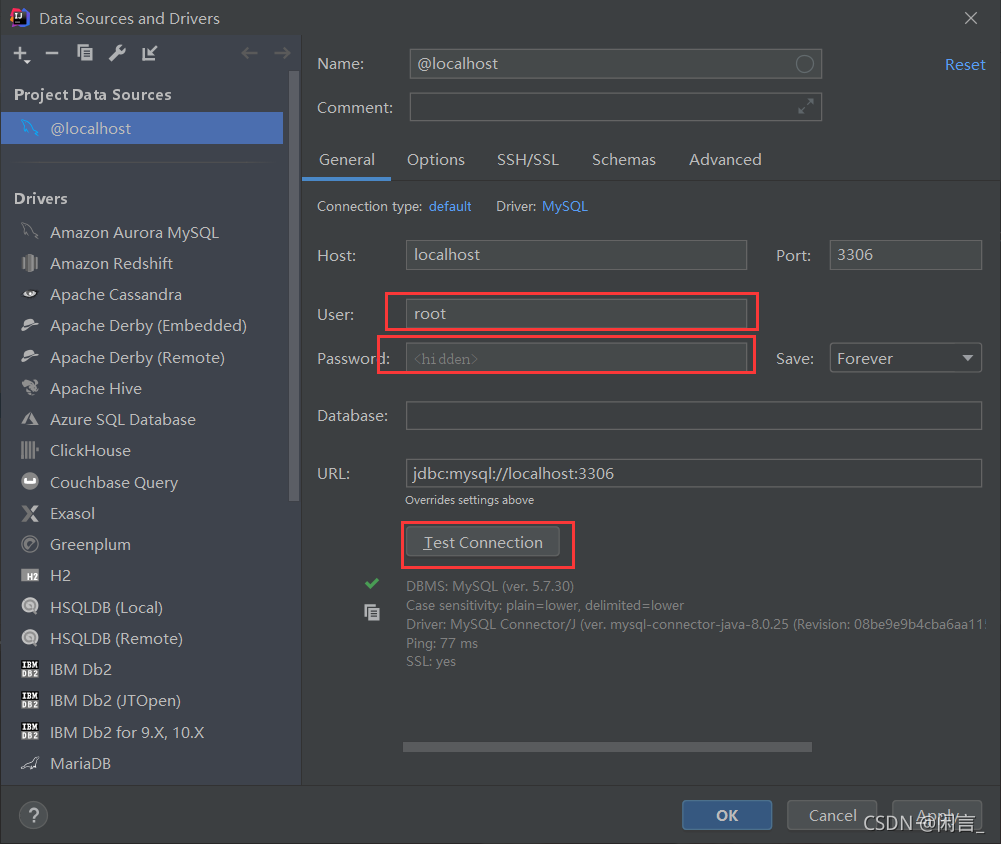
连接成功后可以选择数据库

勾选需要连接的数据库
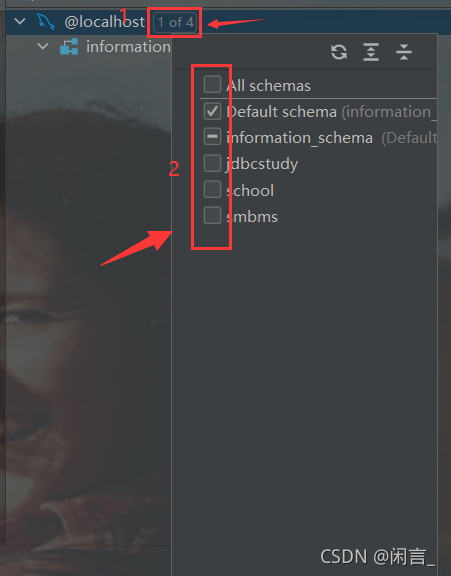
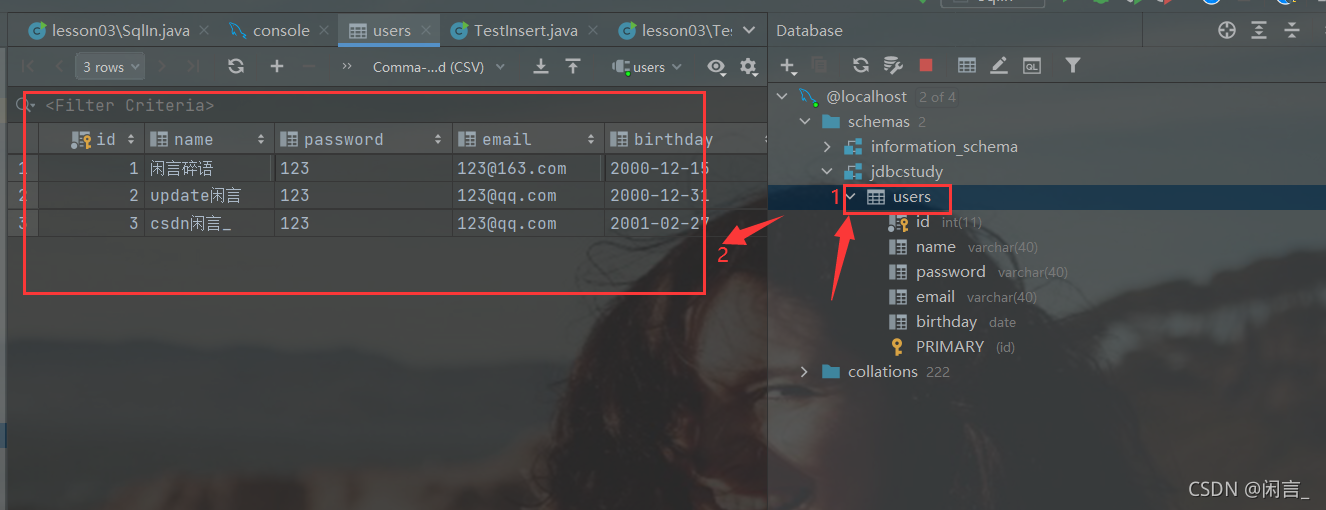
双击表名即可查看表信息




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!