python 二叉树的遍历及常见操作
一、基础
1、 定义节点类
# Definition for a binary tree node. class TreeNode: def __init__(self, x): self.val = x self.left = None self.right = None
2、给定一张图
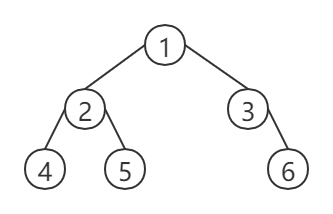
二、基础遍历
1、前序遍历、中序遍历、后续遍历的递归解法
# 前序遍历 [1,2,4,5,3,6]
def preTraverse(root): if root == None: return print(root.value) preTraverse(root.left) preTraverse(root.right) # 中序遍历 [4 2 5 1 3 6] def preTraverse(root): if root == None: return preTraverse(root.left) print(root.value) preTraverse(root.right) # 后序遍历 [4 5 2 3 6 1] def preTraverse(root): if root == None: return preTraverse(root.left) preTraverse(root.right) print(root.value)
2、前序遍历、中序遍历、后续遍历的非递归解法
# 前序遍历 def preTraverse_nonRec(root): if not root: return None stack = [] res = [] while root or len(stack): while root: stack.append(root) res.append(root.val) root = root.left if len(stack): root = stack[-1] stack.pop() root = root.right return res # 中序遍历 def midTraverse_nonRec(root): if not root: return None stack = [] res = [] while root or stack: while root: stack.append(root) root = root.left root = stack.pop() res.append(root.val) root = root.right return res # 后序遍历 def afterTraverse_nonRec(root): if not root: return None stack = [] res = [] pLast = None while root: stack.append(root) root = root.left # 开始出栈 while len(stack): root = stack[-1] stack.pop() # 若无右子树或者右子树被访问,则访问该节点 if not root.right or root.right == pLast: res.append(root.val) pLast = root else: # 节点再次入栈 stack.append(root) root = root.right while root: stack.append(root) root = root.left return res
3、广度优先遍历(BFS)和深度优先遍历(DFS)
3.1 广度优先遍历(BFS)
广度优先遍历(BFS)又叫层次遍历。用队列实现,依次将根,左子树,右子树存入队列,按照队列的先进先出规则来实现层次遍历.
# 定义广度优先遍历(层次遍历)方法
# [1 2 3 4 5 6]
def BFS(root): # 仍然是用队列的方式实现遍历,末端按遍历顺序逐个添加节点,首端逐个弹出先读到的节点 if root: res = [] queue = [root] while queue: currentNode = queue.pop(0) res.append(currentNode.val) if currentNode.left: queue.append(currentNode.left) if currentNode.right: queue.append(currentNode.right) return res
3.2 深度优先遍历(DFS)
用栈实现,先将根入栈,再将根出栈,并将根的右子树,左子树存入栈,按照栈的先进后出规则来实现深度优先遍历。
# 深度优先
# [1,2,4,5,3,6] def DFS(root): if root: res = [] stack = [root] while stack: currentNode = stack.pop() res.append(currentNode.val) if currentNode.right: stack.append(currentNode.right) if currentNode.left: stack.append(currentNode.left) return res
三、常见操作
1、求节点个数
def count_BinTNodes(t): if t is None: return 0 else: return 1 + count_BinTNodes(t.left) \ + count_BinTNodes(t.right)
2、求节点的值得总和
def sum_BinTNodes(t): if t is None: return 0 else: return t.value + sum_BinTNodes(t.left) \ + sum_BinTNodes(t.right)
3、二叉树的最大深度
基本思路就是递归,当前树的最大深度等于(1+max(左子树最大深度,右子树最大深度))。
def maxDepth(root): if not root: return 0 return 1+max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))
4、 二叉树的最小深度
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。可以通过递归求左右节点的最小深度的较小值,也可以层序遍历找到第一个叶子节点所在的层数。
# 递归方法: class Solution: def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: if not root: return 0 if not root.left and not root.right: return 1 if not root.right: return 1+self.minDepth(root.left) if not root.left: return 1+self.minDepth(root.right) return 1+min(self.minDepth(root.left),self.minDepth(root.right)) # 迭代方法: class Solution: def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: if not root: return 0 ans,count = [root],1 while ans: n = len(ans) for i in range(n): r = ans.pop(0) if r: if not r.left and not r.right: return count ans.append(r.left if r.left else []) ans.append(r.right if r.right else []) count+=1
5、二叉树的最大宽度
# 求树的最大宽度 def treeWidth(root): curWidth = 1 maxWidth = 0 myQueue = [] myQueue.append(root) while myQueue: n = curWidth for i in range(n): node = myQueue.pop(0) curWidth -= 1 if node.left != None: myQueue.append(node.left) curWidth += 1 if node.right != None: myQueue.append(node.right) curWidth += 1 if curWidth > maxWidth: maxWidth = curWidth return maxWidth
6、求二叉树的叶子节点
可以使用树的任意一种深度优先遍历方法,在这里用的是先序。
def get_leaves(root): res = [] stack = [] while root or stack: while root: stack.append(root) if not root.left and not root.right: res.append(root.val) root = root.left if stack: root = stack.pop() root = root.right return res





