java.lang包下的类及常用方法
1、包装类
| 数据类型 | 包装类型 | 包装类的默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| byte | Byte | null |
| shrot | Shrot | null |
| int | Integer | null |
| long | Long | null |
| float | Float | null |
| double | Double | null |
| char | Character | |
| boolean | Boolean |
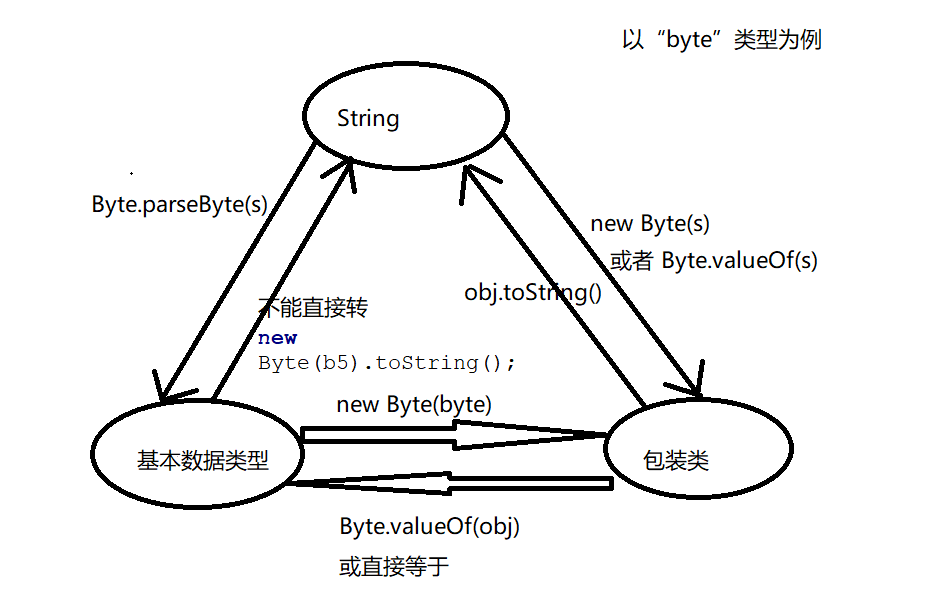
基本数据类型、包装类以及字符串的相互转换(以byte为例)
2、Object类
常用方法
getClass:返回该对象的类型 如何类都有它的类型
equals:java中你的所有的equals方法都是重写Object的equals方法
注意:原生的equals比较的对象地址,我们通常说的equals比较两个对象的值是因为几乎所有的数据类型(包装类,String)都是重写了equals方法的
hashCode():返回该对象的hash值
finalize():资源回收调用该方法,当对象地址不在被引用时,会被GC回收 并调用该方法
toString():返回该对象的字符串表现形式(通常会被子类重写)
wait():线程等待
notify():唤醒其中一个等待的线程
notifyAll:唤醒所有等待中的线程
3、System类
常用方法
System.out:获取控制台的打印流
System.setProperty(“encoding”):设置JVM运行时的系统参数
System.getProperty(“encoding”):打印JVM运行时的系统参数
System.currentTimeMillis():获取当前系统的时间毫秒数
System.exit(0):表示JVM正常退出 -1表示非正常退出
4、String类
常用方法
将此字符串与指定对象进行比较:public boolean equals(Object anobject)
将此字符串与指定对象进行比较,忽略大小写:public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
返回字符串的长度:public int length()
返回指定的字符串连接该字符串的末尾:public String concat(String str)
返回指定索引处的char值:public char charAt(int index)
返回指定字符串第一次出现在该字符串内的索引:public int indexOf(String str)
返回一个子字符串,从beginIndex到endIndex截取字符串。含beginIndex,不含endIndex:public String subString(int beginIndex,int endIndex)
将字符串转换成新的字符数组:public char[] tocharArray()
使用平台的默认字符将该String编码转换成新的字节数组:public byte[ ] getBytes()
将与targer匹配的字符串使用replacement字符串转换:public String raplacement(CharSequence targer,CharSequence replacement)
将字符串按照给定的regex(规则)拆分字符串的数组:public String [ ] split(String regex)
判断字符串以子字符串结尾:public boolean endWith(String str)
判断字符串以子字符串开头:public boolean startsWith(String str)
判断字符串是否为空字符串,对象为空会抛出空指针异常:public boolean isEmpty
将字符串转成小写:public String toupperCase
将字符串转成大写:public String toLowerCase
去点字符串中前后的空格:public String trim()
5、StringBuffer类
常用方法
append():追加字符串
delete(int start,int end):删除指定下标的字符串
insert(int start,String str):插入指定位置的字符串
reverse():反转字符串
StringBuilder与StringBuffer的方法类似!
1、Stringbuffer、StringBuilder和String的区别?
区别1:在运行速度上:StringBuilder>Stringbuffer>String
原因:String是字符串常量,而StringBuilder和StringBuffer是字符串变量,在改变字符串内容时,String重新创建变量并赋值,而StringBuilder和StringBuffer可直接改原有的值,所有效率高。
区别2:在线程安全上:StringBuffer>StringBuilder>String
原因:StringBuffer是线程安全的,而StringBuilder线程不安全,在StringBuffer上的很多方法增加同步关键字(synchronized),导致在多个线程运行时,保持数据的完整性和一致性,而StringBuilder的方法并没有同步,如果在多线程环境下为了确保数据安全,建议使用StringBuffer,如果在单线程环境下,提高效率使用Stringbuilder。
6、Math类
常用方法
Math.random():获取随机数
Math.abs():获取绝对值
Math.cell():向上取整
Math.floor():向下取整
Math.rint():去接近它的整数,如果两个同样近,去接近它的偶数
Math.max(int , int):返回两个数的较大值
Math.min(int , int):返回两个数的较小值
Math.round():四舍五入整数
Math.sqrt():对一个数开平方
Math.pow(double , double):对前一个数的几次幂
7、BigDecimal类
常用方法
add:两个数相加
setScale:设置保留两位整数:四舍五入
subtract:减法
multiply:乘法
divide:除法
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a = 1.2000000;
double b = 1.35433;
double c = a + b;
System.out.println(c);
//会出现精度问题 计算不准确
System.out.println(0.05 + 0.01);
System.out.println(1.0 + 0.42);
//使用bigDecimal,先将类型转成字符串(为了避免精度问题)
BigDecimal num1 = new BigDecimal("0.051");
BigDecimal num2 = new BigDecimal("0.012");
//两个数相加
BigDecimal sum = num1.add(num2);
System.out.println(sum);
//设置保留两位整数 四舍五入
sum = sum.setScale(2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
System.out.println(sum);
//减法
sum = num1.subtract(num2);
System.out.println(sum);
//乘法
sum = num1.multiply(num2);
System.out.println(sum);
//除法
sum = num1.divide(num2, 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
System.out.println(sum);
}
8、NumberFormat类
常用方法
// NumberFormat类是对数值类型的格式化类,其中 DecimalFormat是继承NumberFormat
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
//根据本机环境获取货币格式化对象
NumberFormat fmt = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance();
String m = fmt.format(3650.5);
System.out.println(m);//¥3,650.50
//获取百分比的格式化对象
fmt = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance();
m = fmt.format(0.45567);
System.out.println(m); //默认输出XX% 46%
//根据指定匹配模式格式化数值为字符串(百分比)
fmt = new DecimalFormat("##.##%");
m = fmt.format(0.45567);
System.out.println(m); //45.56%
//根据指定匹配模式格式化数值为字符串(千分比)
fmt = new DecimalFormat("##.##\u2030");
m = fmt.format(0.45567);
System.out.println(m); //455.67‰
//根据指定的模式 转成科学计数法
fmt = new DecimalFormat("#.###E0");
m = fmt.format(198200);
System.out.println(m);
//将一个字符串表达式,根据指定解析为数值类型
String s = "45.6%"; //0.456
fmt = new DecimalFormat("##.#%");
Number num = fmt.parse(s);
double d = num.doubleValue();
System.out.println(d);//0.456
}


