JDK集合框架--综述
接下来的几篇博客总结一下对jdk中常用集合类知识,本篇博客先整体性地介绍一下集合及其主要的api:
从整体上来说,集合分两大类collection和map:
首先来看看Collection:
collection主要分为set(无序)和list(有序)两大类,这里分别以HashSet和ArrayList为例,分析:
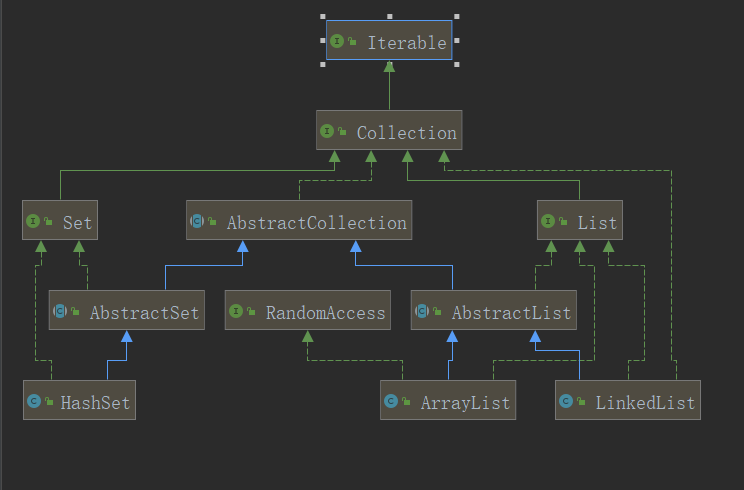
以上是使用idea生成的类图:
collection继承了接口Iterable,用于获取迭代器(Iterator接口的实现类实例),Iterator的实现类都是集合类中的内部类;
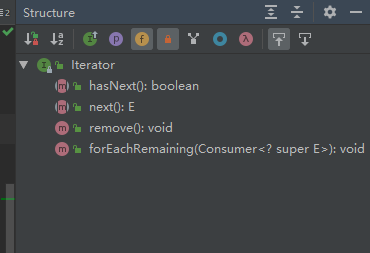
Iterator接口主要用于遍历集合中的元素,接下来看看collection接口
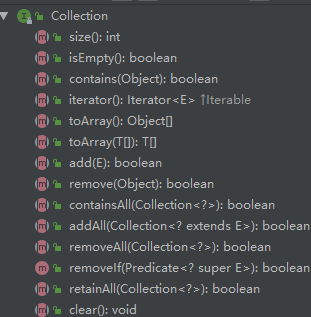
主要都是一些对集合中元素的添加,移除,查找等基础方法,然后看看都继承了collection的set和list接口:


左边是list,右边是set,可以看到set接口并没有添加新的方法,所有方法都是覆盖collection的,并没有拓展父类;然后看看list的方法,用红线圈的起来的是set方法所没有的,其实从这些list特有的方法中,就能看出list和set的区别所在,这些方法无非就是通过索引值获取元素或者获取一个元素的索引值,索引就是元素在集合中的序号,说明list是有序集合,而set是无序集合。
AbstractCollection是一个抽象类,该类中简单地实现了Collection接口中多数的方法,留下两个抽象方法
public abstract Iterator<E> iterator();//获取迭代器 public abstract int size();//元素个数
其他的方法基本上是根据子类所实现的iterator()获取
迭代器(用到模板方法设计模式),然后遍历元素来实现,比如判断集合中是否含有某元素的contains:
public boolean contains(Object o) { Iterator<E> it = iterator();//子类实现 if (o==null) { while (it.hasNext()) if (it.next()==null) return true; } else { while (it.hasNext()) if (o.equals(it.next())) return true; } return false; }
这里需要注意add(E e)方法:
/** * {@inheritDoc} * * <p>This implementation always throws an * <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt>. * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc} * @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} * @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc} * @throws IllegalStateException {@inheritDoc} */ public boolean add(E e) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }
这个方法默认的实现是抛出异常,子类如果没有重写,该方法会抛出UnsupportedOperationException异常(比如:java.util.Arrays#asList()方法,返回的list对象的类就没有覆盖add(E e));
最后看看AbstractList和AbstractSet:
AbstractList实现list,由于list是有序的,可以通过索引访问的方式获取到下一个元素,所以AbstractList通过给出了一种最简单通用的实现迭代器的方法:
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { /** * Index of element to be returned by subsequent call to next. */ int cursor = 0; /** * Index of element returned by most recent call to next or * previous. Reset to -1 if this element is deleted by a call * to remove. */ int lastRet = -1; /** * The modCount value that the iterator believes that the backing * List should have. If this expectation is violated, the iterator * has detected concurrent modification. */ int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size(); } public E next() { checkForComodification(); try { int i = cursor; E next = get(i);//通过索引获取下一个元素 lastRet = i; cursor = i + 1; return next; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { checkForComodification(); throw new NoSuchElementException(); } } public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet);// if (lastRet < cursor) cursor--; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
由于子类中用于存储元素的数据结构不同,通过索引获取值得方法可能不同,比如数组和链表,后续的文章会深入讲到,所以get(int index) 和size()依然是个抽象方法没有实现;
AbstractSet只是重写了三个方法,没什么特别:

再来看看Map:
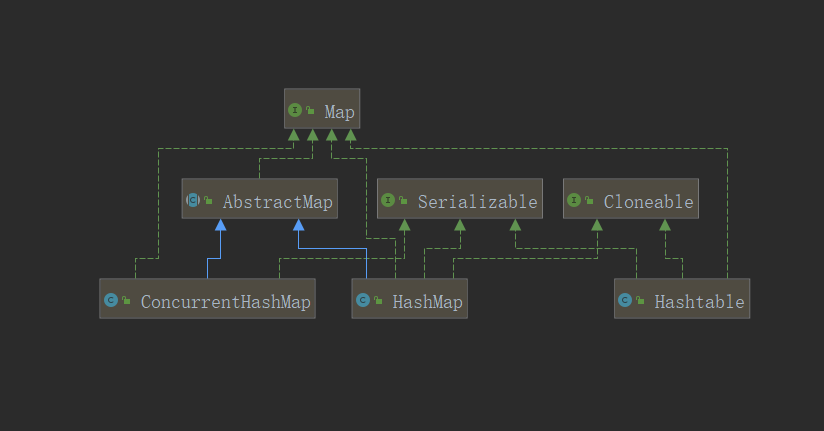
类图层次机构比较简单,没什么特殊;看看Map接口定义的方法:

Map类型相对来说其接口规范,比较统一,不需要后代接口拓展,就是说所有具体的实现类只需要实现Map中操作集合的方法即可。


