二叉树结构与递归实现前中后序遍历
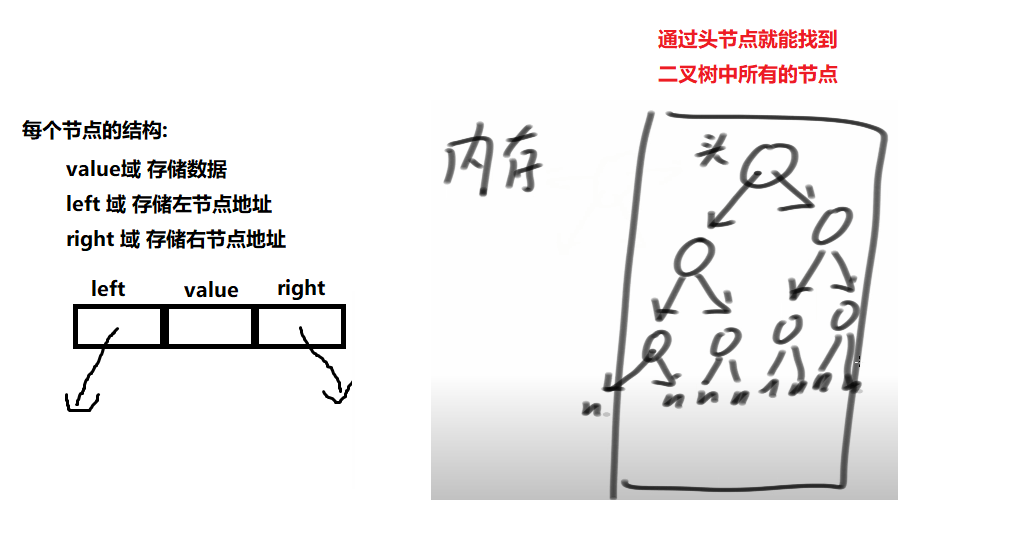
1. 二叉树结构
2. 二叉树节点遍历顺序
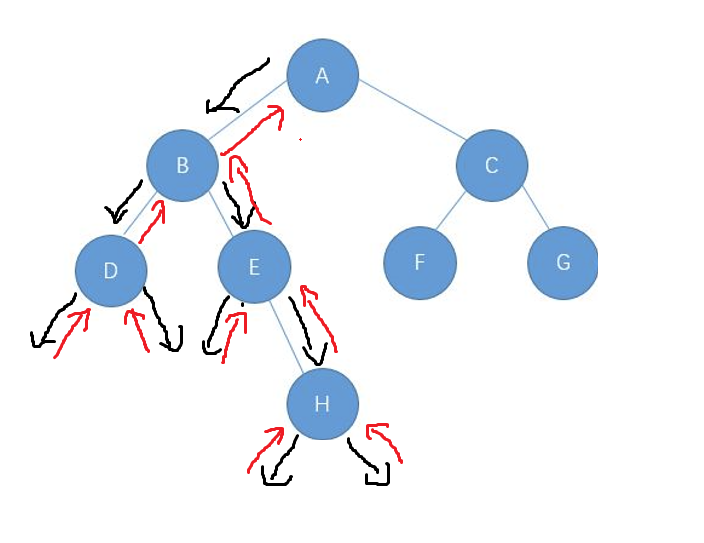
前序:
每颗子树以 中 —》左 —》右 遍历
A B D E H C F G
中序:
每颗子树以 左 —》中 —》右 遍历
D B E H A F C G
后序:
每颗子树以 左 —》右 —》中 遍历
D H E B F G C A
代码实现:
public class BinaryTree { static class TreeNode { public TreeNode left; public char val; public TreeNode right; public TreeNode(char val) { this.val = val; } } public TreeNode createTree() { TreeNode A = new TreeNode('A'); TreeNode B = new TreeNode('B'); TreeNode C = new TreeNode('C'); TreeNode D = new TreeNode('D'); TreeNode E = new TreeNode('E'); TreeNode F = new TreeNode('F'); TreeNode G = new TreeNode('G'); TreeNode H = new TreeNode('H'); A.left = B; B.left = D; B.right = E; E.right = H; A.right = C; C.left = F; C.right = G; return A; } // 前序 - 根左右 public void preOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } System.out.print(root.val + " "); preOrder(root.left); preOrder(root.right); } // 中序 public void inOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } inOrder(root.left); System.out.print(root.val + " "); inOrder(root.right); } // 后序 public void postOrder(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return; } postOrder(root.left); postOrder(root.right); System.out.print(root.val + " "); } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree(); TreeNode root = binaryTree.createTree(); binaryTree.preOrder(root); System.out.println(); binaryTree.inOrder(root); System.out.println(); binaryTree.postOrder(root); } }
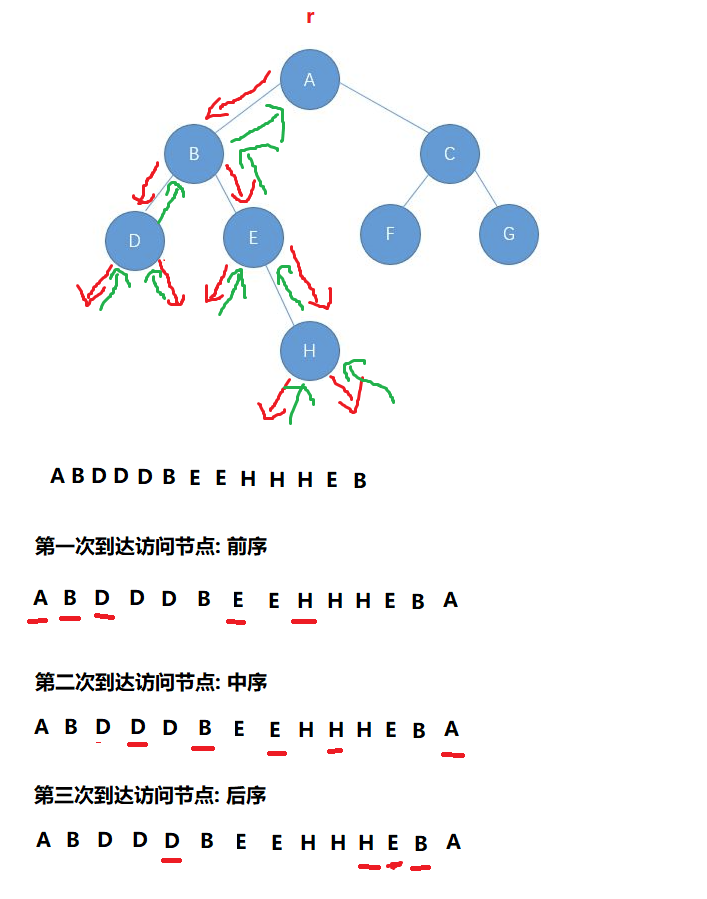
3. 递归序理解二叉树遍历
除了空节点外 每一个节点一定会到达3次
第一次到达访问节点: 前序,第二次到达访问节点: 中序,第三次到达访问节点: 后序
访问节点的时机不同 遍历顺序也就不同
以递归序为例:




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理