201521123037 《Java程序设计》第14周学习总结
1. 本周学习总结
1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多数据库相关内容。
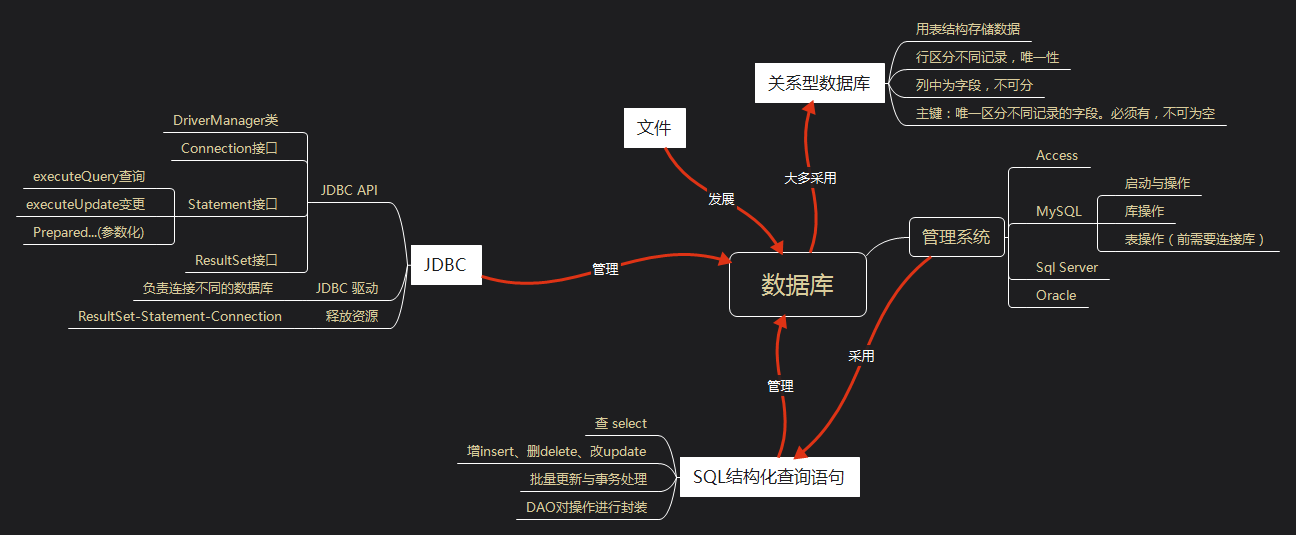
2. 书面作业
1. MySQL数据库基本操作
1.1 建立数据库,将自己的姓名、学号作为一条记录插入。(截图,需出现自己的学号、姓名)

1.2 在自己建立的数据库上执行常见SQL语句(截图)
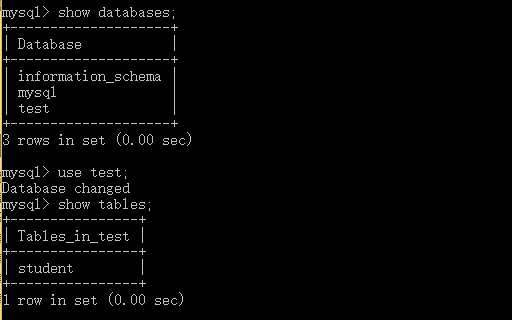


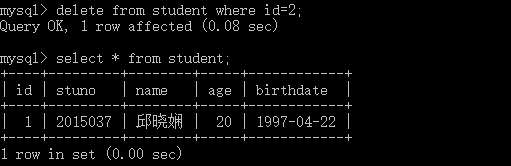
- 参考:实验任务书-题目1
2. 使用JDBC连接数据库与Statement
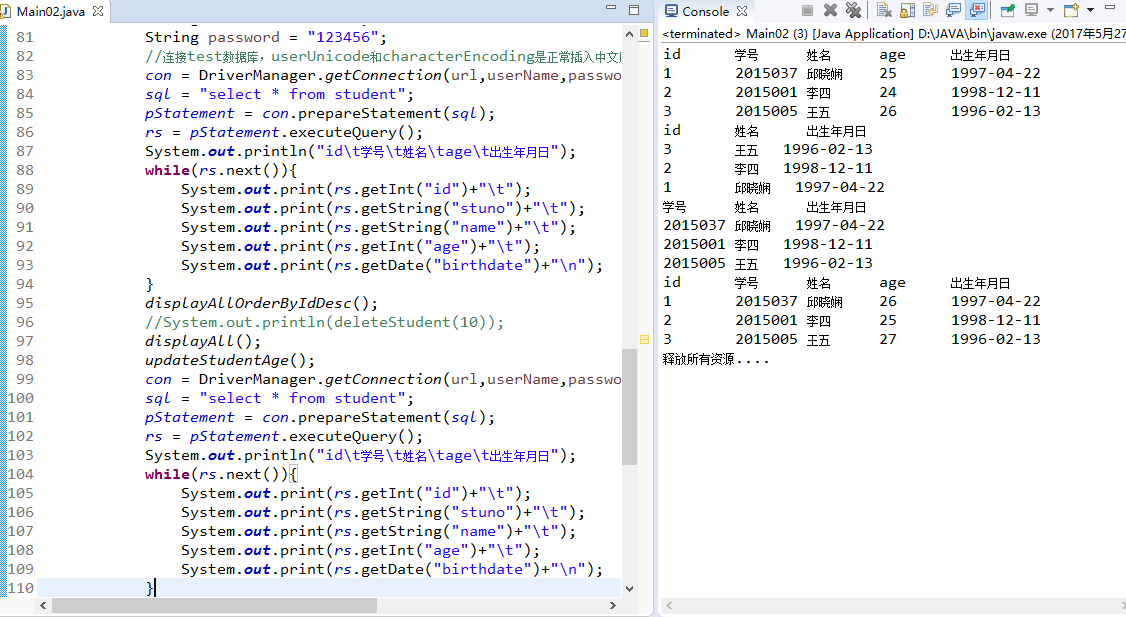
2.1 使用Statement操作数据库。(粘贴一段你认为比较有价值的代码,出现学号)
//学号201521123037,根据题目一编写方法
public static void displayAll() throws SQLException{
//显示所有学生的学号、名字和出生时间,select
sql = "select stuno,name,birthdate from student";
pStatement = con.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pStatement.executeQuery();
System.out.println("学号\t姓名\t出生年月日");
while(rs.next()){
System.out.print(rs.getString("stuno")+"\t");
System.out.print(rs.getString("name")+" ");
System.out.print(rs.getDate("birthdate")+"\n");
}
}
public static int insert(Student stu) throws SQLException{
//插入学生,insert
sql="insert into student(stuno,name,age,birthdate) values(?,?,?,?)";
pStatement = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pStatement.setString(1,stu.stuno);
pStatement.setString(2,stu.name);
pStatement.setInt(3,stu.age);
pStatement.setDate(4,stu.birthdate);
return pStatement.executeUpdate();
}
public static void displayAllOrderByIdDesc() throws SQLException{
//打印出学生的ID号、姓名和出生年日期,并按id降序排列
sql = "select id,name,birthdate from student";
strsql="select * from student order by id desc";
pStatement = con.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = pStatement.executeQuery(strsql);
System.out.println("id\t姓名\t出生年月日");
while(rs.next()){
System.out.print(rs.getInt("id")+"\t");
System.out.print(rs.getString("name")+" ");
System.out.print(rs.getDate("birthdate")+"\n");
}
}
public static int deleteStudent(int id) throws SQLException{
//按id删除某个学生,返回值为删除学生的个数,delete
sql="delete from student where id="+id+"";
pStatement = con.prepareStatement(sql);
return pStatement.executeUpdate();
}
public static int updateStudentAge() throws SQLException{
//将每个学生的年龄+1,update语句
sql="update student set age=age+1;";
pStatement = con.prepareStatement(sql);
return pStatement.executeUpdate();
}
2.2 使用JDBC操作数据库主要包含哪几个步骤?
1.在eclipse中导入连接数据库所需的jar文件
- 在项目下新建lib目录
- 将相关jar包拷贝到lib目录
- 在项目的Build Path中导入该jar包
- 在项目中导入.java文件,尝试运行
2.java文件中
-
注册驱动(注:jdbc4.0后无需进行驱动注册操作)
-
创建连接
-
向数据库发送sql语句
-
获得和处理查询或更新语句返回的结果
-
关闭连接释放资源
-
参考:实验任务书-题目2
3. PreparedStatement与参数化查询
3.1 使用PreparedStatement根据用户指定的查询条件进行查询。(粘贴一段你认为比较有价值的代码,出现学号)
//学号201521123037
public static void displayStudentBetween(String begin,String end) throws SQLException{
//显示出生年月日在某个范围内的所有学生
String sql="select * from student where birthdate between ? and ?";
pStatement=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pStatement.setString(1, begin);
pStatement.setString(2, end);
rs=pStatement.executeQuery();
System.out.println("id\t学号\t姓名\tage\t出生年月日");
while(rs.next()){
id=rs.getInt("id");
System.out.print(id+"\t");
stuno=rs.getString("stuno");
System.out.print(stuno+"\t");
Name=rs.getString("name");
System.out.print(Name+"\t");
age=rs.getInt("age");
System.out.print(age+"\t");
birthdate=rs.getDate("birthdate");
System.out.print(birthdate+"\n");
}
}
public static double getAvgAbove(int age) throws SQLException{
//显示所有年龄超过传入参数age的同学的姓名与年龄平均值(使用avg函数)
double age1 = 0;
String sql1="select name from student where age>?";
String sql2="select avg(age) avgAge from student where age>?";
pStatement=conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
PreparedStatement pStatement1=conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
pStatement.setInt(1, age);
pStatement1.setInt(1, age);
rs=pStatement.executeQuery();
ResultSet rs1=pStatement1.executeQuery();
rs1.next();
System.out.println("姓名\tavgAge");
while(rs.next()){
Name=rs.getString("name");
System.out.print(Name+"\t");
age1 =rs1.getDouble("avgAge");
System.out.println(age1);
}
return age1;
}
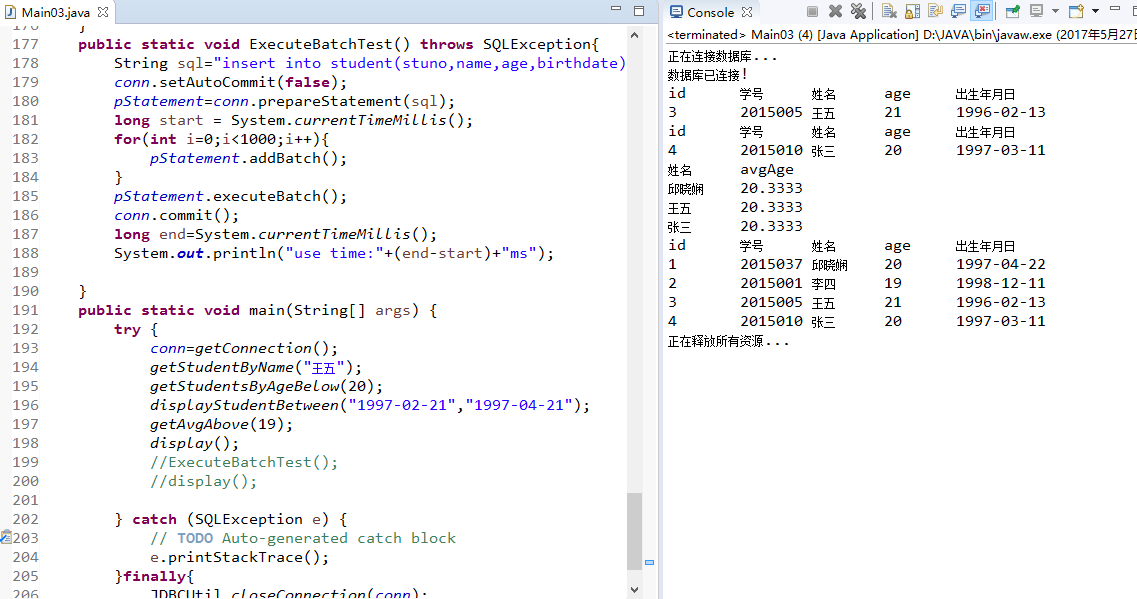
3.2 批量更新-批量插入1000个学生,统计整个操作所消耗的时间。(使用方法executeBatch)
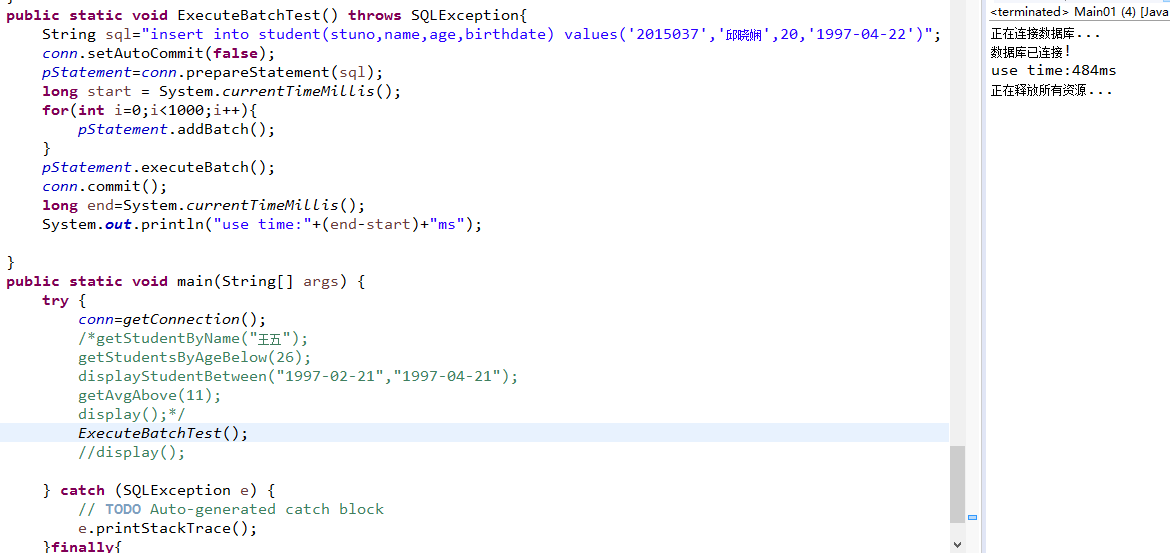
消耗时间约为484ms。这里采用事务和批处理混合处理,主要有四个步骤:不自动提交->收集参数->批量送出参数->提交。
- 参考:实验任务书-题目3
4. JDBCUtil与DAO
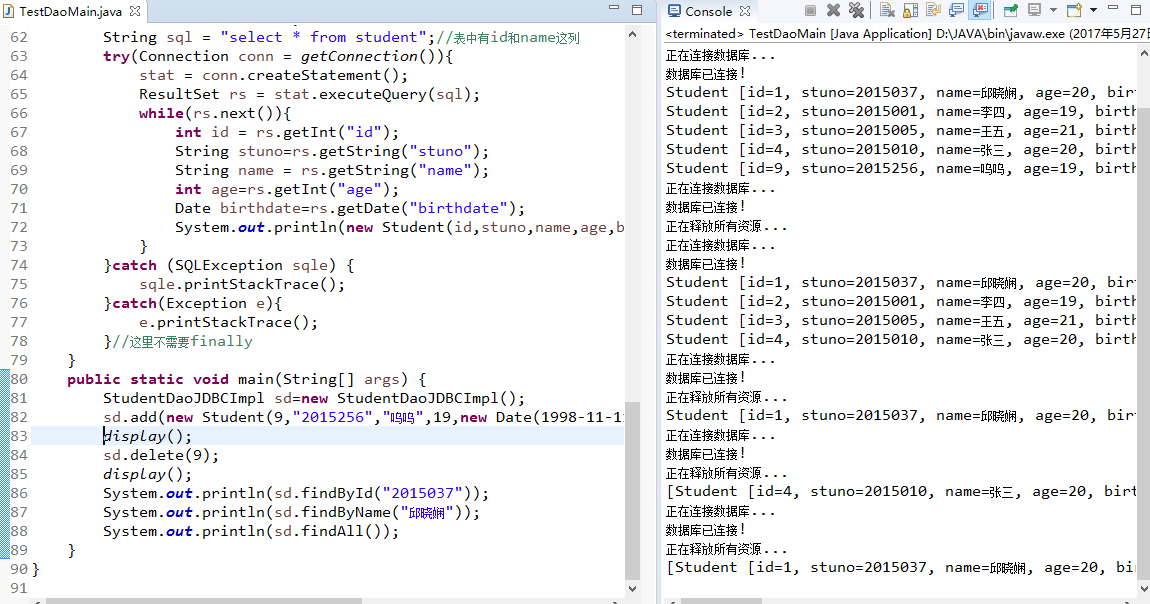
4.1 粘贴一段你认为比较有价值的代码,出现学号
//学号201521123037
@Override
public Student findById(String sid) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Student s = null;
String sql="select * from student where stuno=?";
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstat = null;
try {
conn=TestDaoMain.getConnection();
pstat=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstat.setString(1, sid);;
ResultSet rs=pstat.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
s=new Student(rs.getInt("id"),rs.getString("stuno"),rs.getString("name"),rs.getInt("age"),rs.getDate("birthdate"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
TestDaoMain.realeaseAll(null, pstat, conn);
}
return s;
}
@Override
public List<Student> findByName(String name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
List<Student> list=new ArrayList<Student>();
String sql="select * from student where name like '张%'";
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstat = null;
try {
conn=TestDaoMain.getConnection();
pstat=conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet rs=pstat.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
list.add(new Student(rs.getInt("id"),rs.getString("stuno"),rs.getString("name"),rs.getInt("age"),rs.getDate("birthdate")));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
TestDaoMain.realeaseAll(null, pstat, conn);
}
return list;
}
4.2 使用DAO模式访问数据库有什么好处?
DAO模式指的是将连接与释放连接的操作封装起来,提供访问数据库的同一入口。避免代码的重复使用,将其封装起来也方便出错的时候进行修改。
- 参考:实验任务书-题目5
5. 使用数据库改造购物车系统
5.1 使用数据库改造以前的购物车系统(应有图形界面)。如果以前为完成购物车系统,可编写基于数据库的学生管理系统。包括对学生的增删改查,要求使用。

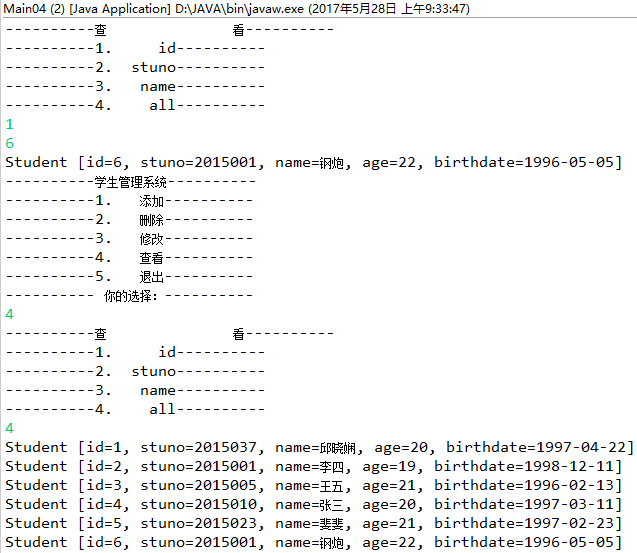


- 相关代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
StudentDaoJDBCImpl sd=new StudentDaoJDBCImpl();
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
boolean flag=true;
Student s=null;
List<Student> list=new ArrayList<Student> ();
while(flag){
System.out.println("----------学生管理系统----------");
System.out.println("----------1. 添加----------");
System.out.println("----------2. 删除----------");
System.out.println("----------3. 修改----------");
System.out.println("----------4. 查看----------");
System.out.println("----------5. 退出----------");
System.out.println("---------- 你的选择:----------");
int choice=sc.nextInt();
switch(choice){
case 1:{
System.out.println("----------添 加----------");
System.out.println("----------请输入学生信息:----------");
if(sd.add(new Student(sc.nextInt(),sc.next(),sc.next(),sc.nextInt(),new Date(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt()-1, sc.nextInt())))==1)
System.out.println("添加成功!");
else System.out.println("添加失败!");
};break;
case 2:{
System.out.println("----------删 除----------");
System.out.println("----------请输入学生id:----------");
if(sd.delete(sc.nextInt())==1) System.out.println("删除成功!");
else System.out.println("删除失败!");
};break;
case 3:{
System.out.println("----------修 改----------");
System.out.println("----------请输入学生id:----------");
if(sd.update(new Student(sc.nextInt(),sc.next(),sc.next(),sc.nextInt(),new Date(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt()-1, sc.nextInt())))==1)
System.out.println("修改成功!");
else System.out.println("修改失败!");
};break;
case 4:{
System.out.println("----------查 看----------");
System.out.println("----------1. id----------");
System.out.println("----------2. stuno----------");
System.out.println("----------3. name----------");
System.out.println("----------4. all----------");
int c=sc.nextInt();
if(c==2) {
if((s=sd.findById(sc.next()))!=null)
System.out.println(s);
else System.out.println("查无此人!");
}
else if(c==3) {
if((list=sd.findByName(sc.next())).size()!=0)
System.out.println(list);
else System.out.println("查无此人!");
}
else if(c==1) {
if((s=sd.findId(sc.nextInt()))!=null)
System.out.println(s);
else System.out.println("查无此人!");
}
else if(c==4) TestDaoMain.display();
};break;
case 5:flag=false;break;
default :System.out.println("输入有误");
}
}
}
5.2 相比较使用文件,使用数据库存储与管理数据有何不一样?
使用数据库可以直接使用sql语句对其操作,管理比较方便。因为数据库一般有备份数据的功能以及保证数据安全的命令,所以数据更加安全。
选做:6. 批量更新测试
数据库课程上,需要测试索引对查找的加速作用。然而在几百或几千的数据量上进行操作无法直观地体验到索引的加速作用。现希望编写一个程序,批量插入1000万条数据,且该数据中的某些字段的内容可以随机生成。
6.1 截图你的代码(出现学号)、统计运行时间
6.2 计算插入的速度到底有多快?(以条/秒、KB/秒两种方式计算)
选做:7. 事务处理
7.1 使用代码与运行结果证明你确实实现了事务处理功能。(粘贴一段你认为比较有价值的代码,出现学号)

7.2 你觉得什么时候需要使用事务处理?
对数据库的数据进行批量或连表操作时,为了保证数据的一致性和正确性,我们需要添加事务管理机制进行管理。当对数据库的数据进行操作失败时,事务管理可以很好保证所有的数据回滚到原来的数据,如果操作成功,则保证所有需要更新的数据持久化。
- 参考:实验任务书-题目4
选做 8. 数据库连接池
使用数据库连接池改写题目5
- 参考:实验任务书-题目4
- 数据连接池参考资料
3. 码云
3.1. 码云代码提交记录
在码云的项目中,依次选择“统计-Commits历史-设置时间段”, 然后搜索并截图

4.课外阅读
4.1 JDBC(TM) Database Access
4.2 代码结构中Dao,Service,Controller,Util,Model是什么意思,为什么划分
Dao是处理基础操作,如增删改查,与底层数据库联系;Service提供服务,可以是多个Util组成;Controller相当于指挥中心,指挥服务的执行;Util相当于工具,有明确的输入和输出结果;Model是数据抽象的定义。划分能够让代码结构更清晰,每个分类都有自己的功能,各司其职,彼此间又互相协作,较高效率完成任务。
4.3 mysq数据库管理工具navicat基本使用方法



