第七周课程总结和实验报告
实验四 类的继承
- 实验目的
- 理解抽象类与接口的使用;
- 了解包的作用,掌握包的设计方法。
- 实验要求
- 掌握使用抽象类的方法。
- 掌握使用系统接口的技术和创建自定义接口的方法。
- 了解 Java 系统包的结构。
- 掌握创建自定义包的方法。
- 实验内容
(一)抽象类的使用
- 设计一个类层次,定义一个抽象类--形状,其中包括有求形状的面积的抽象方法。 继承该抽象类定义三角型、矩形、圆。 分别创建一个三角形、矩形、圆存对象,将各类图形的面积输出。
注:三角形面积s=sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)) 其中,a,b,c为三条边,p=(a+b+c)/2
2.编程技巧
(1) 抽象类定义的方法在具体类要实现;
(2) 使用抽象类的引用变量可引用子类的对象;
(3) 通过父类引用子类对象,通过该引用访问对象方法时实际用的是子类的方法。可将所有对象存入到父类定义的数组中。
(二)使用接口技术
1定义接口Shape,其中包括一个方法size(),设计“直线”、“圆”、类实现Shape接口。分别创建一个“直线”、“圆”对象,将各类图形的大小输出。
- 编程技巧
(1) 接口中定义的方法在实现接口的具体类中要重写实现;
(2) 利用接口类型的变量可引用实现该接口的类创建的对象。
1.实验代码:
public abstract class shape { public String shape; public double area; public String getShape() { return shape; } public void setShape(String shape) { this.shape = shape; } public double getArea() { return area; } public void setArea(double area) { this.area = area; } public void shape() { if(this.area() != 0) System.out.println(this.shape+"的面积为:"+this.area()); else System.out.println("无法计算"); } public abstract double area(); }
1.2实验代码:
public class triangle extends shape {
private double a,b,c; //定义自己的变量
public double getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(double a) {
this.a = a;
}
public double getB() {
return b;
}
public void setB(double b) {
this.b = b;
}
public double getC() {
return c;
}
public void setC(double c) {
this.c = c;
}
public triangle (String shape ,double a, double b, double c ) { //赋值
this.shape = shape;
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
public double area() { //覆写
if(a + b >= c && a + c >= b && b + c >= a) //判断是否为三角形
{
double p = (a + b + c)*0.5;
double q = (p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
return Math.sqrt(q);
}
else
{
System.out.println("不是三角形!");
}
return 0;
}
}
1.3实验代码:
public class rectangle extends shape { private double High ,Width; // //定义自己的变量 public double getHigh() { return High; } public void setHigh(double high) { High = high; } public double getWidth() { return Width; } public void setWidth(double width) { Width = width; } public rectangle (String shape ,double High, double Width ) { //赋值 this.shape = shape; this.High = High; this.Width = Width; } public double area() { //覆写 if(High >= 0 && Width >=0) //判断是否为矩形 { double s = 2*(Width+High); return s; } else { System.out.println("不是矩形"); } return 0; } }
1.4实验代码:
public class circle extends shape { private double r; //定义自己的变量 public double getR() { return r; } public void setR(double r) { this.r = r; } public circle (String shape ,double r) { //赋值 this.shape = shape; this.r = r; } public double area() { //覆写 if(r >= 0) //判断是否为圆 { double S = Math.PI * Math.pow(r, 2); return S; } else { System.out.println("不是圆"); } return 0; } }
1.5实验代码:
public class text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
shape s1= new triangle("三角形",3,4,5);
shape s2= new rectangle("矩形",1,1);
shape s3 =new circle("圆",2);
s1.shape();
s2.shape();
s3.shape();
}
}
截图:
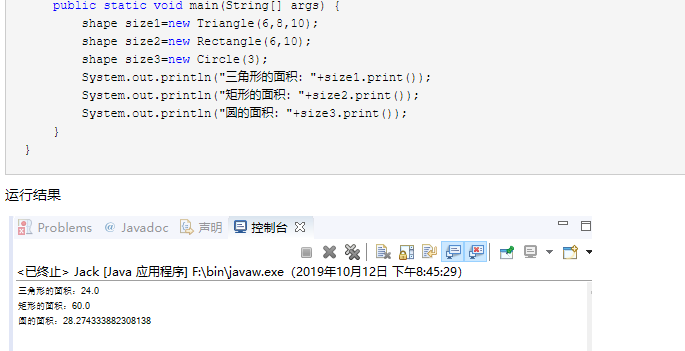
2.实验代码:
public interface Shape { public abstract void size(); } class Straight implements Shape{ private double figure; public Straight(double figure){ this.figure=figure; } public void size() { System.out.println("直线的大小=="+figure); } } class Circle2 implements Shape{ private double radious; public Circle2(double radious){ this.radious=radious; } public void size() { System.out.println("圆的面积=="+Math.PI*radious*radious); } } package 实验5; public class java { public static void main(String[] args){ Shape s1=new Straight(9); Shape s2=new Circle2(5);
s1.size();
s2.size(); } }
截图:
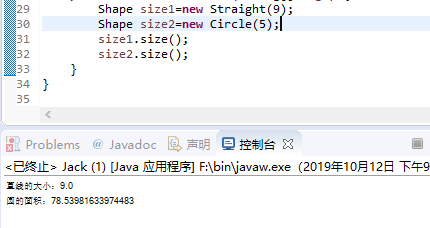
总结:
抽象类与接口
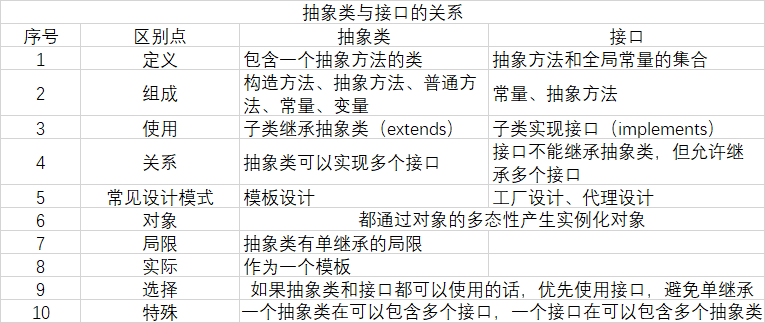
一般可以运用抽象类和接口解决的尽量用接口
抽象类中可以定义多个内部抽象类,接口可以定义多个内部接口。



