【hust数据结构】huffman树及编码/解码实验
做了好久...
最后调出来还是蛮有成就感的,总结一个博客出来吧2333
要求

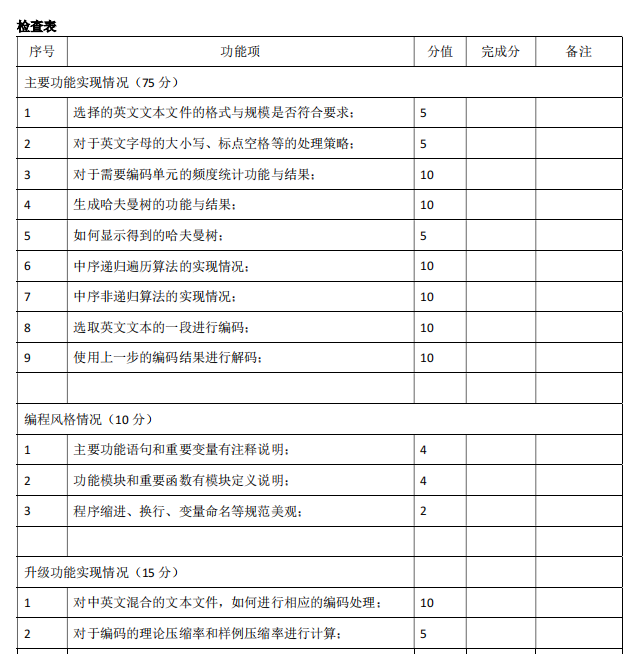
一些细节
中文字符的处理
在头文件之后写:
#ifdef _WIN32 #include<windows.h>//用来修控制台中文乱码 #endif
在main函数的最前面写:
#ifdef _WIN32 SetConsoleOutputCP(65001);//用来修控制台的中文乱码 #endif
就可以改成65001编码了,能正确处理中文字符。
中文字符占三个char,英文字符还是一个char。
map<struct,int>:需重载struct的运算符
以struct为下标的map,需要重载运算符。
struct source_data{ char ch1,ch2,ch3; bool operator < (const source_data &a) const{ return ch1>a.ch1;//升序 } }; map<source_data,int>nod;//存储字符对应的编号
freopen读入多个文件
在freopen读完之后,写:
fclose(stdin);
cin.clear();
就可以把输入流给掰回控制台,也可以继续读入下一个。
vector:当任意长的数组用
「LuoguP3369」 【模板】普通平衡树 (用vector乱搞平衡树
还有vec.push_back(x),可以在vec末尾加数。
指针的优先队列
1 struct NODE{ 2 NODE *lson,*rson;//lson:0 rson:1 3 NODE *fa;//父节点 4 int node=0,tim;//当前点的编号 & 出现次数之和 5 source_data raw; 6 int huff;//huffman编码 7 }; 8 struct cmp{ 9 bool operator() (const NODE *a,const NODE *b){ 10 return (a->tim) > (b->tim); 11 } 12 }; 13 priority_queue<NODE *,vector<NODE*>,cmp>q;
遍历map:iterator的使用
指针置空:赋初值nullptr
1 map<source_data,int>::reverse_iterator iter; 2 for(iter = nod.rbegin();iter != nod.rend();iter++){ 3 source_data c = iter->first; 4 NODE *p = (NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE)); 5 p->lson=p->rson=nullptr;//之后就能直接if(p->lson)了 6 }
总之感觉这个两百来行的代码,学到了很多东西!
代码
1 /* 2 author : qwerta 3 date : 2021.11.04 - 11.11 4 */ 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include<iostream> 7 #include<cstdio> 8 #include<cstring> 9 #include<cstdlib> 10 #include<queue> 11 #include<stack> 12 #include<map> 13 #include<vector> 14 #ifdef _WIN32 15 #include<windows.h>//用来修控制台中文乱码 16 #endif 17 using namespace std; 18 const int ALL_CHARACTER=1000+3;//总字符数 19 struct source_data{ 20 char ch1,ch2,ch3; 21 bool operator < (const source_data &a) const{ 22 return ch1>a.ch1;//升序 23 } 24 }; 25 map<source_data,int>nod;//存储字符对应的编号 26 int cont[ALL_CHARACTER];//记录编号为i的字符的出现次数 27 int tot_char=0;//总字符数,从1开始存 28 int tot_node=0;//总节点数 29 void read_source_txt() 30 { 31 freopen("Sample.txt","r",stdin); 32 char ch; 33 while((ch=getchar())!=EOF) 34 { 35 if(ch>=0)//英文 36 { 37 if(nod.find((source_data){ch,' ',' '})==nod.end()) 38 { 39 nod[((source_data){ch,' ',' '})]=++tot_char; 40 cont[tot_char]=1; 41 } 42 else cont[nod[((source_data){ch,' ',' '})]]++; 43 //putchar(ch); 44 } 45 else 46 { 47 //printf("汉字get\n"); 48 char ch0=getchar(),ch00=getchar(); 49 if(nod.find((source_data){ch,ch0,ch00})==nod.end()) 50 { 51 nod[((source_data){ch,ch0,ch00})]=++tot_char; 52 cont[tot_char]=1; 53 } 54 else cont[nod[((source_data){ch,ch0,ch00})]]++; 55 //putchar(ch);putchar(ch0);putchar(ch00); 56 //putchar(' '); 57 } 58 } 59 fclose(stdin); 60 cin.clear(); 61 //printf("\nread finished\n"); 62 return; 63 } 64 struct NODE{ 65 NODE *lson,*rson;//lson:0 rson:1 66 NODE *fa;//父节点 67 int node=0,tim;//当前点的编号 & 出现次数之和 68 source_data raw; 69 int huff;//huffman编码 70 }; 71 struct cmp{ 72 bool operator() (const NODE *a,const NODE *b){ 73 return (a->tim) > (b->tim); 74 } 75 }; 76 priority_queue<NODE *,vector<NODE*>,cmp>q; 77 NODE *s;//树根root 78 void huffman_build() 79 { 80 map<source_data,int>::reverse_iterator iter; 81 int i; 82 for(iter = nod.rbegin(),i=1;iter != nod.rend();iter++,++i){ 83 source_data c = iter->first; 84 NODE *p = (NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE)); 85 p->node=i; 86 p->tim=cont[nod[c]]; 87 p->lson=p->rson=nullptr; 88 p->raw = c; 89 q.push(p); 90 } 91 tot_node=tot_char; 92 while(q.size()>1){ 93 NODE *p = (NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE)); 94 NODE *c1=q.top();q.pop(); 95 NODE *c2=q.top();q.pop(); 96 p->lson=c1;p->rson=c2;//注意 97 c1->fa = c2->fa = p; 98 p->tim=(c1->tim) + (c2->tim); 99 p->node=++tot_node; 100 p->raw.ch1=0; 101 q.push(p); 102 } 103 s=q.top();q.pop(); 104 //printf("huffman_build finished\n"); 105 return; 106 } 107 int huffman_code[ALL_CHARACTER];//存编号为i的字符的huffman编码 108 void huffman_dfs(NODE *c,int now)//now:储存当前huffman编码(最高位之前,比实际huffman编码多加了一位1) 109 { 110 if(c->lson)huffman_dfs(c->lson,(now<<1)); 111 // 112 if((c->raw).ch1)//到叶子节点了 113 { 114 huffman_code[nod[c->raw]]=c->huff=now; 115 //cout<<" "<<now<<endl; 116 return; 117 } 118 // 119 if(c->rson)huffman_dfs(c->rson,((now<<1)|1)); 120 return; 121 } 122 stack<NODE *>st; 123 void huffman_with_stack()//非递归遍历huffman树 124 { 125 st.push(s); 126 s->huff=1; 127 while(!st.empty()){ 128 NODE *c=st.top();st.pop(); 129 if(c->lson){ 130 (c->lson)->huff = (c->huff)<<1; 131 st.push(c->lson); 132 } 133 // 134 if((c->raw).ch1)huffman_code[nod[c->raw]]=c->huff; 135 if(c->rson){ 136 (c->rson)->huff = ((c->huff)<<1)|1; 137 st.push(c->rson); 138 } 139 } 140 return; 141 } 142 void print_char(source_data c){ 143 if(c.ch1>0)putchar(c.ch1); 144 else{putchar(c.ch1);putchar(c.ch2);putchar(c.ch3);} 145 return; 146 } 147 void print_huffman(int x){ 148 //printf("\n print %d now :",x); 149 bool ans[103]; 150 int tot=0; 151 for(;(1<<tot)<=x;++tot){ 152 if((x>>tot)&1)ans[tot]=1; 153 else ans[tot]=0; 154 } 155 for(int i=tot-2;i>=0;--i) 156 printf("%d",ans[i]); 157 return; 158 } 159 void print_tim(){ 160 printf("\n------------------字符出现次数-------------------\n\n"); 161 map<source_data,int>::reverse_iterator iter; 162 int tot=0; 163 for(iter = nod.rbegin();iter != nod.rend();iter++){ 164 source_data c = iter->first; 165 printf("--%d--//",tot++); 166 print_char(c); 167 printf("//,次数:%d",cont[nod[c]]); 168 putchar('\n'); 169 } 170 return; 171 } 172 void print_tree_dfs(NODE *c)//采用递归遍历该huffman树 173 { 174 if(c->lson)print_tree_dfs(c->lson); 175 if(c->rson)print_tree_dfs(c->rson); 176 printf("序号:%d--W%d--",c->node,c->tim); 177 if(c!=s)printf("//P%d",c->fa->node);else printf("//P0"); 178 if(c->lson)printf("//L%d",c->lson->node);else printf("//L0"); 179 if(c->lson)printf("//R%d//",c->rson->node);else printf("//R0//"); 180 if((c->raw).ch1){ 181 print_char(c->raw); 182 printf("==>"); 183 print_huffman(c->huff); 184 } 185 putchar('\n'); 186 return; 187 } 188 vector<char>txt;//="In the animation industry, cartoon videos are produced from hand drawings of expert animators using a complex and precise procedure. To draw each frame of an animation video manually would consume tremendous time, thus leading to a prohibitively high cost. In practice, the animation producers usually replicate one drawing two or three times to reduce the cost, which results in the actual low frame rate of animation videos. Therefore, it is highly desirable to develop computational algorithms to interpolate the intermediate animation frames automatically.In recent years, video interpolation has made great progress on natural videos. However, in animations, existing video interpolation methods are not able to produce satisfying in-between frames. An example from the film Children Who Chase Lost Voices is illustrated in Figure 1, where the current state-of-the-art methods fail to generate a piece of complete luggage due to the incorrect motion estimation, which is shown in the lower-left corner of the image. The challenges here stem from the two unique characteristics of animation videos: 1) First, cartoon images consist of explicit sketches and lines, which split the image into segments of smooth color pieces. Pixels in one segment are similar, which yields insufficient textures to match the corresponding pixels between two frames and hence increases the difficulty to predict accurate motions. 2) Second, cartoon animations use exaggerated expressions in pursuit of artistic effects, which result in non-linear and extremely large motions between adjacent frames. Two typical cases are depicted in Figure 2 (a) and (b) which illustrate these challenges respectively. Due to these difficulties mentioned above, video interpolation in animations remains a challenging task.";//待编码文件 189 vector<bool>vec;//存编码后的字符串 190 void read_target_txt() 191 { 192 freopen("file.txt","r",stdin); 193 char ch; 194 while((ch=getchar())!=EOF) 195 { 196 txt.push_back(ch); 197 } 198 fclose(stdin); 199 cin.clear(); 200 return; 201 } 202 void huffman_encode(){ 203 for(int i=0;i<txt.size();++i){ 204 int x; 205 if(txt[i]>0){ 206 x = huffman_code[nod[(source_data){txt[i],' ',' '}]]; 207 } 208 else{ 209 x = huffman_code[nod[(source_data){txt[i],txt[i+1],txt[i+2]}]]; 210 i+=2; 211 } 212 bool ans[103]; 213 int tot=0; 214 for(;(1<<tot)<=x;++tot){ 215 if((x>>tot)&1)ans[tot]=1; 216 else ans[tot]=0; 217 } 218 for(int i=tot-2;i>=0;--i) 219 vec.push_back(ans[i]); 220 } 221 // 222 printf("\n------------------对file.txt编码-------------------\n"); 223 printf("\nvec.size : %d \n",vec.size()); 224 printf("txt encoded : "); 225 for(int i=0;i<vec.size();++i) 226 cout<<vec[i]; 227 printf("\n\n"); 228 return; 229 } 230 void huffman_decode(){ 231 printf("vec decoded : "); 232 NODE *p = s; 233 for(int i=0;i<vec.size();++i){ 234 if(!vec[i]){ 235 p = p->lson; 236 } 237 else{ 238 p = p->rson; 239 } 240 // 241 if((p->raw).ch1){ 242 print_char(p->raw); 243 p = s; 244 } 245 } 246 return; 247 } 248 void print_compress_rate(){ 249 double rate=(double)(vec.size())/(8*txt.size()); 250 printf("\nCompress rate for the txt : \n%.6f",rate); 251 return; 252 } 253 int main() 254 { 255 #ifdef _WIN32 256 SetConsoleOutputCP(65001);//用来修控制台的中文乱码 257 #endif 258 // 259 read_source_txt(); 260 huffman_build(); 261 // 262 bool need_dfs = 1; 263 if(need_dfs){ 264 huffman_dfs(s,1);//递归遍历 265 } 266 else{ 267 huffman_with_stack();//非递归遍历 268 } 269 // 270 print_tim(); 271 putchar('\n'); 272 printf("\n------------------递归输出字符huffman编码-------------------\n\n"); 273 print_tree_dfs(s); 274 // 275 bool need_encode = 1; 276 if(need_encode){ 277 read_target_txt(); 278 huffman_encode(); 279 huffman_decode(); 280 print_compress_rate(); 281 } 282 return 0; 283 }


