CUDA学习5 常量内存与纹理内存
1.常量内存
当线程束中的所有线程都访问相同的只读数据时,使用常量内存将获得额外的性能提升。
常量内存大小限制为64k。
以下摘自hackairM的博文CUDA学习--内存处理之常量内存(4)。
常量内存其实只是全局内存的一种虚拟地址形式,并没有特殊保留的常量内存块。常量内存有两个特性,一个是高速缓存,另一个是它支持将单个值广播到线程束中的每个线程。但要注意的是,对于那些数据不太集中或者数据重用率不高的内存访问,尽量不要使用常量内存。
当常量内存将数据分配或广播到线程束中的每个线程时(注意,实际上硬件会将单次内存读取操作广播到半个线程束),广播能够在单个周期内发生,因此这个特性是非常有用的。虽然当所有16个线程都读取相同地址时,这个功能可以极大提高性能,但当所有16个线程分别读取不同的地址时,它实际上会降低性能。如果半个线程束中的所有16个线程需要访问常量内存中的不同数据,那么这个16次不同的读取操作会被串行化,从而需要16倍的时间来发出请求。但如果从全局内存中读取,那么这些请求就会同时发出。这种情况下,从常量内存读取就会慢于从全局内存中读取。
需要注意的是,当我们声明一个内核常量的时候,在编译器将CUDA C代码转换成PTX汇编代码时会用字面值(0x55555555)直接替换常量值(data)的地址。
const int data = 0x55555555; int d = data; //此时data会直接编译为字面值0x55555555但当我们声明的是一个常量数组时,编译器在将C代码转换成PTX汇编代码时将会使用数组地址在汇编代码中。
const int data[3] = {0x11111111, 0x22222222, 0x33333333}; int d = data[1]; //此时data[1]会被编译为data[1]的地址这时,在费米(计算能力为2.x的硬件)架构的设备上,全局内存借助一级缓存也能达到与常量内存相同的访问速度。只有在计算能力为1.x的设备上,由于全局内存没有用到缓存技术,此时使用常量内存才会获得明显的性能提升。
下例中使用常量内存性能并未获得提升(Time to generate与不使用常量内存接近)。
运行《CUDA By Example》第六章示例有约8%的提升(4.8ms到5.2ms,小样本)。
#include <windows.h> #include <iostream> __constant__ float dev_input[5*5*24*24]; //57600<64000 __global__ void MaxPool2d(const int height, const int pooled_height, float* top_data) { int x = blockIdx.x; int y = blockIdx.y; int dx = gridDim.x; int tx = threadIdx.x; int ty = threadIdx.y; int dtx = blockDim.x; int dty = blockDim.y; float s = -10000.0; int index2 = y*dx*dtx*dty + x*dtx*dty + ty*dtx + tx; int index = y*dx*height*height + x*height*height + ty*pooled_height*height + tx*pooled_height; for (int u = 0; u < pooled_height && (u + pooled_height*ty)<height; ++u) for (int v = 0; v < pooled_height && (v + pooled_height*tx)<height; ++v) if (*(dev_input + index + u*height + v)>s) s = *(dev_input + index + u*height + v); *(top_data + index2) = s; } int main() { cudaEvent_t start, stop; cudaEventCreate(&start); cudaEventCreate(&stop); const int N = 5, M = 5, H = 24, W = 24, D = 2; const int PH = H / D + H % D; int image_size = N*M*H*W*sizeof(float); int out_size = N*M*PH*PH*sizeof(float); float mul_by = 0.01; float *input, *output, *dev_output; input = new float[image_size]; output = new float[out_size]; for (int i = 0; i<N*M*H*W; i++) *(input + i) = i*mul_by; cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_output, out_size); //cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_input, image_size); cudaMemcpyToSymbol(dev_input, input, image_size); dim3 grid(M, N); dim3 threads(PH, PH); DWORD start_time = GetTickCount(); cudaEventRecord(start,0); MaxPool2d << <grid, threads >> >( H, D, dev_output); cudaMemcpy(output, dev_output, out_size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); DWORD end_time = GetTickCount(); cudaEventRecord(stop, 0); cudaEventSynchronize(stop); float elapsedTime; cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsedTime, start, stop); std::cout << "Time to generate: "<<elapsedTime<< "ms\n"; cudaEventDestroy(start); cudaEventDestroy(stop); std::cout << "Cost: " << end_time - start_time << "ms." << std::endl; for (int i = 0; i<10; i++) std::cout << *(output + i) << std::endl; //cudaFree(dev_input); cudaFree(dev_output); delete[] output; delete[] input; system("pause"); } /* Time to generate: 0.071552ms Cost: 0ms. 0.25 0.27 0.29 0.31 0.33 0.35 0.37 0.39 0.41 0.43 */
2.纹理内存
和常量内存一样,纹理内存是另一种类型的只读内存,在特定的访问模式中(以下例子并非这种特定的访问模式),纹理内存同样能够提升性能。
介绍摘自《GPU高性能编程CUDA实战》。
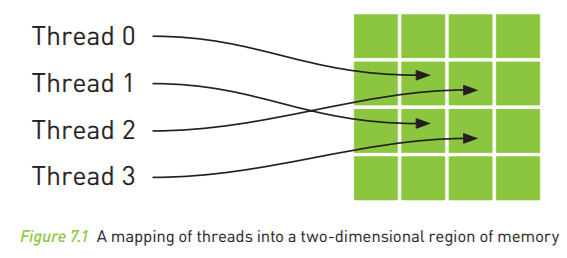
纹理内存缓存在芯片上,因此在某些情况中,它能够减少对内存的请求并提供更高效的内存带宽。纹理缓存是专门为那些在内存访问模式中存在大量空间局部性(Spatial Locality)的图形应用程序而设计的。在某个计算应用程序中,这意味着一个线程读取的位置可能与邻近线程的读取位置“非常接近”,如下图所示。
从数学的角度,上图中的4个地址并非连续的,在一般的CPU缓存中,这些地址将不会缓存。但由于GPU纹理缓存是专门为了加速这种访问模式而设计的,因此如果在这种情况中使用纹理内存而不是全局内存,那么将会获得性能的提升。
#include "device_launch_parameters.h" #include "cuda_runtime.h" #include <iostream> #define max(a,b) (a>b?a:b) texture<float> t_input; __global__ void MaxPool2d(const int height, const int pooled_height, float* top_data) { int x = blockIdx.x; int y = blockIdx.y; int dx = gridDim.x; int tx = threadIdx.x; int ty = threadIdx.y; int dtx = blockDim.x; int dty = blockDim.y; float s = -10000.0; float a1, a2, a3, a4, a12, a34; int index2 = y*dx*dtx*dty + x*dtx*dty + ty*dtx + tx; int index = y*dx*height*height + x*height*height + ty*pooled_height*height + tx*pooled_height; int index3 = 0; bool b1 = 1 + 2 * ty == height; bool b2 = 1 + 2 * tx == height; if (b1&&b2) { a1 = tex1Dfetch(t_input, index ); s = max(a1, s); } if ( !b2) { a1 = tex1Dfetch(t_input, index ); a2 = tex1Dfetch(t_input, index + 1); a12 = max(a1,a2); s = max(a12, s); index3 = height + 1; } if (!b1) { a3 = tex1Dfetch(t_input, index + index3); a4 = tex1Dfetch(t_input, index + height); a34 = max(a3, a4); s = max(a34, s); } *(top_data + index2) = s; } int main() { cudaEvent_t start, stop; cudaEventCreate(&start); cudaEventCreate(&stop); const int N = 5, M = 5, H = 25, W = 25, D = 2; const int PH = H / D + H % D; const int image_size = N*M*H*W*sizeof(float); const int out_size = N*M*PH*PH*sizeof(float); float mul_by = 0.01; float *input, *output, *dev_input, *dev_output; input = new float[image_size]; output = new float[out_size]; for (int i = 0; i<N*M*H*W; i++) *(input + i) = i*mul_by; cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_output, out_size); cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_input, image_size); cudaBindTexture(NULL, t_input, dev_input, image_size); cudaMemcpy(dev_input, input, image_size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); dim3 grid(M, N); dim3 threads(PH, PH); cudaEventRecord(start, 0); MaxPool2d <<<grid, threads >>>(H, D, dev_output); cudaMemcpy(output, dev_output, out_size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); cudaEventRecord(stop, 0); cudaEventSynchronize(stop); float elapsedTime; cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsedTime, start, stop); std::cout << "Time to generate: " << elapsedTime << "ms\n"; cudaEventDestroy(start); cudaEventDestroy(stop); for (int i = 0; i<10; i++) std::cout << *(output + i) << std::endl; cudaFree(dev_input); cudaFree(dev_output); cudaUnbindTexture(t_input); delete[] output; delete[] input; system("pause"); } /* Time to generate: 0.128448ms */