Logistic回归
逻辑斯蒂回归
对于目标值是离散变量的两类分类问题,假设目标值为{0,1},所以先改变模型使其预测值在[0,1]之间,我们选择这样一个函数:
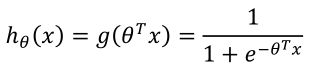
分类概率值:
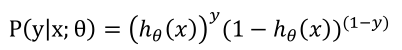
似然函数:
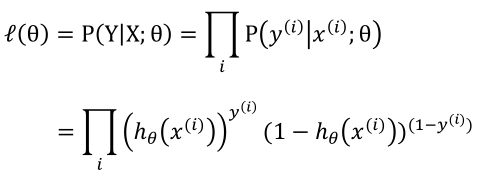
对数似然函数:
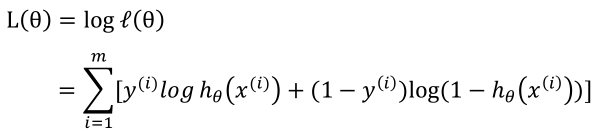
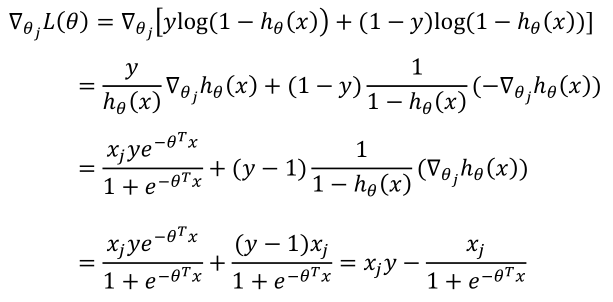

更新规则:
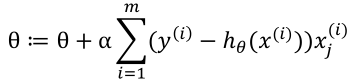
1 # coding:utf-8 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import numpy as np 4 5 def dataN(length):#生成数据 6 x = np.ones(shape = (length,3)) 7 y = np.zeros(length) 8 for i in np.arange(0,length/100,0.02): 9 x[100*i][1]=i 10 x[100*i][2]=i + 1 + np.random.uniform(0,1.2) 11 y[100*i]=1 12 x[100*i+1][1]=i+0.01 13 x[100*i+1][2]=i+0.01 + np.random.uniform(0,1.2) 14 return np.mat(x),np.mat(y).T 15 16 def sigmoid(x): #simoid 函数 17 return 1.0/(1+np.exp(-x)) 18 19 def alphA(x,y): #选取前20次迭代cost最小的alpha 20 c=float("inf") 21 for k in range(1,1000): 22 a=1.0/k**3 23 f=gD(x,y,20,a)[1][-1] 24 if f>c: 25 break 26 c=f 27 alpha=a 28 return alpha 29 30 def gD(x,y,iter,alpha):#梯度下降 31 theta=np.ones((3,1)) 32 33 cost=[] 34 for i in range(iter): 35 hypothesis =sigmoid(np.dot(x,theta)) 36 loss = hypothesis-y 37 cost.append(np.sum(loss[0]**2)) 38 gradient = np.dot(x.transpose(),loss) 39 theta = theta -alpha * gradient 40 return theta,cost 41 42 def tesT(theta, x, y):#准确率 43 length=len(x) 44 count=0 45 for i in xrange(length): 46 predict = sigmoid(x[i, :] * theta)[0, 0] > 0.5 47 if predict == bool(y[i, 0]): 48 count+= 1 49 accuracy = float(count)/length 50 return accuracy 51 52 length=200 53 iter=1000 54 x,y=dataN(length) 55 theta,cost=gD(x,y,iter,alphA(x,y)) 56 print tesT(theta, x, y) #0.92 57 58 plt.figure(1) 59 plt.plot(range(iter),cost) 60 plt.figure(2) 61 color=['or','ob'] 62 for i in xrange(length): 63 plt.plot(x[i, 1], x[i, 2],color[int(y[i])]) 64 theta = theta.getA() 65 plt.plot([0,length/100],[-theta[0],-theta[0]-theta[1]*length/100]/theta[2]) 66 plt.show()






