先贴出自己写的测试代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | int* M2(int* p){ return p+1;}int M(int a, char b){ int* pp = M2(&a); return *pp;}int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]){ int e=0; int d = M(3,'c'); getchar(); return 0;} |
然后来一层一层的分析:
调用函数Main
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | 008B1030 push ebp // 将ebp的值压入栈 008B1031 mov ebp,esp // 将esp的值赋值给ebp008B1033 sub esp,8 // esp-8,为了空出变量e,d的空间 int e=0;008B1036 mov dword ptr [e],0 // 将e的值设置为0 int d = M(3,'c');008B103D push 63h // 将'c'压入栈008B103F push 3 // 将整数3压入栈008B1041 call M (8B1010h) // 调用函数M |
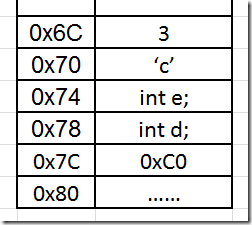
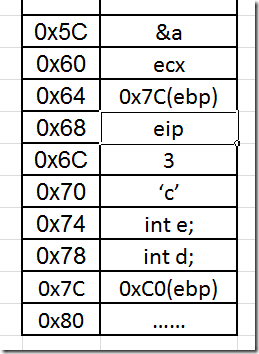
此时函数堆栈的情况大致如下:
调用函数M
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | int M(int a, char b){01391010 push ebp // 将ebp的值压入栈 01391011 mov ebp,esp // 将esp的值赋值给ebp01391013 push ecx // ecx压入栈 int* pp = M2(&a);01391014 lea eax,[a] // 将变量a的地址赋给eax01391017 push eax // 将eax压入栈01391018 call M2 (1391000h) // 调用函数M2() |
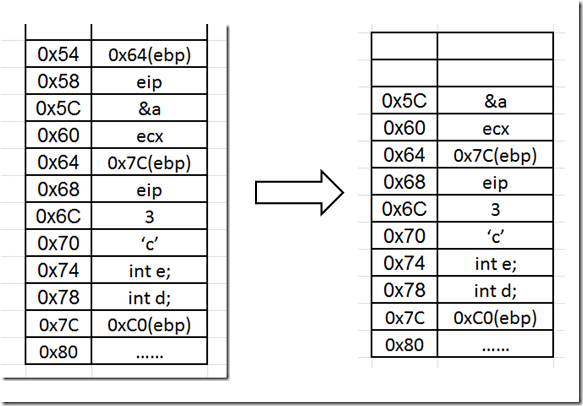
调用函数M2
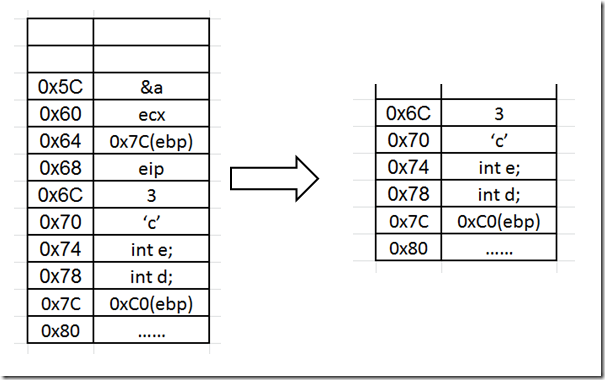
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | int* M2(int* p){01391000 push ebp // ebp入栈 01391001 mov ebp,esp // ebp = esp return p+1;01391003 mov eax,dword ptr [p] // eax = p;01391006 add eax,4 // eax+=4;}01391009 pop ebp // 将栈顶的值弹出给ebp0139100A ret // 返回 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | 01391018 call M2 (1391000h) // 调用函数M2()0139101D add esp,4 // esp+=4 01391020 mov dword ptr [pp],eax // eax的值赋给pp return *pp;01391023 mov ecx,dword ptr [pp] // 将pp指向的地址赋值给ecx01391026 mov eax,dword ptr [ecx] // 将ecs指向的地址赋值为eax}01391028 mov esp,ebp 0139102A pop ebp 0139102B ret |




【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步