Spring MVC学习
三层架构是 web 程序的纵向结构,是 web 程序的身体,而MVC 模式只存在于三层架构的展现层,是 web 程序展示时相互沟通的一种好的方式。
Spring MVC 使我们可以简单地,开发灵活且松耦合的Web项目。
在Servlet 2.5及以下,servlet类需要在web.xml文件中,配置<servlet>元素,才能访问这个Servlet。
但在Spring MVC + Servlet 3.0下,通过实现WebApplicationInitializer 接口,便可实现等同web.xml的配置,做到无web.xml。然后可以在WebApplicationInitializer实现类中,通过Spring MVC的 DispatcherServlet配置Servlet。
下面用Maven构建一个,基于注解和Java配置的,无web.xml配置的Spring MVC工程:
1、构建Maven项目,pom.xml文件如下:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.qfedu</groupId> <artifactId>MySpringMVC</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <properties> <!-- Generic properties --> <java.version>1.8</java.version> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <!-- build plugins --> <compiler.version>3.6.1</compiler.version> <war.version>3.1.0</war.version> <!-- Web --> <jsp.version>2.2</jsp.version> <jstl.version>1.2</jstl.version> <servlet.version>3.1.0</servlet.version> <!-- Spring --> <spring-framework.version>4.3.9.RELEASE</spring-framework.version> <!-- Logging --> <logback.version>1.2.3</logback.version> <slf4j.version>1.7.25</slf4j.version> </properties> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>${compiler.version}</version> <configuration> <source>${java.version}</source> <target>${java.version}</target> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> <version>${war.version}</version> <configuration> <failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>javax</groupId> <artifactId>javaee-web-api</artifactId> <version>7.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <!-- Spring MVC --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>${spring-framework.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- Other web dependency --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>${jstl.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>${servlet.version}</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId> <version>${jsp.version}</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <!-- Spring and Transactions --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId> <version>${spring-framework.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- 使用 SLF4J 和 LogBack 作为日志 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> <version>${slf4j.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId> <version>${slf4j.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> <version>${logback.version}</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> <artifactId>logback-core</artifactId> <version>${logback.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> <artifactId>logback-access</artifactId> <version>${logback.version}</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
2、在Maven的src / main / resources 目录下,新建logback.xml文件,用来配置日志:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <configuration sacn="true" scanPeriod="1 seconds"> <contextListener class="ch.qos.logback.classic.jul.LevelChangePropagator"> <resetJUL>true</resetJUL> </contextListener> <jmxConfiguration /> <appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <encoder> <pattern>logbak: %d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern> </encoder> </appender> <!-- 将org.springframework.web包下的类的日志级别, 设置为DEBUG, 可以看到Web开发中的, 更详细的错误信息 --> <logger name="org.springframework.web" level="DEBUG" /> <root level="info"> <appender-ref ref="console" /> </root> </configuration>
3、依然在 src / main / resources 下,建立 views 目录,然后在 views 目录下,新建 index.jsp 页面(内容随意) —— 页面没有放在Maven标准的 src /main / webapp / WEB-INF 下,这里的目的是,让大家熟悉 Spring Boot 的页面放置习惯,即放在 src / main / resources 目录下。(在Eclipse,用模板创建 jsp 页面时,不知道为什么,文件自动被移到了 webapp 目录下,因此如果是这样,需要再移回来)。
4、Spring MVC 的配置类:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc; import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver; import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView; @Configuration @EnableWebMvc @ComponentScan("com.qfedu.MySpringMVC") public class MyMvcConfig { @Bean public InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver() { InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver(); viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/classes/views/"); viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp"); viewResolver.setViewClass(JstlView.class); return viewResolver; } }
ViewResolver 用于映射开发时的路径,与视图的真实位置。因此,对于开发路径 src / main / resource / views,ViewResolver 需要将路径前缀配置为 / WEB-INF / classes / views / ,因为运行时页面会自动编译到该目录下。如图:
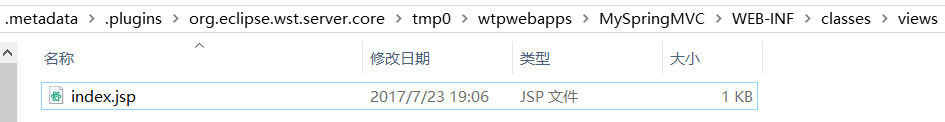
5、Web —— Servlet配置:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.config; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRegistration.Dynamic; import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer; import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext; import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet; //实现了WebApplicationInitializer接口, 将会被启动容器的类SpringServletContainerInitializer获取到并完成配置, 就和web.xml一样 public class WebInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer { @Override public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException { //新建WebApplicationContext,并注册配置类(注册配置类中返回的ViewResolver bean),关联当前的ServletContext AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); context.register(MyMvcConfig.class); context.setServletContext(servletContext); //DispatcherServlet:前端控制器 //用WebApplicationContext新建Spring MVC的 DispatcherServlet,然后注册并返回Servlet注册对象 Dynamic servlet = servletContext.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet(context)); //设置DispatcherServlet的Mapping和LoadOnStartUp次序 servlet.addMapping("/"); servlet.setLoadOnStartup(1); } }
6、一个基本的控制器:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller public class HomeContoller { @RequestMapping("/index") public String index() { return "index"; } }
最后部署到服务器上,即可访问 http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/index。
以上步骤即可完成一个比较 基本的Spring MVC 项目。
Spring MVC 的常用注解:
1、@Controller:将类声明为 Bean,并作为 Spring MVC 的 Controller,Dispatcher Servlet 会根据配置类自动扫描 Controller,并将 Web 请求映射到注解了@RequestMapping 的类、方法上。值得注意的是,在声明普通 Bean 时,使用@Component、@Service、@Repository、@Controller 都是一样的(这一点可以查看 Spring 的源码);但是在声明 Spring MVC 的 Controller 时,只能使用 @Controller。
2、@RequestMapping:可注解在类和方法上,用来将 Web 请求(访问路径和参数)和处理类,以及方法进行映射。注解在方法上的路径会继承类上的路径;可选择 Servlet 的 request 和 response 作为方法的参数;通过 produces 参数,对 request 和 response 的 contentType(包括字符集 charset)进行配置。
3、@ResponseBody:支持将返回值放在 response 内,而不是返回一个页面(即通过 response 返回一些数据,这一点对基于 Ajax 的程序很友好)。可注解在返回值之前,或方法之上。
4、@RequestBody:允许请求的参数在 request 内,通过 POST 方式请求。注解在参数前,则参数为请求体内对应的数据。
5、@PathVariable:用来接收路径参数,如 / news / 001 的号数 001 可作为参数,而不是请求参数 /new ? id = 001。
6、@RestController:是一个组合注解,组合了@Controller 和@ResponseBody,即这是一个只用于数据交互的 Controller(所有的方法都返回数据到 response,而不是页面)。
测试用例:
添加 Jackson Dataformat XML 的依赖,以便对象和 json 或 xml 之间的转换(目前可能由于阿里云镜像的原因,添加了这个依赖的比较新的版本之后,程序就卵了,如果这样,就换个旧点的版本):
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
或者只使用 Jackson 对 json 的支持(即上面的依赖包含下面的依赖):
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
实体类 Entity —— POJO:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.domain; public class DemoEntity { private Long id; private String name; public DemoEntity() { //必须有一个空构造函数,作为 default,不然 Spring MVC 无法自动将对象转换成 json 格式 } public DemoEntity(Long id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } // 省略getter and setter }
普通控制器 Controller:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller @RequestMapping("/foo") public class FooController { // 具体的方法,下面分别介绍 }
上面的控制器的方法:
演示@RequestMapping 和@ResponseBody:
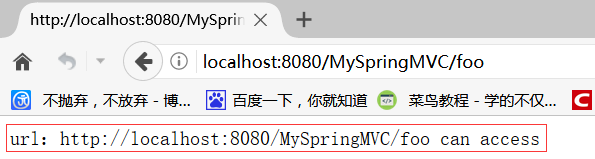
@RequestMapping(produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8") public @ResponseBody String index(HttpServletRequest request) { return "url:" + request.getRequestURL() + " can access"; }
@RequestMapping 未标注路径,则继承类路径 /foo,而返回值有@ResponseBody,方法根据 produces 的设置直接返回 contentType="text/plain; charset=UTF-8" 的数据。直接访问 http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/foo,将浏览一个 plain 的 html 页面,如下:
演示指定方法路径的@RequestMapping,以及获取 request 参数(访问结果如:http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/foo/requestParam?id=1):
@RequestMapping(value = "/requestParam", produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8") public @ResponseBody String DemoRequestParam(Long id) { return "id:" + id; }
Spring 很爽的地方是,会自动拆装,而且要什么给什么(包括实体类和Spring内置的类,这个功能使得处理表单提交变得更简单):
结果如:http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/foo/obj?id=1&name=wangyunfei。
@RequestMapping(value = "/obj", produces = "text/plain;charsetF-8") public @ResponseBody String DemoRequestObj(DemoEntity obj) { return "id:" + obj.getId() + ",name:" + obj.getName(); }
也可以将不同的路径,映射到相同的方法(即 value 为 String 的数组,结果如:http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/foo/name2,也可以访问 name1):
@RequestMapping(value = {"name1", "name2"}, produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8")
public @ResponseBody String DemoMutilplePath(HttpServletRequest request) {
return "url:" + request.getRequestURL() + " can access";
}
演示@PathVariable(注意与上面的地址的区别,结果如:http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/foo/pathvar/paramValue):
@RequestMapping(value = "/pathvar/{param}", produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8")
public @ResponseBody String demoPathVar(@PathVariable String param) {
return "param:" + param;
}
组合了@ResponseBody(不用为每个返回数据的方法注解) 的控制器 RestController:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/rest") public class DemoRestController { // 具体的方法,下面分别介绍 }
上面控制器的方法:
演示返回 json 数据:
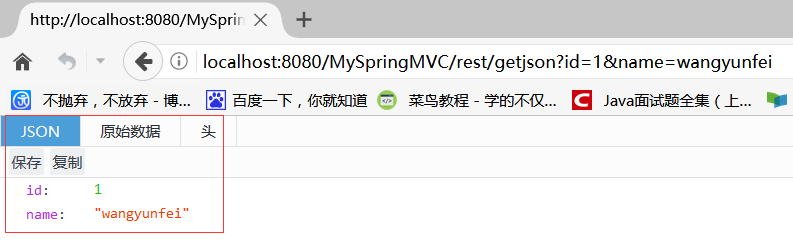
@RequestMapping(value = "/getjson", produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8") //MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE public DemoEntity getJson(DemoEntity obj) { return obj; }
contentType 为 json。访问如:http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/rest/getjson?id=1&name=wangyunfei:
演示返回 xml 数据:
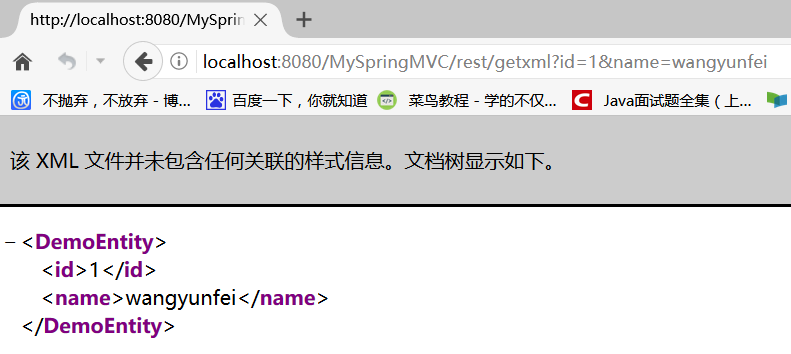
@RequestMapping(value = "getxml", produces = "application/xml;charset=UTF-8") public DemoEntity getXml(DemoEntity obj) { return new DemoEntity(obj.getId(), obj.getName()); }
访问如:http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/rest/getxml?id=1&name=wangyunfei,结果:
Spring MVC 基本配置:
将之前的 Spring MVC 配置类升 一下级,继承 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 类(或者实现 WebMvcConfigurer 接口:Adapter 类是这个接口的实现类),通过重写这个类的一些方法,可以定制一些基本的配置(依然要@EnableWebMvc,开启对 Spring MVC 的支持,否则以下的配置将无效)。
静态资源映射:
若程序的静态文件(如图片等)需要直接访问,或者 html 页面需要访问,可以为配置类重写 addResourceHandlers 方法来实现。
演示用例:
添加静态资源:
在 src / main / resource 下建立 assets 目录,该目录下存放所有的静态资源。再如下图新建一个资源:

配置类:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver; import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView; @Configuration @EnableWebMvc @ComponentScan("com.qfedu.MySpringMVC") public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { @Override public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { // 映射:addResourceHandler方法的参数是对外的访问路径(URI),addResourceLocations方法的参数是文件存放的位置 // URI如果是 '/assets/**',则可以访问映射的assets目录下的多级资源 // 如果是 '/assets/*',则只能访问assets目录,如果有多级目录,也不能访问 registry.addResourceHandler("/assets/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/assets/"); } // 其他配置省略(下同) }
访问如 http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/assets/images/test.jpg:
拦截器设置:
拦截器(Interceptor)会对每一个请求处理的前后,进行相关的业务处理,有点类似于 Servlet 的 Filter。
演示用例:
自定义 Interceptor 由一个实现了 HandlerInterceptor 接口,或者继承了 HandlerInterceptorAdapter 类的、普通的 Bean 实现:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.interceptor; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerInterceptorAdapter; public class DemoInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); request.setAttribute("startTime", startTime); return true; } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { long startTime = (long) request.getAttribute("startTime"); request.removeAttribute("startTime"); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("本次请求处理时间为:" + new Long(endTime - startTime) + "ms"); request.setAttribute("handleTime", endTime - startTime); } }
为配置类重写 addInterceptors 方法,在方法中注册自定义的拦截器:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver; import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView; import com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.interceptor.DemoInterceptor; @Configuration @EnableWebMvc @ComponentScan("com.qfedu.MySpringMVC") public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { @Bean public DemoInterceptor demoInterceptor() { return new DemoInterceptor(); } @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { registry.addInterceptor(demoInterceptor()); } }
访问任意路径,如 http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/index,查看控制台:

@ControllerAdvice:
通过@ControllerAdvice,可以将对控制器的全局配置放在同一个位置,注解了@ControllerAdvice 的类的方法可使用注解@ExcpetionHandler、@InitBinder、@ModelAttribute,这些配置对所有的控制器内注解了@RequestMapping 的方法有效,即全局控制控制器。
1、@ExceptionHandler:用于全局处理控制器里发生的异常。
2、@ModelAttribute:绑定键值对到 Model 里。
3、@InitBinder:用来设置 WebDataBinder —— WebDataBinder 用于选择性的,自动绑定前台请求的参数到 Model 中。
演示用例:
定制 ControllerAdvice:
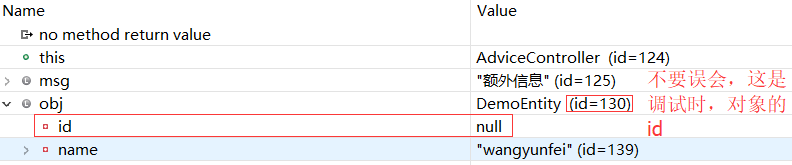
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.advice; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.WebDataBinder; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.InitBinder; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute; import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; // 控制器建言,属于Spring的Bean,下面的建言都是全局的 // Advice for all controllers @ControllerAdvice public class HandlerAdvice { // 其value属性指定捕获的异常类型 // 下面的异常处理,会将异常信息以键值对的形式保存到Model中,并跳转到对应的View @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) public ModelAndView exception(Exception exception, WebRequest request) { ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView("error"); modelAndView.addObject("errorMessage", exception.getMessage()); return modelAndView; } @ModelAttribute public void addAttribute(Model model) { // 由于是在@ControllerAdvice的类中,因此@RequestMapping都能获得下面添加的键值对 // 在@RequestMapping的方法中,注解@ModelAttribute("key")在参数上,即可注入 model.addAttribute("msg", "额外信息"); } @InitBinder public void initBinder(WebDataBinder webDataBinder) { webDataBinder.setDisallowedFields("id"); // 过滤掉request的id属性,然后WebDataBinder自动将request绑定到Model中 } }
演示控制器(直接抛异常):
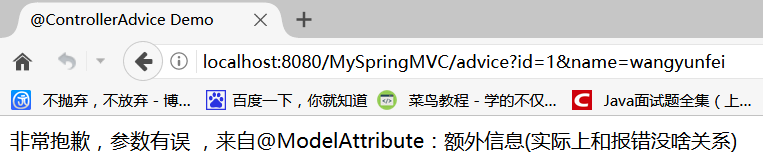
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.domain.DemoEntity; @Controller public class AdviceController { @RequestMapping("/advice") public String getSomething(@ModelAttribute("msg") String msg, DemoEntity obj) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("非常抱歉,参数有误 ,来自@ModelAttribute:" + msg + "(实际上和报错没啥关系)"); } }
在 src / main / resource / views 目录下,新建 error.jsp:
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>@ControllerAdvice Demo</title> </head> <body> ${ errorMessage } </body> </html>
访问 http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/advice?id=1&name=wangyunfei:
在对应的@RequestMapping 的方法中,打断点调试启动再访问(可以看到 request 给的 obj 对象,已经过滤掉了 id 属性):
其他配置:
1、快捷的 ViewController:
前面使用@RequestMapping 配置页面跳转的时候,存在着无任何业务处理,只是简单的页面跳转,如:
@Controller public class HomeController { @RequestMapping("/index") public String index() { return "index"; // viewName } }
通常在实际开发中,会涉及到大量这样的情况,如果都这样写则会很麻烦。简化配置:可以在配置类中重写 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 的 addViewControllers 方法,直接统一注册 viewController:
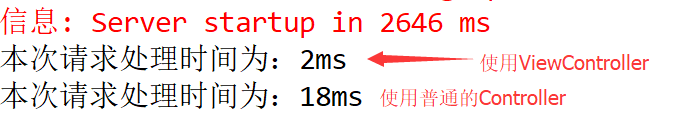
@Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/index").setViewName("index"); }
这样一来,代码将会更简洁,更加容易管理,而且程序因此效率更高:
2、路径匹配参数配置:
在 Spring MVC 中,默认情况下,如果路径末尾的参数带 "." 的话,如使用之前的@RequestMapping:localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/foo/pathvar/xx.yy,那么 "." 以及后缀都会被忽略掉:
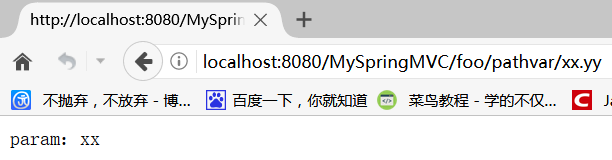
重写之前配置类的 configurePathMatch 方法:
@Override public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) { // 当匹配到后缀时,是否使用后缀。如果是enabled,例如匹配为 /users.* ,则会映射为 /users configurer.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(true); // 默认为true:enabled }
现在后缀将不会被忽略:

在开发中,更多基本配置请查看 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 或 WebMvcConfigurer 的 API 文档,或者直接查看其源码。
Spring MVC 高级配置:
文件上传配置:
演示用例:
添加文件上传依赖(为了简化文件操作,添加 Commons IO 的依赖):
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
在 src / main / resources / views 目录下,新建 upload.jsp(其中表单必须有 enctype 属性,method 必须为 post):
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>upload page</title> </head> <body> <div class="upload"> <form action="upload" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post"> <input type="file" name="file" /> <br /> <input type="submit" value="上传" /> </form> </div> </body> </html>
注册对应的 ViewController:
@Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { // 其他省略 registry.addViewController("/toUpload").setViewName("upload"); }
添加文件上传解析器 MutilpartResolver 的 Bean:
@Bean public MultipartResolver multipartResolver() { // 这是Spring的Resolver,不是Apache的 CommonsMultipartResolver multipartResolver = new CommonsMultipartResolver(); multipartResolver.setMaxUploadSize(1000000); multipartResolver.setDefaultEncoding("UTF-8"); //解决文件名中文乱码问题 return multipartResolver; }
文件上传业务,控制器:
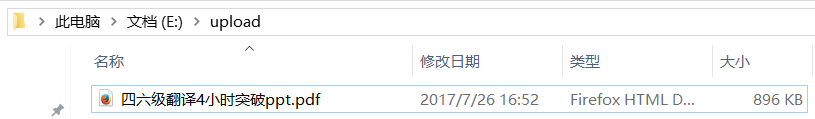
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.controller; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile; @RestController public class UploadController { @RequestMapping(value = "/upload", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String upload(MultipartFile file) { try { // 本来应该上传到文件服务器上,为了演示更直接简单,直接将上传文件写到本机上 FileUtils.writeByteArrayToFile(new File("E:/upload/" + file.getOriginalFilename()), file.getBytes()); //快速写文件到磁盘。好用而且效率高 return "ok"; } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return "wrong"; } } }
部署并启动服务器,访问 http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/toUpload,进行文件上传,如下:
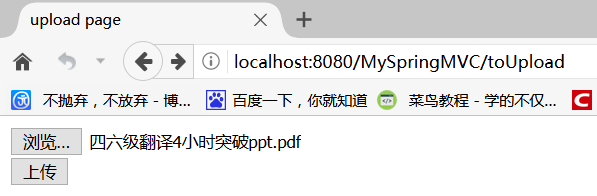
点击上传,如果返回 ok,则上传成功,查看本地文件,如:
自定义 HttpMessageConverter:
HttpMessageConverter 是用来处理 request 和 response 内的数据的。Spring 内置了大量 HttpMessageConverter,例如 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter、StringHttpMessageConverter 等,也可以根据自己的业务需求,自定义 HttpMessageConverter(需要在配置类中注册为 Bean,并通过重写 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter 的方法注册到 MVC 环境中)。
Spring 的 HttpMessageConverter 都是直接或间接继承抽象类 AbstractHttpMessageConverter<T>:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.messageconvert; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import org.springframework.http.HttpInputMessage; import org.springframework.http.HttpOutputMessage; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.converter.AbstractHttpMessageConverter; import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotReadableException; import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotWritableException; import org.springframework.util.StreamUtils; import com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.domain.DemoEntity; public class MyMessageConverter extends AbstractHttpMessageConverter<DemoEntity> { public MyMessageConverter() { // 新建一个自定义的媒体类型 contentType="application/x-qfedu"; super(new MediaType("application", "x-qfedu", Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); } @Override protected boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) { // 返回值表明,当前MessageConverter只支持处理DemoEntity类 return DemoEntity.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz); } @Override protected DemoEntity readInternal(Class<? extends DemoEntity> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException { // 处理媒体类型为x-qfedu的@RequestMapping的请求数据,@RequestBody拿到的是处理后的数据 String temp = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputMessage.getBody(), Charset.forName("UTF-8")); String[] tempArr = temp.split("-"); return new DemoEntity(new Long(tempArr[0]), tempArr[1]); } @Override protected void writeInternal(DemoEntity obj, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException { // 处理@RequestMapping的方法的返回值,@ResponseBody返回的也是处理后的数据 String out = "hello:" + obj.getId() + "-" + obj.getName(); outputMessage.getBody().write(out.getBytes()); } }
注册为 Bean,然后在注册为 HttpMessageConverter。在 Spring MVC 中,注册 HttpMessageConverter 有两个方法:
- configurerMessageConverters:会覆盖掉 Spring MVC 默认注册的多个内置 HttpMessageConverter。
- extendMessageConverters:仅添加一个自定义的 HttpMessageConverter,不会有覆盖。
@Bean public MyMessageConverter myConverter() { return new MyMessageConverter(); } @Override public void extendMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) { converters.add(myConverter()); }
添加请求页面 converter.jsp:
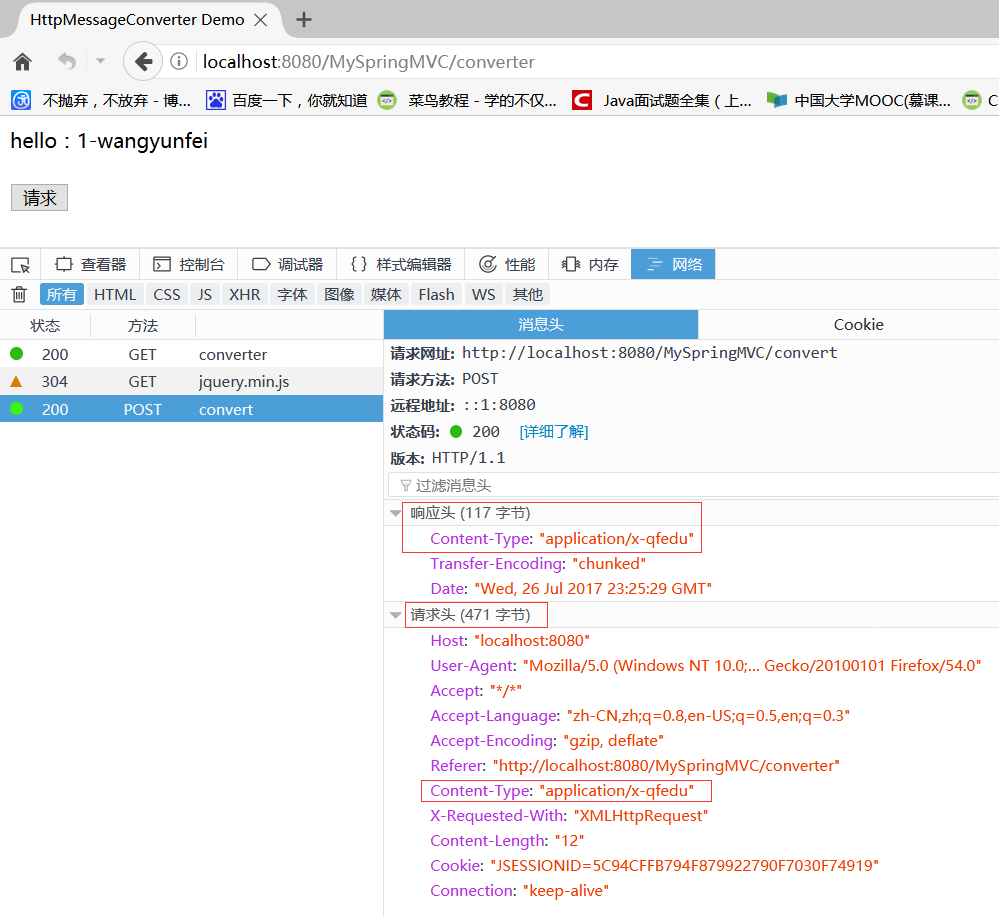
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>HttpMessageConverter Demo</title> <script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script> <script> function request() { $.ajax({ url : "convert", data : "1-wangyunfei", type : "POST", contentType : "application/x-qfedu", success : function(data) { $("#resp").html(data); } }); } </script> </head> <body> <div id="resp"></div> <br /> <input type="button" onclick="request();" value="请求" /> </body> </html>
相应的 ViewController:
@Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/converter").setViewName("converter"); }
要请求的 Controller:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.domain.DemoEntity; @RestController public class ConverterController { @RequestMapping(value = "/convert", produces = "application/x-qfedu") public DemoEntity convert(@RequestBody DemoEntity obj) { return obj; } }
访问 http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/converter,请求后的结果:
服务器端推送技术:
在日常开发中,很多类型的网站需要服务器端推送技术,最容易理解和实现的解决方案是:客户端使用 Ajax 向服务器轮询消息,但是由于客户端不知道服务端什么时候有数据,因此不知道什么时候该请求消息,轮询的频率不好控制,因此服务器的压力会很大。
为了,服务器端主动推送信息,客户端则随时监听推送事件,准备接受消息。下面将演示基于 SSE(Server Send Event 服务端发送事件)的推送。该方法需要新式浏览器的支持,是半双工通信。除此之外,还有一种全双工的新技术 —— WebSocket。
演示 SSE:
控制器(SSE 服务端,输出的媒体类型为 text/event-stream 是对服务端的支持):
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.controller; import java.util.Random; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class SseController { @RequestMapping(value = "/push", produces = "text/event-stream") public String push() { Random r = new Random(); try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 消息传输格式:data:消息体\n\n。前缀:data:。后缀:\n\n。 return "data:Testing 1, 2, 3... " + r.nextInt() + "\n\n"; } }
新建 sse.jsp —— SSE 客户端(使用浏览器内置的 EventSource 对象,建立对服务端的监听,并绑定一系列监听处理事件):
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>SSE Demo</title> <script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script> <script> $(function() { // 只有新式的浏览器才有 EventSource 对象:SSE客户端 if (!!window.EventSource) { var source = new EventSource("push"); var s = ""; source.addEventListener('message', function(e) { s = s + e.data + "<br />"; $("#msgFromPush").html(s); }); source.addEventListener('open', function(e) { console.log("连接打开."); }, false); source.addEventListener('error', function(e) { if (e.readyState == EventSource.CLOSED) { console.log("连接关闭"); } else { console.log(e.readyState); } }, false); } else { console.log("你的浏览器不支持SSE"); } }); </script> </head> <body> <div id="msgFromPush"></div> </body> </html>
配置 see.jsp 的访问映射:
@Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/sse").setViewName("sse"); }
然后运行,访问 http://localhost:8080/MySpringMVC/sse:
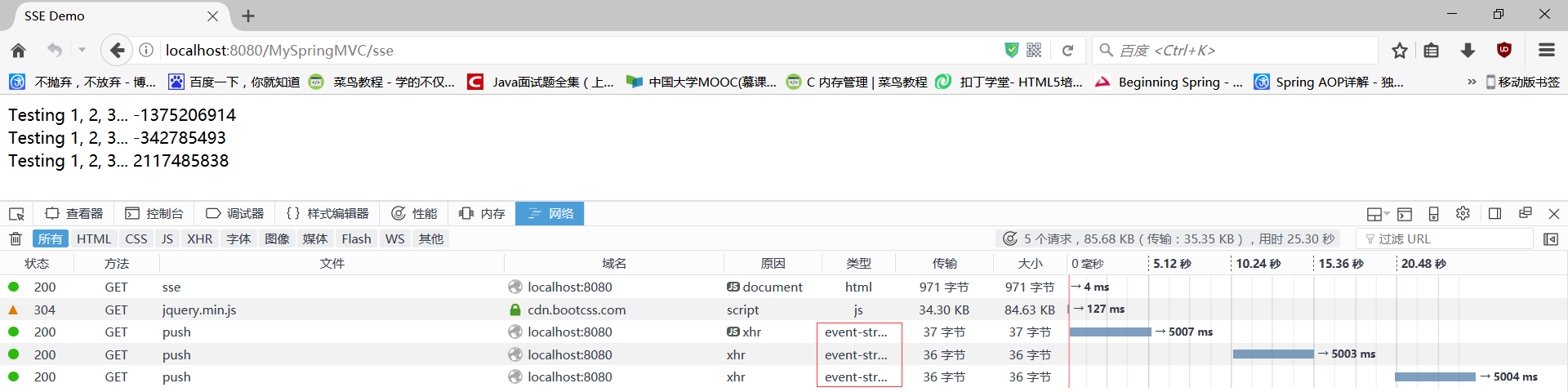
Spring MVC 的测试:
MVC 相关的测试主要针对控制器。测试 Web 项目通常不需要发布、部署、启动,为此需要一些 Servlet 相关的模拟对象(Mock 对象),比如:MockMvc、MockHttpServletRequest、MockHttpServletResponse、MockHttpSession 等。
测试是非常有用的,让测试用例通过测试,才能保证软件的质量和可控性。在现实开发中,会事先确定项目需求(即先要知道产品是什么样子的,然后按照需求去开发),因此有一个概念叫测试驱动开发(Test Driven Development,TDD):设计人员先按照需求,写一个预期结果的测试用例(此时还没有实现代码,测试肯定是无法通过的),为了让测试用例通过,不断编码和重构,最终通过,一个项目模型也驱动而生。
演示用例(使用 Spring TestContext Framework 对普通控制器和 RestController 的页面跳转进行单元测试):
添加 Spring Test 依赖(基于JUnit):
<!-- Spring Test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
单例 Bean:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class DemoService { public String sayHello() { return "hello"; } }
测试用例(没有编译错误,但此时测试无法通过):
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC; import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get; import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content; import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.forwardedUrl; import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.model; import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status; import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.view; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.mock.web.MockHttpServletRequest; import org.springframework.mock.web.MockHttpSession; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import org.springframework.test.context.web.WebAppConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc; import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders; import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; import com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.config.MyMvcConfig; import com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.service.DemoService; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = MyMvcConfig.class) // 为WebApplicationContext容器指定 web 程序资源的根目录:不能包含Spring资源前缀,如classpath:、file:(即解释为文件系统资源);不能以slash(斜线/)结尾 // 默认为文件系统 src / main / webapp 。注:在发布为WAR的标准Maven工程中,这是作为web程序根的标准目录 @WebAppConfiguration("src/main/resources") public class TestControllerIntergrationTests { private MockMvc mockMvc; @Autowired private DemoService demoService; // 获得容器(已经被@RunWith、@ContextConfiguration配置好了) // WebApplicationContext容器需要额外配置 @WebAppConfiguration @Autowired private WebApplicationContext context; // 此处仅作演示,并未使用 @Autowired MockHttpSession session; @Autowired MockHttpServletRequest request; @Before public void setup() { mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(context).build(); } @Test public void testNormalController() throws Exception { // forwardedUrl:页面转向的真正路径;status-OK:200 mockMvc.perform(get("/testNormal")) .andExpect(status().isOk()) .andExpect(view().name("page")) .andExpect(forwardedUrl("/WEB-INF/classes/views/page.jsp")) .andExpect(model().attribute("msg", demoService.sayHello())); } @Test public void testRestController() throws Exception { mockMvc.perform(get("/testRest")) .andExpect(status().isOk()) .andExpect(content().contentType("text/plain;charset=UTF-8")) .andExpect(content().string(demoService.sayHello())); } }
运行:
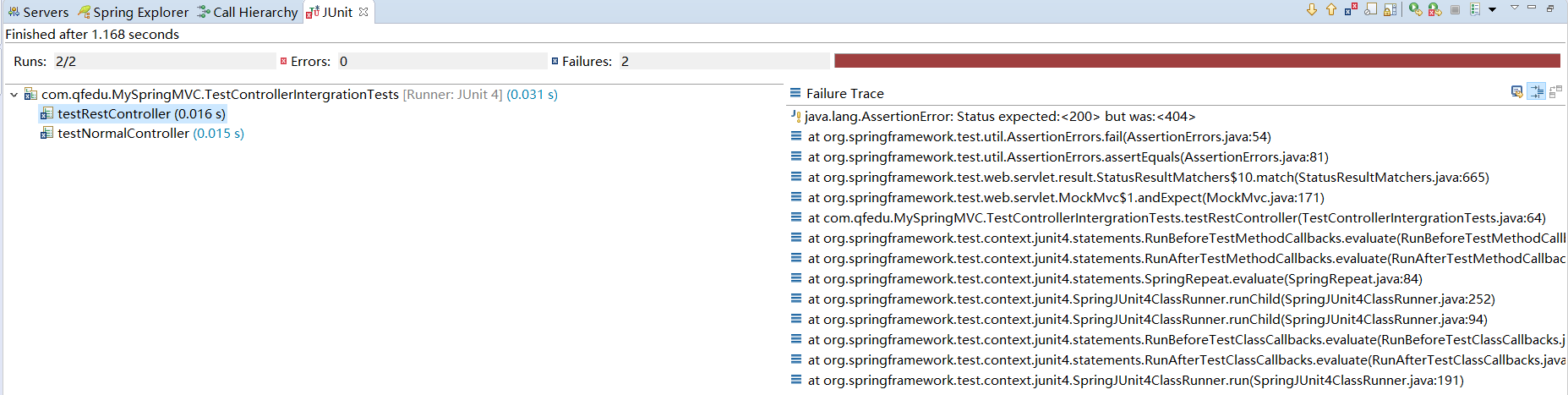
因此,增加两个测试控制器:
普通控制器:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.service.DemoService; @Controller public class NormalController { @Autowired DemoService demoService; @RequestMapping("/testNormal") public String testPage(Model model) { model.addAttribute("msg", demoService.sayHello()); return "page"; } }
对应视图 page.jsp 内容随意。
RestController:
package com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import com.qfedu.MySpringMVC.service.DemoService; @RestController public class MyRestController { @Autowired DemoService demoService; @RequestMapping(value = "/testRest", produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8") public String testRest() { return demoService.sayHello(); } }
再次测试控制器能否成功页面跳转,以及相应请求信息是否正确:






