python高级特性
1.切片
取元素或列表其中几项,主要操作如下所示:
>>> L = ['Michael', 'Sarah', 'Tracy', 'Bob', 'Jack'] >>> L[0:3] #取前三个元素,从0开始取,取0、1、2,第三位不取 ['Michael', 'Sarah', 'Tracy'] >>> L[:3] ['Michael', 'Sarah', 'Tracy'] >>> L[1:3] #从索引为1开始取,取1,2,索引为3不取 ['Sarah', 'Tracy'] >>> L[-2:] ['Bob', 'Jack'] >>> L = list(range(100)) >>> L [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99] >>> L[:10] [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] >>> L[-10:] [90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99] >>> L[10:20] [10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19] >>> L[:10:2] #前10个元素每两个取一个 [0, 2, 4, 6, 8] >>> L[::5] [0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60, 65, 70, 75, 80, 85, 90, 95] >>> L[:] [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99] >>> (0,1,2,3,4,5)[:3] (0, 1, 2) >>> >>> "wkwjdepok"[:3] #字符串也可以看成一种list 'wkw'
2.迭代
在python中用for循环遍历list或者tuple称为迭代
d = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
for key in d:
print(key)
结果:
a
b
c
>>> for ch in "ABC": print(ch) A B C
collections模块的Iterable类型判断:
>>> from collections import Iterable >>> isinstance('abc', Iterable) # str是否可迭代 True >>> isinstance([1,2,3], Iterable) # list是否可迭代 True >>> isinstance(123, Iterable) # 整数是否可迭代 False
Python内置的enumerate函数可以把一个list变成索引-元素对,这样就可以在for循环中同时迭代索引和元素本身:
>>> for i,value in enumerate(['A','B','C']): print(i,value) 0 A 1 B 2 C >>> for x,y in [(1,2),(2,4),(4,5)]: print(x,y) 1 2 2 4 4 5
3.列表生成式
>>> for i,value in enumerate(['A','B','C']): print(i,value) 0 A 1 B 2 C >>> for x,y in [(1,2),(2,4),(4,5)]: print(x,y) 1 2 2 4 4 5 >>> list(range(1,11)) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] >>> L = [] >>> for x in range(1,11): L.append(x*x) >>> L [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100] >>> [x*x for x in range(1,11)] [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100] >>> [x*x for x in range(1,11) if x % 2 == 0] [4, 16, 36, 64, 100] >>> [m+n for m in 'ABC' for n in 'xyz'] ['Ax', 'Ay', 'Az', 'Bx', 'By', 'Bz', 'Cx', 'Cy', 'Cz'] >>> import os >>> [d for d in os.listdir('.')] #可以列出文件和目录 ['DLLs', 'Doc', 'include', 'Lib', 'libs', 'LICENSE.txt', 'NEWS.txt', 'python.exe', 'python3.dll', 'python37.dll', 'pythonw.exe', 'Scripts', 'tcl', 'Tools', 'vcruntime140.dll'] >>> d = {'x':'A','y':'B','z':'c'} >>> for k,v in d.items(): print(k,'=',v) x = A y = B z = c >>> [k+'=' + v for k,v in d.items()] ['x=A', 'y=B', 'z=c'] >>> L = ["Hello","World","IBM","Apple"] >>> [s.lower() for s in L] ['hello', 'world', 'ibm', 'apple']
4.生成器
相比较列表,较为节省空间。表现为一边循环一边计算的机制
第一种生成器方式:
>>> L = [x*x for x in range(10)] >>> L [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81] >>> g = (x*x for x in range(10)) >>> g <generator object <genexpr> at 0x0000000002D69B88>
generator保存的是算法,每次调用next(g),就计算出g的下一个元素的值,直到计算到最后一个元素,没有更多的元素时,抛出StopIteration的错误。
> >>> next(g) 0 >>> next(g) 1 >>> next(g) 4 >>>
通过for循环迭代输出
>>> for n in g: print(n) 9 16 25 36 49 64 81
如果较为复杂,用列表生成式无法表示,我们采用函数的形式进行表示
第二种生成器,含有yield
著名的菲波拉契数:1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, ...
def fib(max): n, a, b = 0, 0, 1 while n < max: print(b) a, b = b, a + b n = n + 1 return 'done'
def fib(max): n, a, b = 0, 0, 1 while n < max: yield b a, b = b, a + b n = n + 1 return 'done'
生成器是在每次调用next时执行,遇到yield时返回,返回一个生成器对象
杨辉三角:
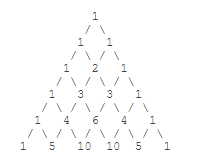
def triangles(): L=[1] while True: yield L L=[1]+[L[i]+L[i+1] for i in range(len(L)-1)]+[1]
5.迭代器
可以使用for循环的都是可迭代的,如:列表、字典、字符串,可通过iter转换成迭代器
含有-next()函数的对象为迭代器,表示计算惰性计算的序列



