Spring AOP
Spring中的AOP
一.AOP简介
什么是AOP
Aspect Oriented Programing 面向切面编程,AOP采取横向抽取机制,取代了传统纵向继承体系重复性代码
SpringAOP就是在运行期通过动态代理的方式向目标类织入增强代码,为目标类中的方法添加额外的功能
二.AOP底层原理
AOP底层原理:就是代理机制
动态代理:
特点:在不修改源代码的基础上对目标中的方法进行增强分类:
基于接口的动态代理
基于子类的动态代理Spring的AOP代理:
JDK动态代理:被代理对象必须要实现接口,才能产生代理对象,如果没有接口将不能使用动态代理技术
CGLib动态代理:第三方代理技术,cglib代理可以对任何类生成代理,代理的原理是对目标对象进行继承代理,如果目标对象被final修饰,那么该类无法被cglib代理结论:Spring框架如果类实现了接口,就使用JDK动态代理生成代理对象,如果这个类没有实现任何接口,使用CGLIB生成代理对象
三.装饰器模式
装饰器模式:对象本身增强
代理模式:代理对象(代理过程)增强
3.1Info
package com.qf.decorator;
//抽象类:有抽象方法的类一定时抽象类,但是抽象类可以有普通方法和抽象方法
public abstract class Info {
//自我介绍
public abstract void info();
}
3.2PersonInfo
package com.qf.decorator;
//继承Info类,实现方法
public class PersonInfo extends Info {
@Override
public void info() {
System.out.println("自我介绍...");
}
}
3.3Decorator
package com.qf.decorator;
//装饰器,继承Info
public abstract class Decorator extends Info{
private Info info;
//传入被装饰对象
public Decorator(Info info) {
this.info = info;
}
@Override
public void info() {
info.info();
}
}
3.4Singer
package com.qf.decorator;
public class Singer extends Decorator {
public Singer(Info info) {
super(info);
}
public void singing(){
System.out.println("唱歌...");
}
@Override
public void info() {
super.info();
singing();
}
}
3.5Dancer
package com.qf.decorator;
public class Dancer extends Decorator {
public Dancer(Info info) {
super(info);
}
public void dancing(){
System.out.println("跳舞...");
}
@Override
public void info() {
super.info();
dancing();
}
}
3.6Magic
package com.qf.decorator;
public class Magic extends Decorator {
public Magic(Info info) {
super(info);
}
public void magic(){
System.out.println("变魔术");
}
@Override
public void info() {
super.info();
magic();
}
}
3.7测试
package com.qf.decorator;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//单独测试
// Info personInfo = new PersonInfo();
// personInfo.info();
//
// Decorator singer = new Singer(personInfo);
// singer.info();
//
// Decorator dancer = new Dancer(personInfo);
// dancer.info();
//增强测试
Info personInfo = new PersonInfo();
Decorator singer = new Singer(personInfo);//第一次增强
Decorator dancer = new Dancer(singer);//第二次增强
Decorator magic1 = new Magic(dancer);//第三次增强
Decorator magic2 = new Magic(magic1);//第四次增强
magic2.info();
}
}
四.代理模式
4.1静态代理
通过代理类的对象,为目标类的对象(原始类)添加功能
缺点:要实现目标接口中的所有方法,代理类的功能代码冗余,修改时,维护性差
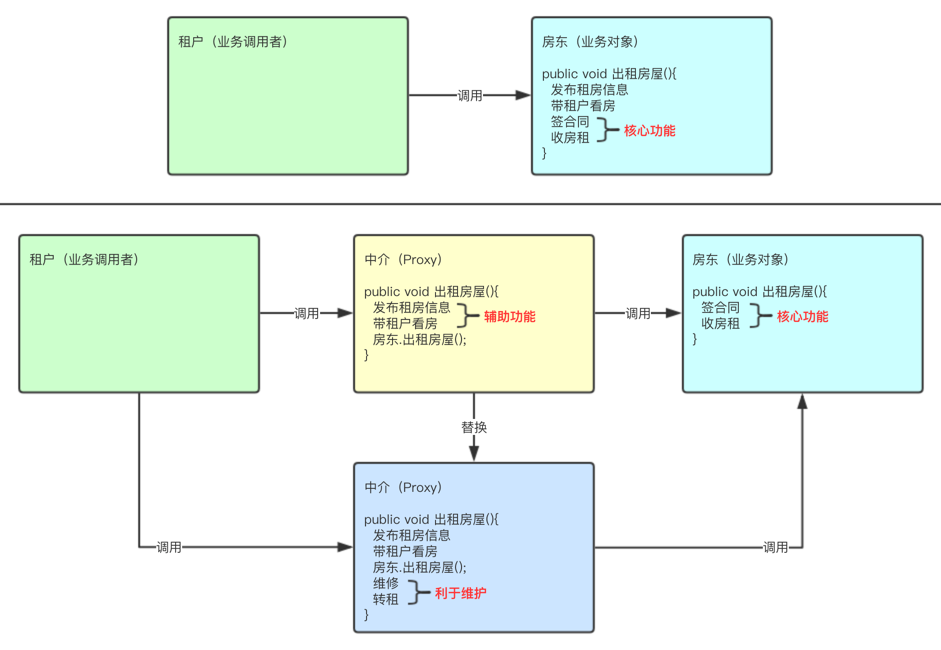
4.1.1Rent
package com.qf.proxy.demo1;
//出租房子
public interface Rent {
//出租
public void rent();
//还有一些其他方法
//public void test();
}
4.1.2Owner
package com.qf.proxy.demo1;
//房东
public class Owner implements Rent{
@Override
public void rent() {
System.out.println("房东出租房子");
}
}
4.1.3OwnerProxy
package com.qf.proxy.demo1;
//中介:静态代理类
//代理:动态代理(JDK 和 Cglib)和静态代理
public class OwnerProxy implements Rent{
private Owner owner;
public OwnerProxy(Owner owner) {
this.owner = owner;
}
public void publish(){
System.out.println("发布租房信息");
}
public void seeHouse(){
System.out.println("带租户看房");
}
@Override
public void rent() {
publish();
owner.rent();
seeHouse();
}
}
4.1.4测试
package com.qf.proxy.demo1;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Owner owner = new Owner();
owner.rent();
System.out.println("-------------------------");
OwnerProxy ownerProxy = new OwnerProxy(owner);
ownerProxy.rent();
}
}
4.2Jdk动态代理
4.2.1Rent
package com.qf.proxy.demo2;
//出租房子
public interface Rent {
//出租
public void rent();
//还有一些其他方法
public void test();
}
4.2.2Owner
package com.qf.proxy.demo2;
//房东
public class Owner implements Rent {
@Override
public void rent() {
System.out.println("房东出租房子");
}
@Override
public void test() {
System.out.println("测试方法");
}
}
4.2.3RentJdkProxy
package com.qf.proxy.demo2;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
//JDK动态代理
public class RentJdkProxy implements InvocationHandler{
private Rent rent;
public void setRent(Rent rent) {
this.rent = rent;
}
//生成代理对象
public Rent getRent(){
return (Rent) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
rent.getClass().getClassLoader(),
rent.getClass().getInterfaces(),
this);
}
//对接口中的方法进行扩展(增强),不需要实现接口中所有方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//声明方法的返回值
Object result = null;
//判断方法名,对其增强
if("rent".equals(method.getName())){
publish();
result = method.invoke(rent,args);
seeHouse();
}else{
result = method.invoke(rent,args);
}
return result;
}
public void publish(){
System.out.println("发布租房信息");
}
public void seeHouse(){
System.out.println("带租户看房");
}
}
4.2.4测试
package com.qf.proxy.demo2;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Owner owner = new Owner();
owner.rent();
System.out.println("-------------------------");
RentJdkProxy rentJdkProxy = new RentJdkProxy();
rentJdkProxy.setRent(owner);
Rent proxyRent = rentJdkProxy.getRent();//获取代理对象
proxyRent.rent();
proxyRent.test();
}
}
五.AOP的术语
AOP的术语:
Joinpoint(连接点):所谓连接点是指那些被拦截到的点,在spring中,这些点指的是方法,spring只支持方法类型的连接点。
Pointcut(切入点):所谓切入点是指我们要对哪些Joinpoint进行拦截的定义。
Advice(通知/增强):所谓通知是指拦截到Joinpoint之后所要做的事情就是通知,通知分为前置通知,后置通知,异常通知,最终通知,环绕通知。
Introduction(引介):可以在运行期为类动态地添加一些方法或Field。
Target(目标对象):代理的目标对象。
Weaving(织入):是指把增强应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程。
Proxy(代理):一个类被AOP织入增强后,就产生一个代理类。
Aspect(切面):是切入点和通知(引介)的结合
如下图:
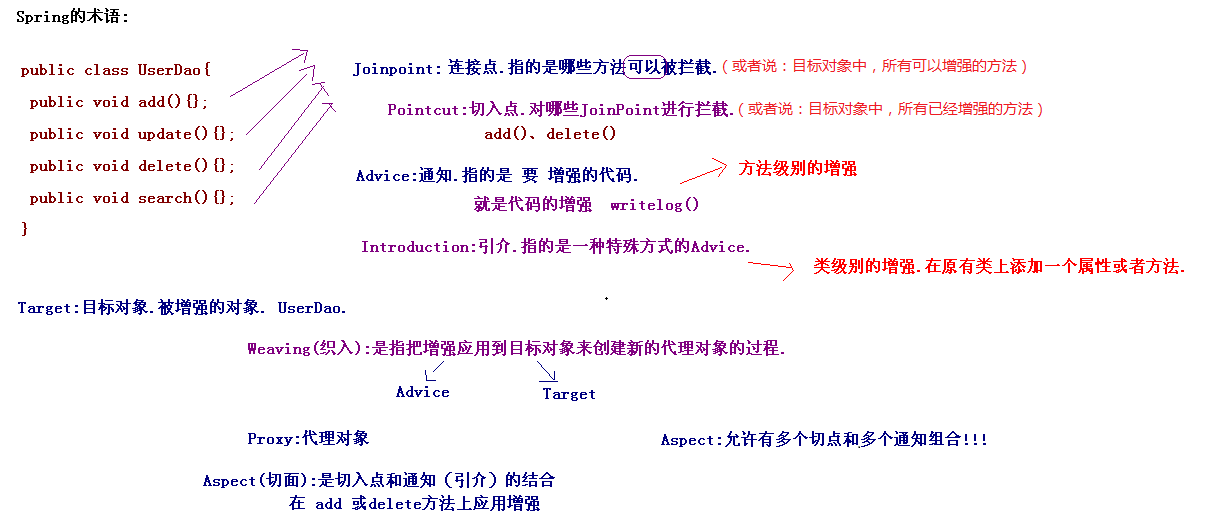
六.Spring中的XML配置AOP
4.1在pom.xml添加aop依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.20</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.9.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
4.2创建UserService
package com.qf.service;
//目标对象target
public interface UserService {
//未增强的方法叫做连接点JoinPoint
//已增强的方法叫做切入点PointCut
public void add();
public void delete();
}
4.3创建UserServiceImpl
package com.qf.service.impl;
import com.qf.service.UserService;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("添加用户..");
//int i = 1/0;
}
@Override
public void delete() {
System.out.println("删除用户..");
}
}
4.4创建通知类
前置通知(before):目标方法运行之前调用
后置通知(after-returning):在目标方法运行之后调用 (如果出现异常不会调用)
环绕通知(around):在目标方法之前和之后都调用(ProceedingJoinPoint对象 -->> 调用proceed方法)
异常拦截通知(after-throwing):如果出现异常,就会调用
最终通知(after):在目标方法运行之后调用 (无论是否出现 异常都会调用)
package com.qf.advice;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
//通知类,增强的代码(方法)Advice
public class MyAdvice {
public void before(){
System.out.println("前置通知,目标对象调用方法前执行");
}
public void after(){
System.out.println("后置通知(最终通知),目标对象调用方法后执行,无论是否发生异常都执行");
}
public void after_returning(){
System.out.println("后置通知,目标对象调用方法后执行,发生异常不执行");
}
public void after_throwing(){
System.out.println("异常通知,发生异常执行");
}
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知,目标对象调用方法之前");
joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知,目标对象调用方法之后");
}
}
4.5创建applicationContext.xml(添加aop约束)
使用xml方式配置AOP
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here -->
<bean id="userService" class="com.qf.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 通知 -->
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.qf.advice.MyAdvice"></bean>
<!-- aop -->
<!-- 默认使用JDK动态代理 -->
<!-- proxy-target-class="true" 使用cglib -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<!-- 配置切入点 切入点表达式的写法:execution(表达式)
public void com.abyg.service.UserServiceImpl.save()
void com.qf.service.UserServiceImpl.save() 其他修饰符无返回值的save空参方法
* com.qf.service.UserServiceImpl.save() 有或者无返回值的save空参方法
* com.qf.service.UserServiceImpl.*() 有或者无返回值的所有空参方法
* com.qf.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..) 有或者无返回值的所有有参或者空参方法
* com.qf.service..*ServiceImpl.*(..) 一般不用,service包下的子包和孙包以ServiceImpl结尾的类中的方法
-->
<!-- 切入点 -->
<!-- <aop:pointcut id="pc" expression="execution(public void com.qf.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.add())"/>-->
<aop:pointcut id="pc" expression="execution(* com.qf.service.impl.*ServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!-- 切面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
<!-- 配置前置通知对应的方法 -->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pc"></aop:before>
<!-- 配置后置通知(最终通知)对应的方法 -->
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pc"></aop:after>
<!-- 配置后置通知对应的方法,发生异常不执行 -->
<aop:after-returning method="after_returning" pointcut-ref="pc"></aop:after-returning>
<!-- 配置异常通知对应的方法,发生异常执行 -->
<aop:after-throwing method="after_throwing" pointcut-ref="pc"></aop:after-throwing>
<!-- 配置环绕通知对应的方法 -->
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pc"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
4.6测试
package com.qf.test;
import com.qf.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void testUserService(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService)applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.add();
userService.delete();
}
}
七.Spring中的注解配置AOP
使用注解方式配置AOP
7.1创建bean.xml文件配置注解方式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here -->
<!-- 准备工作: 导入aop(约束)命名空间 -->
<!-- 1.配置目标对象 -->
<bean id="userService" class="com.qf.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 2.配置通知对象 -->
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.qf.advice.MyAdvice"></bean>
<!-- 3.开启使用注解完成织入 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
</beans>
7.2在通知类上使用相关注解
@Aspect
//表示该类是一个通知类
//通知类,增强的代码(方法)Advice
public class MyAdvice {
//自己设置一个切点,管理重复代码
@Pointcut("execution(* com.qf.service.impl.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void pc(){}
//前置通知
//指定该方法是前置通知,并制定切入点
@Before("MyAdvice.pc()")
public void before(){
System.out.println("前置通知,目标对象调用方法前执行");
}
//最终通知
@After("execution(* com.qf.service.impl.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("后置通知(最终通知),目标对象调用方法后执行,无论是否发生异常都执行");
}
//后置通知
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.qf.service.impl.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after_returning(){
System.out.println("后置通知,目标对象调用方法后执行,发生异常不执行");
}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.qf.service.impl.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after_throwing(){
System.out.println("异常通知,发生异常执行");
}
//环绕通知
@Around("execution(* com.qf.service.impl.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知,目标对象调用方法之前");
joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知,目标对象调用方法之后");
}
}
7.3测试
@Test
public void testUserService(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService)applicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.add();
userService.delete();
}





