javascript 执行过程
1.语法检测(有没有基本的语法错误,例如中文,关键字错误...)
2.词法分析(预编译)
(1)创建全局GO(global object)对象
(2)对var声明的变量进行声明提升但不赋值,放入GO对象中
(3)对函数体整体进行提升,放入GO对象中
3.逐行执行
一.全局 直接是script标签中的代码,不包括函数执行
<script type="text/javascript"> console.log(a); var a = 100; console.log(a) var b = 200 var c = 300 function a(){ } function fun(){ } </script>
执行前:
1.首先生成一个GO(global object)对象,看不到,但是可以模拟出来用来分析
GO = { ...//省略自带属性 }
2.分析变量声明,变量名为属性名,值为undefined
GO = {
a : undefined,
b : undefined,
c : undefined
}
3.分析<b>函数声明</b>,函数名为属性名,值为函数体,如果函数名和变量名相同,则将其覆盖
GO = { a : function a(){ }, b : undefined, c : undefined, fun : function fun(){ } }
此时,GO就是预编译完成的最终对象,词法分析结束
4.逐行执行,分析过变量声明,函数声明,这里就不用管了,只管赋值(变量赋值)
当执行到“var a = 100;”的时候,a赋了一次值,值改变为100
GO = { a : 100, b : undefined, c : undefined, fun : function fun(){ } }
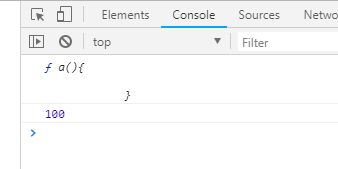
所以代码的执行结果是:
二.函数执行时
函数执行时
创建AO对象 activation object
找形参和变量声明,将变量和形参名作为AO属性名,值为undefined
将实参和形参统一
在函数体里面找到函数声明,值赋予函数体
function test(){ console.log(b); if(a){ //undefined转换成false var b = 100; } c = 123; console.log(c); } var a; test(); a = 20; test(); console.log(c);
执行过程:
生成GO
GO = {
}
变量声明
GO = {
a : undefined
}
函数声明
GO = { a : undefined, test : function }
逐行执行;
test调用,生成test.AO ={}
参数 没有,跳过
变量声明
test.AO = {
b : undefined
}
函数声明 没有,跳过
得到结果
test.AO = {
b : undefined
}
逐行执行
改变GO
GO = { a : undefined, test : function, c : 123 }
a值发生改变
GO = { a : 20, test : function, c : 123 }
test调用 生成test.AO={}
参数 没有 跳过
变量声明
test.AO = {
b : undefined
}
函数声明 没有
结果
test.AO = {
b : undefined
}
逐行执行
test.AO = { b : 100 }
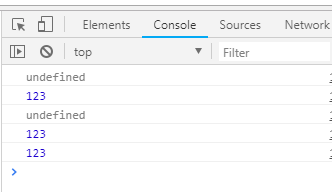
执行结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号