实验十一 集合
实验时间 2018-11-8
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握Vetor、Stack、Hashtable三个类的用途及常用API;
Vector类实现了长度可变的数组。
Stack类是Vector的子类。
Hashtable通过键来查找元素。 Hashtable用一个特殊的值来确定键,名为hashcode(散列码)。所有对象都有一个散列码,可以通过Object 类的hashCode()方法获得。
(2) 了解java集合框架体系组成;
集合框架为程序员提供了一个功能强大的设计方案以解决编程过程中面临的大多数任务。下一次当你需要存储和检索信息时,可考虑使用类集。记住,类集不仅仅是专为那些“大型作业”,例如联合数据库,邮件列表或产品清单系统等所专用的。它们对于一些小型作业也是很有效的。例如,TreeMap可以给出一个很好的类集以保留一组文件的字典结构。TreeSet在存储工程管理信息时是十分有用的。坦白地说,对于采用基于类集的解决方案而受益的问题种类只受限于你的想象力。
(3) 掌握ArrayList、LinkList两个类的用途及常用API。
ArrayList内存中是顺序存储的。
LinkedList内存中是以链表方式存储的。
将线性表中的数据元素依次存放在某个存储区域中,所形成的表称为顺序表。一维数组就是用顺序方式存储的线性表。
ArrayList封装了一个动态再分配的对象数组,
(4) 了解HashSet类、TreeSet类的用途及常用API。
HashSet扩展AbstractSet并且实现Set接口。它创建一个使用散列表存储的集合。散列表(hash table)是通过使用称为散列法的机制来存储信息的。在散列法中,键的信息内容用于确定一个唯一的值,称为它的散列码。然后散列码作为与键相关的数据存储之处的索引使用。键到它的散列码的转化是自动完成的,我们不会看到散列码本身,同样,散列码也不能直接索引散列表。
(5)了解HashMap、TreeMap两个类的用途及常用API;
Map接口用来维持很多“键-值”对,以便通过键来查找相应的值。
HashMap基于散列表实现(替代Hashtable)。
HashMap是一个基于散列表完成的一个实现类,可以用它来取代Hashtable。 HashMap类的构造器: public HashMap() public HashMap(int initialCapacity) public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) public HashMap(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m)
TreeMap在一个二叉树的基础上实现。
TreeMap是底层基于树完成的一个Map。
当我们遍历它时,会以排序形式出现,次序由Comparable或Comparator比较器决定。 TreeMap类的构造器: public TreeMap() public TreeMap(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> c) public TreeMap(SortedMap<K,? extends V> m)
(6) 结对编程(Pair programming)练习,体验程序开发中的两人合作。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第9章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 使用JDK命令运行编辑、运行以下三个示例程序,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握Vetor、Stack、Hashtable三个类的用途及常用API。
|
//示例程序1 import java.util.Vector;
class Cat { private int catNumber;
Cat(int i) { catNumber = i; }
void print() { System.out.println("Cat #" + catNumber); } }
class Dog { private int dogNumber;
Dog(int i) { dogNumber = i; }
void print() { System.out.println("Dog #" + dogNumber); } }
public class CatsAndDogs { public static void main(String[] args) { Vector cats = new Vector(); for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) cats.addElement(new Cat(i)); cats.addElement(new Dog(7)); for (int i = 0; i < cats.size(); i++) ((Cat) cats.elementAt(i)).print(); } } |
|
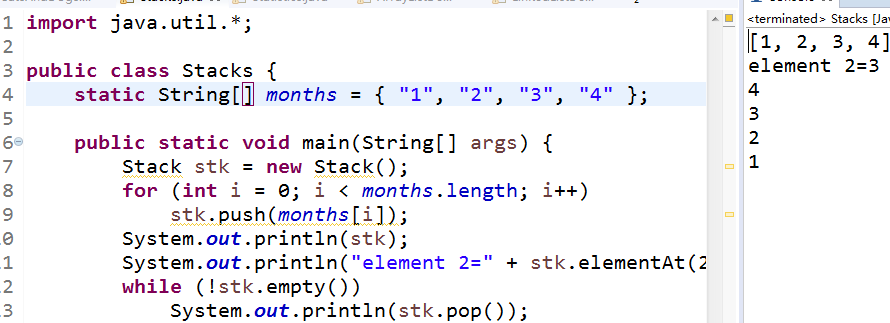
//示例程序2 import java.util.*;
public class Stacks { static String[] months = { "1", "2", "3", "4" };
public static void main(String[] args) { Stack stk = new Stack(); for (int i = 0; i < months.length; i++) stk.push(months[i]); System.out.println(stk); System.out.println("element 2=" + stk.elementAt(2)); while (!stk.empty()) System.out.println(stk.pop()); } } |
|
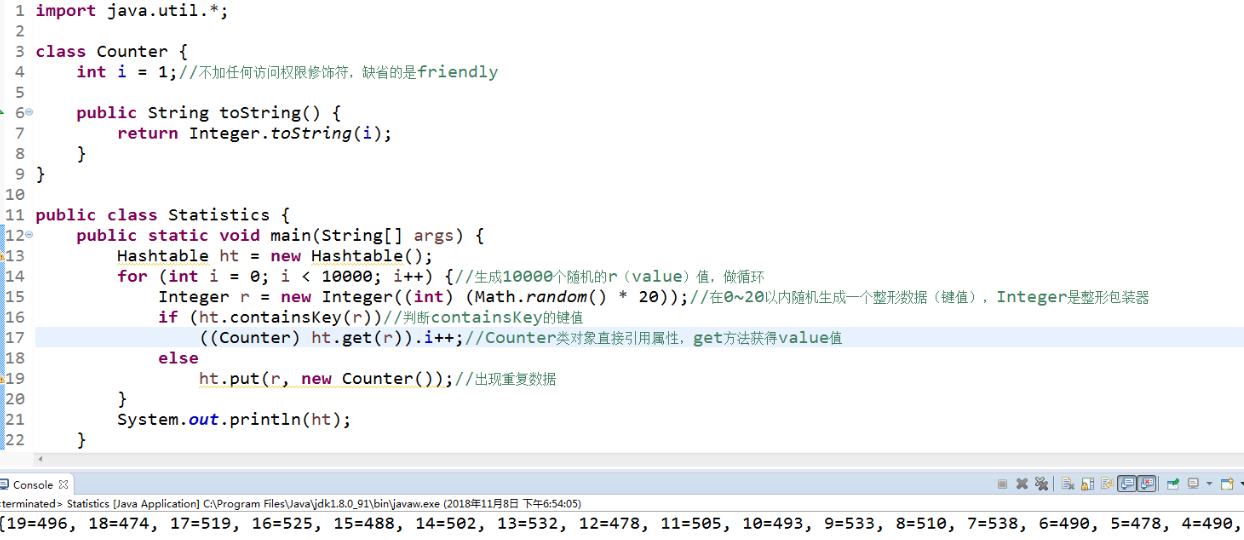
//示例程序3 import java.util.*;
class Counter { int i = 1;
public String toString() { return Integer.toString(i); } }
public class Statistics { public static void main(String[] args) { Hashtable ht = new Hashtable(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { Integer r = new Integer((int) (Math.random() * 20)); if (ht.containsKey(r)) ((Counter) ht.get(r)).i++; else ht.put(r, new Counter()); } System.out.println(ht); } }
|
1 import java.util.Vector; 2 3 class Cat { 4 private int catNumber; 5 6 Cat(int i) { 7 catNumber = i; 8 } 9 10 void print() { 11 System.out.println("Cat #" + catNumber); 12 } 13 } 14 15 class Dog { 16 private int dogNumber; 17 18 Dog(int i) { 19 dogNumber = i; 20 } 21 22 void print() { 23 System.out.println("Dog #" + dogNumber); 24 } 25 } 26 27 public class CatsAndDogs { 28 public static void main(String[] args) { 29 Vector cats = new Vector(); 30 for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) 31 cats.addElement(new Cat(i)); 32 cats.addElement(new Dog(7)); 33 for (int i = 0; i < cats.size(); i++) 34 if(cats.elementAt(i) instanceof Cat) { //instanceof判断类型是否匹配 35 ((Cat) cats.elementAt(i)).print(); 36 } 37 else { 38 ((Dog) cats.elementAt(i)).print(); 39 } 40 } 41 }

测试程序2:
l 使用JDK命令编辑运行ArrayListDemo和LinkedListDemo两个程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
|
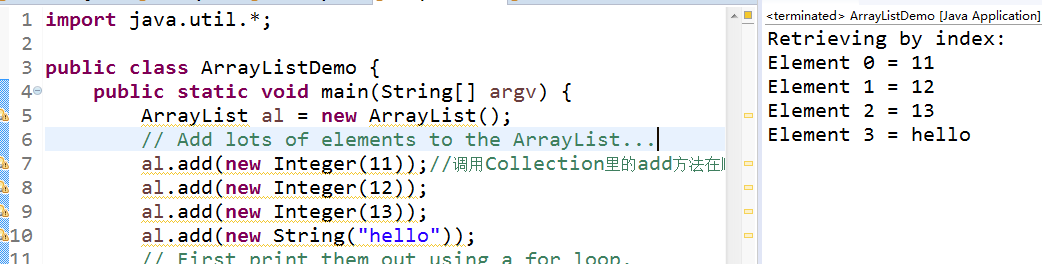
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { ArrayList al = new ArrayList(); // Add lots of elements to the ArrayList... al.add(new Integer(11)); al.add(new Integer(12)); al.add(new Integer(13)); al.add(new String("hello")); // First print them out using a for loop. System.out.println("Retrieving by index:"); for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) { System.out.println("Element " + i + " = " + al.get(i)); } } } |
|
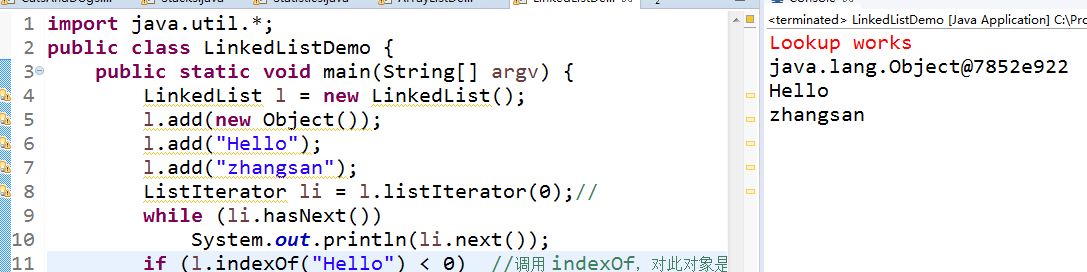
import java.util.*; public class LinkedListDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { LinkedList l = new LinkedList(); l.add(new Object()); l.add("Hello"); l.add("zhangsan"); ListIterator li = l.listIterator(0); while (li.hasNext()) System.out.println(li.next()); if (l.indexOf("Hello") < 0) System.err.println("Lookup does not work"); else System.err.println("Lookup works"); } } |
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class ArrayListDemo { 4 public static void main(String[] argv) { 5 ArrayList al = new ArrayList(); 6 // 向ArrayList添加很多元素… 7 al.add(new Integer(11)); 8 al.add(new Integer(12)); 9 al.add(new Integer(13));//整型包装器类对象 10 al.add(new String("hello"));//字符串类对象,说明集合中的元素的类型可以不同 11 // 首先使用for循环将它们打印出来。 12 System.out.println("Retrieving by index:"); 13 for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) { 14 System.out.println("Element " + i + " = " + al.get(i)); 15 } 16 } 17 }
l 在Elipse环境下编辑运行调试教材360页程序9-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握ArrayList、LinkList两个类的用途及常用API。
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 /** 4 * This program demonstrates operations on linked lists. 5 * @version 1.11 2012-01-26 6 * @author Cay Horstmann 7 */ 8 public class LinkedListTest 9 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) 11 { 12 List<String> a = new LinkedList<>(); 13 a.add("Amy"); 14 a.add("Carl"); 15 a.add("Erica"); 16 17 List<String> b = new LinkedList<>(); 18 b.add("Bob"); 19 b.add("Doug"); 20 b.add("Frances"); 21 b.add("Gloria"); 22 23 // merge the words from b into a 24 25 ListIterator<String> aIter = a.listIterator(); 26 Iterator<String> bIter = b.iterator();//一开始迭代器(Iterator)在所有元素的左边,调用next()之后,迭代器移到第一个和第二个元素之间,next()方法返回迭代器刚刚经过的元素。 27 28 while (bIter.hasNext()) 29 { 30 if (aIter.hasNext()) aIter.next(); 31 aIter.add(bIter.next()); 32 } 33 34 System.out.println(a); 35 36 // remove every second word from b 37 38 bIter = b.iterator(); 39 while (bIter.hasNext()) 40 { 41 bIter.next(); // skip one element 42 if (bIter.hasNext()) 43 { 44 bIter.next(); // skip next element 45 bIter.remove(); // remove that element 46 } 47 } 48 49 System.out.println(b); 50 51 // bulk operation: remove all words in b from a 52 53 a.removeAll(b); 54 55 System.out.println(a); 56 } 57 }

测试程序3:
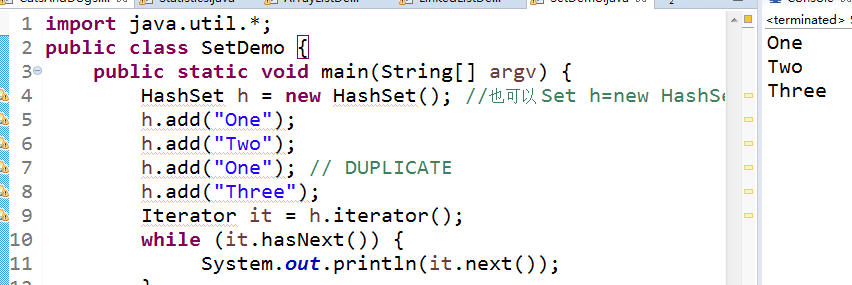
l 运行SetDemo程序,结合运行结果理解程序;
|
import java.util.*; public class SetDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { HashSet h = new HashSet(); //也可以 Set h=new HashSet() h.add("One"); h.add("Two"); h.add("One"); // DUPLICATE h.add("Three"); Iterator it = h.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } } } |
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材365页程序9-2,结合运行结果理解程序;了解HashSet类的用途及常用API。
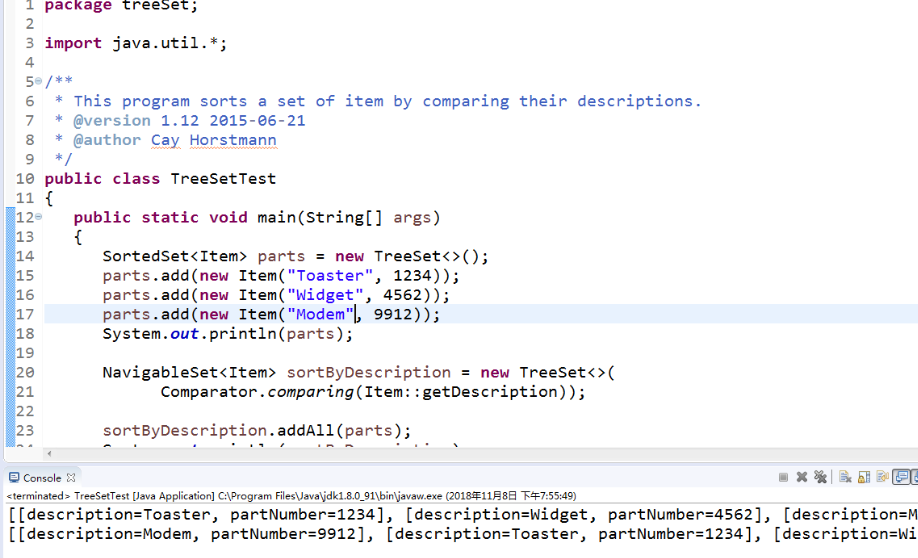
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材367页-368程序9-3、9-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;了解TreeSet类的用途及常用API。
1 package Set; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * This program uses a set to print all unique words in System.in. 7 * @version 1.12 2015-06-21 8 * @author Cay Horstmann 9 */ 10 public class SetTest 11 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) 13 { 14 Set<String> words = new HashSet<>(); // HashSet implements Set 15 long totalTime = 0; 16 17 try (Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in)) 18 { 19 while (in.hasNext()) 20 { 21 String word = in.next(); 22 long callTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); 23 words.add(word); 24 callTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - callTime; 25 totalTime += callTime; 26 } 27 } 28 29 Iterator<String> iter = words.iterator(); 30 for (int i = 1; i <= 20 && iter.hasNext(); i++) 31 System.out.println(iter.next()); 32 System.out.println(". . ."); 33 System.out.println(words.size() + " distinct words. " + totalTime + " milliseconds."); 34 } 35 }
1 package treeSet; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * An item with a description and a part number. 7 */ 8 public class Item implements Comparable<Item> 9 { 10 private String description; 11 private int partNumber; 12 13 /** 14 * Constructs an item. 15 * 16 * @param aDescription 17 * the item's description 18 * @param aPartNumber 19 * the item's part number 20 */ 21 public Item(String aDescription, int aPartNumber) 22 { 23 description = aDescription; 24 partNumber = aPartNumber; 25 } 26 27 /** 28 * Gets the description of this item. 29 * 30 * @return the description 31 */ 32 public String getDescription() 33 { 34 return description; 35 } 36 37 public String toString() 38 { 39 return "[description=" + description + ", partNumber=" + partNumber + "]"; 40 } 41 42 public boolean equals(Object otherObject) 43 { 44 if (this == otherObject) return true; 45 if (otherObject == null) return false; 46 if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; 47 Item other = (Item) otherObject; 48 return Objects.equals(description, other.description) && partNumber == other.partNumber; 49 } 50 51 public int hashCode() 52 { 53 return Objects.hash(description, partNumber); 54 } 55 56 public int compareTo(Item other) 57 { 58 int diff = Integer.compare(partNumber, other.partNumber); 59 return diff != 0 ? diff : description.compareTo(other.description); 60 } 61 }
1 package treeSet; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * An item with a description and a part number. 7 */ 8 public class Item implements Comparable<Item> 9 { 10 private String description; 11 private int partNumber; 12 13 /** 14 * Constructs an item. 15 * 16 * @param aDescription 17 * the item's description 18 * @param aPartNumber 19 * the item's part number 20 */ 21 public Item(String aDescription, int aPartNumber) 22 { 23 description = aDescription; 24 partNumber = aPartNumber; 25 } 26 27 /** 28 * Gets the description of this item. 29 * 30 * @return the description 31 */ 32 public String getDescription() 33 { 34 return description; 35 } 36 37 public String toString() 38 { 39 return "[description=" + description + ", partNumber=" + partNumber + "]"; 40 } 41 42 public boolean equals(Object otherObject) 43 { 44 if (this == otherObject) return true; 45 if (otherObject == null) return false; 46 if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; 47 Item other = (Item) otherObject; 48 return Objects.equals(description, other.description) && partNumber == other.partNumber; 49 } 50 51 public int hashCode() 52 { 53 return Objects.hash(description, partNumber); 54 } 55 56 public int compareTo(Item other) 57 { 58 int diff = Integer.compare(partNumber, other.partNumber); 59 return diff != 0 ? diff : description.compareTo(other.description); 60 } 61 }
测试程序4:
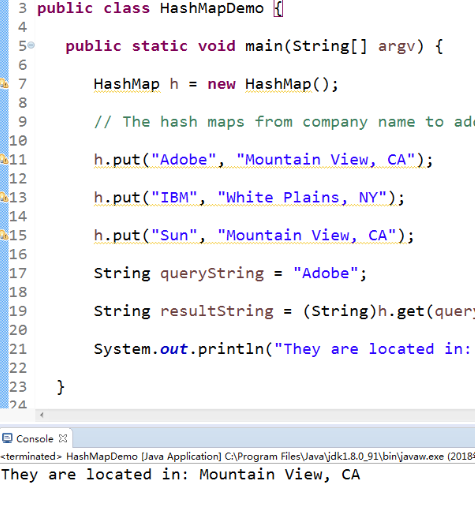
l 使用JDK命令运行HashMapDemo程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
|
import java.util.*; public class HashMapDemo { public static void main(String[] argv) { HashMap h = new HashMap(); // The hash maps from company name to address. h.put("Adobe", "Mountain View, CA"); h.put("IBM", "White Plains, NY"); h.put("Sun", "Mountain View, CA"); String queryString = "Adobe"; String resultString = (String)h.get(queryString); System.out.println("They are located in: " + resultString); } } |
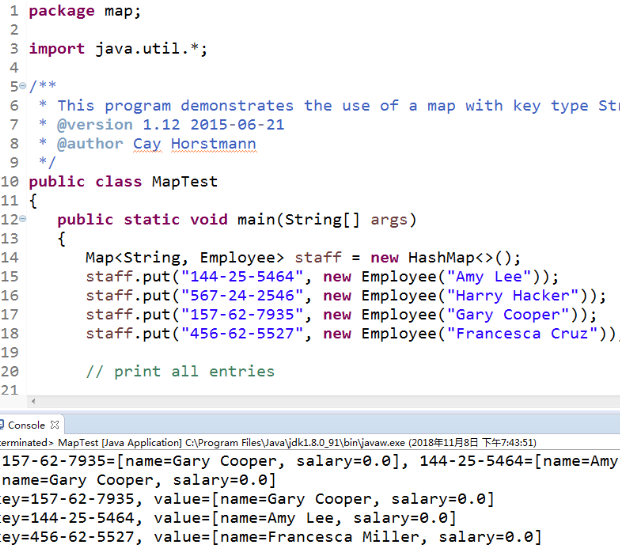
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材373页程序9-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解HashMap、TreeMap两个类的用途及常用API。
1 package map; 2 3 /** 4 * A minimalist employee class for testing purposes. 5 */ 6 public class Employee 7 { 8 private String name; 9 private double salary; 10 11 /** 12 * Constructs an employee with $0 salary. 13 * @param n the employee name 14 */ 15 public Employee(String name) 16 { 17 this.name = name; 18 salary = 0; 19 } 20 21 public String toString() 22 { 23 return "[name=" + name + ", salary=" + salary + "]"; 24 } 25 }
1 package map; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * This program demonstrates the use of a map with key type String and value type Employee. 7 * @version 1.12 2015-06-21 8 * @author Cay Horstmann 9 */ 10 public class MapTest 11 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) 13 { 14 Map<String, Employee> staff = new HashMap<>(); 15 staff.put("144-25-5464", new Employee("Amy Lee")); 16 staff.put("567-24-2546", new Employee("Harry Hacker")); 17 staff.put("157-62-7935", new Employee("Gary Cooper")); 18 staff.put("456-62-5527", new Employee("Francesca Cruz")); 19 20 // print all entries 21 22 System.out.println(staff); 23 24 // remove an entry 25 26 staff.remove("567-24-2546"); 27 28 // replace an entry 29 30 staff.put("456-62-5527", new Employee("Francesca Miller")); 31 32 // look up a value 33 34 System.out.println(staff.get("157-62-7935")); 35 36 // iterate through all entries 37 38 staff.forEach((k, v) -> 39 System.out.println("key=" + k + ", value=" + v)); 40 } 41 }
实验2:结对编程练习:
l 关于结对编程:以下图片是一个结对编程场景:两位学习伙伴坐在一起,面对着同一台显示器,使用着同一键盘,同一个鼠标,他们一起思考问题,一起分析问题,一起编写程序。
l 关于结对编程的阐述可参见以下链接:
http://www.cnblogs.com/xinz/archive/2011/08/07/2130332.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pair_programming
l 对于结对编程中代码设计规范的要求参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/xinz/archive/2011/11/20/2255971.html
以下实验,就让我们来体验一下结对编程的魅力。
l 确定本次实验结对编程合作伙伴;
l 各自运行合作伙伴实验九编程练习1,结合使用体验对所运行程序提出完善建议;
1 package test1; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.File; 5 import java.io.FileInputStream; 6 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 9 import java.util.ArrayList; 10 import java.util.Collections; 11 import java.util.Scanner; 12 13 public class Main{ 14 private static ArrayList<Student> studentlist; 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 studentlist = new ArrayList<>(); 17 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 18 File file = new File("F:\\身份证号.txt"); 19 try { 20 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); 21 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); 22 String temp = null; 23 while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { 24 25 Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); 26 27 linescanner.useDelimiter(" "); 28 String name = linescanner.next(); 29 String number = linescanner.next(); 30 String sex = linescanner.next(); 31 String age = linescanner.next(); 32 String province =linescanner.nextLine(); 33 Student student = new Student(); 34 student.setName(name); 35 student.setnumber(number); 36 student.setsex(sex); 37 int a = Integer.parseInt(age); 38 student.setage(a); 39 student.setprovince(province); 40 studentlist.add(student); 41 42 } 43 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 44 System.out.println("学生信息文件找不到"); 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } catch (IOException e) { 47 System.out.println("学生信息文件读取错误"); 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 } 50 boolean isTrue = true; 51 while (isTrue) { 52 System.out.println("选择你的操作,输入正确格式的选项"); 53 System.out.println("A.按姓名字典排序"); 54 System.out.println("B.输出年龄最大和年龄最小的人"); 55 System.out.println("C.寻找老乡"); 56 System.out.println("D.寻找年龄相近的人"); 57 System.out.println("F.退出"); 58 String m = scanner.next(); 59 switch (m) { 60 case "A": 61 Collections.sort(studentlist); 62 System.out.println(studentlist.toString()); 63 break; 64 case "B": 65 int max=0,min=100; 66 int j,k1 = 0,k2=0; 67 for(int i=1;i<studentlist.size();i++) 68 { 69 j=studentlist.get(i).getage(); 70 if(j>max) 71 { 72 max=j; 73 k1=i; 74 } 75 if(j<min) 76 { 77 min=j; 78 k2=i; 79 } 80 81 } 82 System.out.println("年龄最大:"+studentlist.get(k1)); 83 System.out.println("年龄最小:"+studentlist.get(k2)); 84 break; 85 case "C": 86 System.out.println("老家?"); 87 String find = scanner.next(); 88 String place=find.substring(0,3); 89 for (int i = 0; i <studentlist.size(); i++) 90 { 91 if(studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1,4).equals(place)) 92 System.out.println("老乡"+studentlist.get(i)); 93 } 94 break; 95 96 case "D": 97 System.out.println("年龄:"); 98 int yourage = scanner.nextInt(); 99 int near=agenear(yourage); 100 int value=yourage-studentlist.get(near).getage(); 101 System.out.println(""+studentlist.get(near)); 102 break; 103 case "F": 104 isTrue = false; 105 System.out.println("退出程序!"); 106 break; 107 default: 108 System.out.println("输入有误"); 109 110 } 111 } 112 } 113 public static int agenear(int age) { 114 int j=0,min=53,value=0,k=0; 115 for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++) 116 { 117 value=studentlist.get(i).getage()-age; 118 if(value<0) value=-value; 119 if (value<min) 120 { 121 min=value; 122 k=i; 123 } 124 } 125 return k; 126 } 127 128 }
1 package test1; 2 3 public class Student implements Comparable<Student> { 4 5 private String name; 6 private String number ; 7 private String sex ; 8 private int age; 9 private String province; 10 11 public String getName() { 12 return name; 13 } 14 public void setName(String name) { 15 this.name = name; 16 } 17 public String getnumber() { 18 return number; 19 } 20 public void setnumber(String number) { 21 this.number = number; 22 } 23 public String getsex() { 24 return sex ; 25 } 26 public void setsex(String sex ) { 27 this.sex =sex ; 28 } 29 public int getage() { 30 31 return age; 32 } 33 public void setage(int age) { 34 // int a = Integer.parseInt(age); 35 this.age= age; 36 } 37 38 public String getprovince() { 39 return province; 40 } 41 public void setprovince(String province) { 42 this.province=province ; 43 } 44 45 public int compareTo(Student o) { 46 return this.name.compareTo(o.getName()); 47 } 48 49 public String toString() { 50 return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+number+"\t"+province+"\n"; 51 } 52 }
l 各自运行合作伙伴实验十编程练习2,结合使用体验对所运行程序提出完善建议;
1 package shiyan; 2 import java.util.Scanner; 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.PrintWriter; 5 6 public class Main { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 9 PrintWriter output = null; 10 try { 11 output = new PrintWriter("E:/test.txt"); 12 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 13 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 14 System.out.println("文件输出失败"); 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 int sum=0; 18 jisuanji js=new jisuanji(); 19 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 20 int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 21 int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 22 int n = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 4 ); 23 24 switch(n) 25 { 26 case 1: 27 System.out.println(a+"/"+b+"="); 28 while(b==0){ 29 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 30 } 31 while(a%b!=0) { 32 a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 33 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 34 } 35 double c = in.nextDouble(); 36 output.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c); 37 if (c == js.chu(a,b)) { 38 sum += 10; 39 System.out.println("答案正确"); 40 } 41 else { 42 System.out.println("答案错误"); 43 } 44 45 break; 46 47 case 2: 48 System.out.println(a+"*"+b+"="); 49 int c1 = in.nextInt(); 50 output.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c1); 51 if (c1 == js.chen(a, b)) { 52 sum += 10; 53 System.out.println("答案正确"); 54 } 55 else { 56 System.out.println("答案错误"); 57 } 58 break; 59 case 3: 60 System.out.println(a+"+"+b+"="); 61 int c2 = in.nextInt(); 62 output.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c2); 63 if (c2 == js.jia(a, b)) { 64 sum += 10; 65 System.out.println("答案正确"); 66 } 67 else { 68 System.out.println("答案错误"); 69 } 70 71 break ; 72 case 4: 73 System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"="); 74 while(a<b) { 75 a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 76 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 77 } 78 int c3 = in.nextInt(); 79 output.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c3); 80 if (c3 == js.jian(a,b)) { 81 sum += 10; 82 System.out.println("答案正确"); 83 } 84 else { 85 System.out.println("答案错误"); 86 } 87 break ; 88 89 } 90 91 } 92 System.out.println("成绩"+sum); 93 output.println("成绩:"+sum); 94 output.close(); 95 } 96 }
1 package shiyan; 2 3 public class jisuanji<T> { 4 private T a; 5 private T b; 6 public jisuanji() { 7 a=null; 8 b=null; 9 } 10 public jisuanji(T a,T b) { 11 this.a=a; 12 this.b=b; 13 } 14 public int jia(int a,int b) 15 { 16 return a+b; 17 } 18 public int jian(int a,int b) 19 { 20 return a-b; 21 } 22 public int chen(int a,int b) 23 { 24 return a*b; 25 } 26 public int chu(int a,int b) 27 { 28 if(b!=0&&a%b==0) 29 return a/b; 30 else 31 return 0; 32 } 33 }
l 采用结对编程方式,与学习伙伴合作完成实验九编程练习1;
1 package test1; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.File; 5 import java.io.FileInputStream; 6 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 9 import java.util.ArrayList; 10 import java.util.Collections; 11 import java.util.Scanner; 12 13 public class Main{ 14 private static ArrayList<Student> studentlist; 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 studentlist = new ArrayList<>(); 17 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 18 File file = new File("F:\\身份证号.txt"); 19 try { 20 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); 21 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); 22 String temp = null; 23 while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { 24 25 Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); 26 27 linescanner.useDelimiter(" "); 28 String name = linescanner.next(); 29 String number = linescanner.next(); 30 String sex = linescanner.next(); 31 String age = linescanner.next(); 32 String province =linescanner.nextLine(); 33 Student student = new Student(); 34 student.setName(name); 35 student.setnumber(number); 36 student.setsex(sex); 37 int a = Integer.parseInt(age); 38 student.setage(a); 39 student.setprovince(province); 40 studentlist.add(student); 41 42 } 43 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 44 System.out.println("学生信息文件找不到"); 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } catch (IOException e) { 47 System.out.println("学生信息文件读取错误"); 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 } 50 boolean isTrue = true; 51 while (isTrue) { 52 System.out.println("选择你的操作,输入正确格式的选项"); 53 System.out.println("A.按姓名字典排序"); 54 System.out.println("B.输出年龄最大和年龄最小的人"); 55 System.out.println("C.寻找老乡"); 56 System.out.println("D.寻找年龄相近的人"); 57 System.out.println("F.退出"); 58 String m = scanner.next(); 59 switch (m) { 60 case "A": 61 Collections.sort(studentlist); 62 System.out.println(studentlist.toString()); 63 break; 64 case "B": 65 int max=0,min=100; 66 int j,k1 = 0,k2=0; 67 for(int i=1;i<studentlist.size();i++) 68 { 69 j=studentlist.get(i).getage(); 70 if(j>max) 71 { 72 max=j; 73 k1=i; 74 } 75 if(j<min) 76 { 77 min=j; 78 k2=i; 79 } 80 81 } 82 System.out.println("年龄最大:"+studentlist.get(k1)); 83 System.out.println("年龄最小:"+studentlist.get(k2)); 84 break; 85 case "C": 86 System.out.println("老家?"); 87 String find = scanner.next(); 88 String place=find.substring(0,3); 89 for (int i = 0; i <studentlist.size(); i++) 90 { 91 if(studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1,4).equals(place)) 92 System.out.println("老乡"+studentlist.get(i)); 93 } 94 break; 95 96 case "D": 97 System.out.println("年龄:"); 98 int yourage = scanner.nextInt(); 99 int near=agenear(yourage); 100 int value=yourage-studentlist.get(near).getage(); 101 System.out.println(""+studentlist.get(near)); 102 break; 103 case "F": 104 isTrue = false; 105 System.out.println("退出程序!"); 106 break; 107 default: 108 System.out.println("输入有误"); 109 110 } 111 } 112 } 113 public static int agenear(int age) { 114 int j=0,min=53,value=0,k=0; 115 for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++) 116 { 117 value=studentlist.get(i).getage()-age; 118 if(value<0) value=-value; 119 if (value<min) 120 { 121 min=value; 122 k=i; 123 } 124 } 125 return k; 126 } 127 128 }
1 package test1; 2 3 public class Student implements Comparable<Student> { 4 5 private String name; 6 private String number ; 7 private String sex ; 8 private int age; 9 private String province; 10 11 public String getName() { 12 return name; 13 } 14 public void setName(String name) { 15 this.name = name; 16 } 17 public String getnumber() { 18 return number; 19 } 20 public void setnumber(String number) { 21 this.number = number; 22 } 23 public String getsex() { 24 return sex ; 25 } 26 public void setsex(String sex ) { 27 this.sex =sex ; 28 } 29 public int getage() { 30 31 return age; 32 } 33 public void setage(int age) { 34 // int a = Integer.parseInt(age); 35 this.age= age; 36 } 37 38 public String getprovince() { 39 return province; 40 } 41 public void setprovince(String province) { 42 this.province=province ; 43 } 44 45 public int compareTo(Student o) { 46 return this.name.compareTo(o.getName()); 47 } 48 49 public String toString() { 50 return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+number+"\t"+province+"\n"; 51 } 52 }
l 采用结对编程方式,与学习伙伴合作完成实验十编程练习2。
1 package shiyan; 2 import java.util.Scanner; 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.PrintWriter; 5 6 public class Main { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 9 PrintWriter output = null; 10 try { 11 output = new PrintWriter("E:/test.txt"); 12 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 13 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 14 System.out.println("文件输出失败"); 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 int sum=0; 18 jisuanji js=new jisuanji(); 19 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 20 int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 21 int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 22 int n = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 4 ); 23 24 switch(n) 25 { 26 case 1: 27 System.out.println(a+"/"+b+"="); 28 while(b==0){ 29 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 30 } 31 while(a%b!=0) { 32 a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 33 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 34 } 35 double c = in.nextDouble(); 36 output.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c); 37 if (c == js.chu(a,b)) { 38 sum += 10; 39 System.out.println("答案正确"); 40 } 41 else { 42 System.out.println("答案错误"); 43 } 44 45 break; 46 47 case 2: 48 System.out.println(a+"*"+b+"="); 49 int c1 = in.nextInt(); 50 output.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c1); 51 if (c1 == js.chen(a, b)) { 52 sum += 10; 53 System.out.println("答案正确"); 54 } 55 else { 56 System.out.println("答案错误"); 57 } 58 break; 59 case 3: 60 System.out.println(a+"+"+b+"="); 61 int c2 = in.nextInt(); 62 output.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c2); 63 if (c2 == js.jia(a, b)) { 64 sum += 10; 65 System.out.println("答案正确"); 66 } 67 else { 68 System.out.println("答案错误"); 69 } 70 71 break ; 72 case 4: 73 System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"="); 74 while(a<b) { 75 a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 76 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 77 } 78 int c3 = in.nextInt(); 79 output.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c3); 80 if (c3 == js.jian(a,b)) { 81 sum += 10; 82 System.out.println("答案正确"); 83 } 84 else { 85 System.out.println("答案错误"); 86 } 87 break ; 88 89 } 90 91 } 92 System.out.println("成绩"+sum); 93 output.println("成绩:"+sum); 94 output.close(); 95 } 96 }
1 package shiyan; 2 3 public class jisuanji<T> { 4 private T a; 5 private T b; 6 public jisuanji() { 7 a=null; 8 b=null; 9 } 10 public jisuanji(T a,T b) { 11 this.a=a; 12 this.b=b; 13 } 14 public int jia(int a,int b) 15 { 16 return a+b; 17 } 18 public int jian(int a,int b) 19 { 20 return a-b; 21 } 22 public int chen(int a,int b) 23 { 24 return a*b; 25 } 26 public int chu(int a,int b) 27 { 28 if(b!=0&&a%b==0) 29 return a/b; 30 else 31 return 0; 32 } 33 }
实验总结:
对数据结构中的一些基本类型有了进一步的了解,通过注释,编译逐渐理解了本周理论知识所讲的知识,感受到了它们的区别和联系,在本周实验中还增加了一个结对实验,这个合作实验让我们发现了彼此的不足和需要改进的地方,是 一个很好的相互学习的过程。复习了前面学过的知识细节,例如强制转换类型时进行判断的instanceof语句。初步体会了合作编程,互相提高的过程和乐趣。