Java中几个常用类
1.1 包装类
把八大基本数据类型封装到一个类中,并提供属性和方法,更方便的操作基本数据类型。
包装类的出现并不是用于取代基本数据类型,也取代不了。
包装类位于java.lang包中
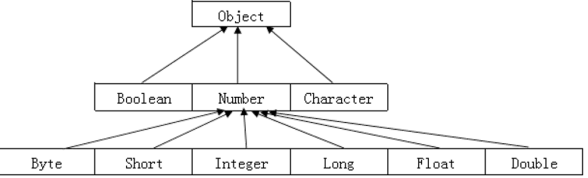
Number 类
Number数值类型是byte、double、float、int、long 和 short类的抽象父类,提供把包装类转化成基本数据类型的方法(xxxValue)。
1.2 Integer
Interger 是int基本数据类型的包装类,在Integer内部封装了一个final int value的属性。
1.2.1 常用方法
[1] 构造方法.创建出对应的 int 类型的值
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 // 【1】Integer 属性 3 //System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE); 4 //System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE); 5 6 // 【2】构造方法 7 int a = 10; 8 String bStr = "20"; 9 Integer i1 = new Integer(a); 10 // 可能抛出NumberFormatException异常 11 Integer i2 = new Integer(bStr); 12 System.out.println(i1.toString()); 13 System.out.println(i2.toString()); 14 }
[2] int<->Integer<->string
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 4 5 // int->Integer 6 7 Integer i1 = new Integer(10); 8 9 Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf(20); 10 11 12 13 // Integer->int 14 15 int a = i1.intValue(); 16 17 18 19 // String->Integer 20 21 Integer i3 = new Integer("30"); 22 23 Integer i4 = Integer.valueOf("40"); 24 25 26 27 //Integer->String 28 29 System.out.println(i3.toString()); 30 31 32 33 // String->int 34 35 int b = Integer.parseInt("50"); 36 37 38 39 // int->String 40 41 String str = Integer.toString(10); 42 43 //String str2 = Integer.toString(8, 2); 44 45 //System.out.println(str2); 46 47 }
[3] Comparable接口
Comparable 表示具有比较能力,对象可比较大小,此接口强行对实现它的每个类的对象进行整体排序。这种排序被称为类的自然排序。
Comparable 定义了a.compareTo(b),返回值表示
|
a.compareTo(b) |
返回值 |
排序 |
|
a < b |
负整数 |
升序 |
|
a = b |
0 |
相等 |
|
a > b |
正整数 |
降序 |
1 // 【2】Integer的比较 2 3 Integer i2 = new Integer(20); 4 5 Integer i3 = new Integer(10); 6 7 8 9 System.out.println(i2.equals(i3)); 10 11 System.out.println(i2.compareTo(i3));
1.2.2 自动装箱和自动拆箱
自动装箱
把基本数据类型自动转化成对象的包装类的过程称为自动装箱(auto-boxing)
1 Integer i = 10;
把包装类自动转化成对于的基本数据类型的过程称为自动拆箱(auto-unboxing)
int a = i;
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 4 5 // Integer i1 = new Integer(10); 6 7 // 自动装箱 8 9 Integer i2 = 20; // i2 = new Integer(20); 10 11 System.out.println(i2.toString()); 12 13 14 15 // 自动拆箱 16 17 Integer i3 = new Integer(30); 18 19 int a = i3; // i3.intValue(); 20 21 }
注意:
[1]自动装箱和自动拆箱是jdk1.5开始的
[2]不要过于频繁的使用拆装箱操作
1.3 其他基本数据类型包装类
其他包装类学习方法和Integer完全一样。
1.4 String
1.4.1 字符串本质
String 类代表字符串。Java 程序中的所有字符串字面值(如 "abc" )都作为此类的对象。
字符串本质上是一个字符数组,它们的值在创建之后不能更改,所以字符串是常量;
可以把字符串看出是字符数组的包装类,内部声明一个private final char value[];
因为 String 对象是不可变的,所以可以共享。
通过字面量创建的字符串分配在常量区。
1.4.2 字符串常用方法
[1]构造方法
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 // 在堆区初始化一个空字符串 4 5 String str1 = new String(); 6 7 8 9 // 通过一个字节数组构建一个字符串 10 11 byte[] bytes = {97,98,99}; 12 13 // 通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的 byte 数组 14 15 // System.out.println(Charset.defaultCharset()); 16 17 String str2 = new String(bytes); 18 19 System.out.println(str2); 20 21 22 23 byte[] byte2 = {-42,-48}; 24 25 String str3 = null; 26 27 try { 28 29 // 使用指定的字符集对字节序列进行解码 30 31 str3 = new String(byte2,"GBK"); 32 33 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { 34 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 37 } 38 39 System.out.println(str3); 40 41 42 43 // 需求:对一个utf-8的字节序列进行解码 44 45 byte[] byte3 = {-28,-72,-83,-28,-72,-83}; 46 47 try { 48 49 // sssString str4 = new String(byte3, "UTF-8"); 50 51 String str4 = new String(byte3,0,3, "UTF-8"); 52 53 System.out.println("str4:"+str4); 54 55 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { 56 57 e.printStackTrace(); 58 59 } 60 61 62 63 // 通过字符数组构建字符串 64 65 char[] c1 = {'a','b','c','中','国'}; 66 67 // String str5 = new String(c1); 68 69 String str5 = new String(c1,0,3); 70 71 System.out.println(str5); 72 73 74 String str6 = new String("abc"); 75 76 String str7 = "abc"; 77 78 System.out.println(str6 == str7); 79 80 81 }
常见计算机编码
GB2312/GBK/Unicode/UTF-8
[2] 字符串的比较
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 // 【3】字符串比较 4 5 String str1 = "abc"; 6 7 String str2 = "Abc"; 8 9 10 11 System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2)); 12 13 // 忽略大小写比较 14 15 System.out.println(str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2)); 16 17 18 19 // 需求:请输入验证码 20 21 /*String validCode = "a4Df"; 22 23 System.out.println("请输入验证码:"+validCode); 24 25 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 26 27 String inputStr = sc.next(); 28 29 30 31 if(inputStr.compareToIgnoreCase(validCode) == 0) { 32 33 System.out.println("验证码正确"); 34 35 }else { 36 37 System.out.println("验证码错误"); 38 39 }*/ 40 41 42 43 System.out.println(str1.contentEquals(str2)); 44 45 System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); 46 47 System.out.println(str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2)); 48 49 }
CharSequence 接口把字符串看出一个可读序列,提供了charAt(index)获取指定索引处的字符;length() 字符数组或者字符串的长度。
[3]查找、搜索字符串
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 // 【3】查找、搜索字符串中是否包含其他子串 4 5 String str1 = "hello world"; 6 7 8 9 // 是否包含子串 10 11 System.out.println(str1.contains("world")); 12 13 14 15 System.out.println(str1.startsWith("he")); 16 17 System.out.println(str1.endsWith("world")); 18 19 System.out.println(str1.startsWith("ll", 2)); 20 21 22 23 // 需求:判断一个文件是否是png图片 24 25 String fileName = "logo.png"; 26 27 if(fileName.endsWith(".png")) { 28 29 System.out.println(fileName+"是一张图片"); 30 31 } 32 33 34 35 36 37 // 查找字符串 38 39 String str2 = "hello world hello"; 40 41 // 从左向右查找字符'o'第一次出现的位置,找到返回索引,没找到返回-1 42 43 System.out.println(str2.indexOf('t')); 44 45 System.out.println(str2.indexOf('o',5)); 46 47 // 从左向右查找字符串“ll”第一次出现的位置,找到返回索引,没找到返回-1 48 49 System.out.println(str2.indexOf("ll")); 50 51 System.out.println(str2.indexOf("ll",5)); 52 53 54 55 // 从右向左查找字符'o'第一次出现的位置,找到返回索引,没找到返回-1 56 57 System.out.println(str2.lastIndexOf('o')); 58 59 // lastIndex(char,fromIndex) 60 61 // lastIndex(string); 62 63 // lastIndex(string,fromIndex); 64 65 }
[4]格式化字符串
通过指定占位符(%开始)格式化字符串
|
%d |
格式化整形 |
|
%f |
格式化浮点型 |
|
%.nf |
格式化浮点型四舍五入保留n为小数, |
|
%c |
格式化字符 |
|
%s |
格式化字符串 |
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 // 【4】格式化字符串 4 5 float price = 998.126f; 6 7 int a = 10; 8 9 int b = 2; 10 11 // 10 / 2 = 5 12 13 14 15 String str1 = String.format("%d / %d = %d", a,b,(a/b)); 16 17 System.out.println(str1); 18 19 // 四舍五入保留两位小数 20 21 String str2 =String.format("$%.2f", price); 22 23 System.out.println(str2); 24 25 }
[5] 把字符串按指定编码集编码成对于的字节序列
1 // String str3 = "abc"; 2 3 String str3 = "中国"; 4 5 // 使用默认的字符集(GBK) 6 7 byte[] byte1 = str3.getBytes(); 8 9 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(byte1)); 10 11 12 13 14 15 //String str4 = "abc"; 16 17 String str4 = "中国"; 18 19 // 使用utf8编码 20 21 byte[] bytes2 = str4.getBytes("UTF-8"); 22 23 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes2));
[6]替换字符串
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 4 5 String str1 = "hello,world"; 6 7 String newStr1 = str1.replace('o', '8'); 8 9 System.out.println(newStr1); 10 11 12 13 String newStr2 = str1.replace("ll", ""); 14 15 System.out.println(newStr2); 16 17 18 19 // 需求:186-1234-2234 20 21 String str3 = "186-1234-2234"; 22 23 System.out.println(str3.replace("-", "")); 24 25 26 27 // 正则表达式专门用于验证字符串是否符合特定的格式。 28 29 String str4 = "6764"; 30 31 // 验证str4是否输入的是一串数字 32 33 boolean r = str4.matches("\\d+"); 34 35 System.out.println(r); 36 37 38 39 // 需求:abc123te23daf去掉数字 40 41 String str5 = "abc123te23daf"; 42 43 // String newStr5 = str5.replaceAll("\\d+", ""); 44 45 String newStr5 = str5.replaceFirst("\\d+", ""); 46 47 System.out.println(newStr5); 48 49 50 51 }
[7]拆分字符串
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 4 5 //【7】 根据指定字符串拆分字符串 6 7 String str1 = "abc-123"; 8 9 String[] arr = str1.split("-"); 10 11 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); 12 13 14 15 // 需求:请快速构建一个26个小写英文字母的数组 16 17 String str2= "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"; 18 19 String[] arr2 = str2.split(""); 20 21 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2)); 22 23 24 25 // 根据正则拆分字符串 26 27 String str3 = "abc123ta12asd"; 28 29 String[] arr3 = str3.split("\\d+"); 30 31 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr3)); 32 33 34 35 36 // 需求:请获取一个文件的文件名 37 38 String fileName = "logo.png"; 39 40 String[] arr4 = fileName.split("\\."); 41 42 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr4)); 43 44 45 }
[8] 求子串、大小写转换
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 4 5 //【8】 求子串 6 7 String str1 = "abc123"; 8 9 // fromIndex:开始位置,endInde 结束的位置 10 11 // 含头不含尾 12 13 String sub1 = str1.substring(0, 3); 14 15 System.out.println(sub1); 16 17 18 19 String sub2 = str1.substring(3); 20 21 System.out.println(sub2); 22 23 24 25 26 // 【9】大小写转换 27 28 String str3 = "Abc"; 29 30 System.out.println(str3.toUpperCase()); 31 32 System.out.println(str3.toLowerCase()); 33 34 35 36 }
[9]其他方法
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 4 5 // 去掉前导空格和后导空格 6 7 String str1 = " abc "; 8 9 String newStr1 = str1.trim(); 10 11 System.out.println(str1.length()); 12 13 14 15 // 获取字符串的字符数组 16 17 char[] arr = str1.toCharArray(); 18 19 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); 20 21 22 23 24 // 把其他数据类型转化为字符串 25 26 String str2 = String.valueOf(10); 27 28 System.out.println(str2); 29 30 }
1.5 StringBuffer
StringBuffer是字符的可变容器。可以在程序运行过程中向容器中添加、删除、修改字符。
StringBuffer 本质上是一个字符数组的包装类,并提供了很多方法向这个字符数组中添加、删除、修改字符。
StringBuffer 是线程安全的
1.5.1 StringBuffer工作原理
StringBuffer 内部维护了一个字符数组,默认字符数组的长度是16.当开发者向这个字符数组中添加元素时,如果有额外空间,直接添加到数组中,如果没有额外空间,StringBuffer内部自动拓容,拓容规则:当前容量*2+2,根据拓容的新空间,复制当前的数组内容到新数组中。
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 3 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); 4 sb.append("a"); 5 sb.append("b"); 6 System.out.println(sb.capacity()); 7 8 sb.append("1234567890ABCD"); 9 sb.append('x'); 10 System.out.println(sb); 11 System.out.println(sb.capacity()); 12 13 // 未来如果确定不再向sb中添加字符, 14 // 优化内部的数组到指定的长度 15 sb.trimToSize(); 16 System.out.println(sb.capacity()); 17 }
1.5.2 常用方法
1 package cn.sxt03.string02; 2 3 4 5 public class Test01 { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 9 10 11 StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer(); 12 13 // 【1】添加 14 15 sb1.append("hello"); 16 17 sb1.append('d'); 18 19 20 21 // 返回字符串的长度 22 23 System.out.println(sb1.length()); 24 25 // 返回容器的大小 26 27 System.out.println(sb1.capacity()); 28 29 30 31 // 【2】删除 32 33 //System.out.println(sb1); 34 35 //sb1.delete(0, 5); 36 37 //System.out.println(sb1); 38 39 40 41 // 【3】insert(index,t) 在指定位置index添加t 42 43 sb1.insert(0, "123"); 44 45 System.out.println(sb1); 46 47 48 49 // 【4】修改 50 51 sb1.setCharAt(0, 'A'); 52 53 System.out.println(sb1); 54 55 56 57 // 【5】setLength 58 59 sb1.setLength(0); // 清空容器内容 60 61 sb1.append("中国"); 62 63 System.out.println(sb1); 64 65 } 66 67 }
1.6 StringBuilder
StringBuffer 是线程安全的,执行效率低,JDK1.0
StringBuiler 就是为了缓解执行效率低而产生的,但线程不安全。JDK 1.5



