IP地址和端口号
端口号是用两个字节(16位的二进制数)表示的,它的取值范围是0~65535,其中,0~1023之间的端口号用于一些知名的网络服务和应用,
用户的普通应用程序需要使用1024以上的端口号,从而避免端口号被另外一个应用或服务所占用。
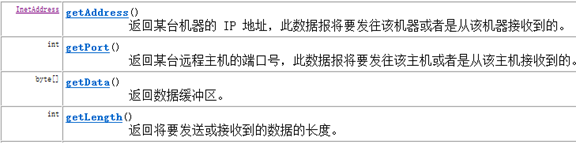
InetAddress
常用方法

代码演示:
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException { //InetAddress inet=InetAddress.getLocalHost(); //主机名+ip地址 InetAddress inet=InetAddress.getByName("DESKTOP-KCD8G34"); System.out.println(inet); String host=inet.getHostName(); String ip=inet.getHostAddress(); System.out.println(host+"..."+ip); }
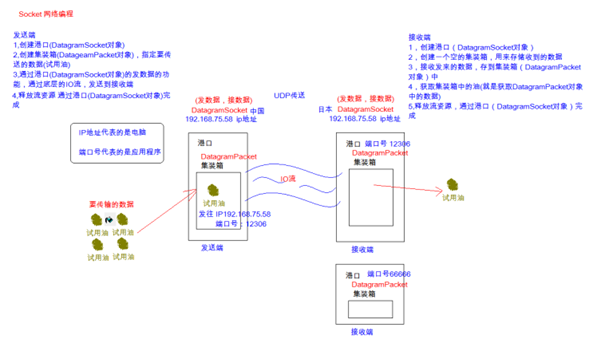
UDP通信
DatagramPacket


DatagramSocket



UDP网络程序
代码演示:
//发送端 public class UDPSend { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.打包 //明确数据 byte[] bytes="你好吗".getBytes(); //明确目的地的IP地址 InetAddress inet=InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"); //装包 DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length,inet,8888); //2.创建快递公司 DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(); //3.发送 ds.send(dp); //4.释放资源 ds.close(); } }
//接收端 public class UDPReceive { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //明确端口号 DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(8888); //创建接收数据的字节数组 byte[] bytes=new byte[1024]; //创建接收的数据包 DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length); //接收 ds.receive(dp); //获取接收包上的数据 int length=dp.getLength(); String ip=dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); int port=dp.getPort(); System.out.println("ip地址为:"+ip+"端口号为:"+port+"发送的内容为:"+new String(bytes,0,length)); //释放资源 ds.close(); } }
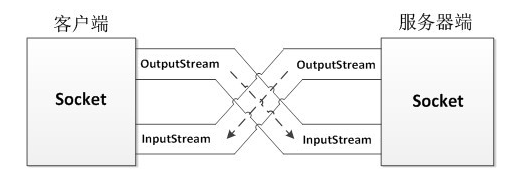
TCP通信
一个是ServerSocket类,用于表示服务器端,一个是Socket类,用于表示客户端。
ServerSocket


Socket


|
方法声明 |
功能描述 |
|
int getPort() |
该方法返回一个int类型对象,该对象是Socket对象与服务器端连接的端口号 |
|
InetAddress getLocalAddress() |
该方法用于获取Socket对象绑定的本地IP地址,并将IP地址封装成InetAddress类型的对象返回 |
|
void close() |
该方法用于关闭Socket连接,结束本次通信。在关闭socket之前,应将与socket相关的所有的输入/输出流全部关闭,这是因为一个良好的程序应该在执行完毕时释放所有的资源 |
|
InputStream getInputStream() |
该方法返回一个InputStream类型的输入流对象,如果该对象是由服务器端的Socket返回,就用于读取客户端发送的数据,反之,用于读取服务器端发送的数据 |
|
OutputStream getOutputStream() |
该方法返回一个OutputStream类型的输出流对象,如果该对象是由服务器端的Socket返回,就用于向客户端发送数据,反之,用于向服务器端发送数据 |
图解:
代码演示:
//发送端 public class UDPSend { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.打包 //明确数据 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); //明确目的地的IP地址 InetAddress inet=InetAddress.getByName("192.168.1.171"); //2.创建快递公司 DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(); while(true){ String mes=sc.next(); byte[] bytes=mes.getBytes(); //装包 DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length,inet,6666); //3.发送 ds.send(dp); } //4.释放资源 //ds.close(); }
//接收端 public class UDPReceive { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //明确端口号 DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(8888); //创建接收数据的字节数组 byte[] bytes=new byte[1024]; //创建接收的数据包 while(true){ DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length); //接收 ds.receive(dp); //获取接收包上的数据 int length=dp.getLength();//明确发送的字节长度 String ip=dp.getAddress().getHostAddress(); int port=dp.getPort(); System.out.println("ip地址为:"+ip+"端口号为:"+port+"发送的内容为:" +new String(bytes,0,length)); } }
//服务器端 public class TCPServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建服务器套接字 ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(7777); //调用accept方法与客户端创建链接 Socket socket=server.accept(); InputStream in=socket.getInputStream(); byte[] bytes=new byte[1024]; int len=in.read(bytes); System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len)); //服务器给客户端回复 OutputStream out=socket.getOutputStream(); out.write("收到!over!".getBytes()); server.close(); }
//客户端 public class TCPCLient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建Socket对象,连接服务器 Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",7777); //2.通过客户端套接字对象Socket对象中的获取字节输出流的方法 OutputStream out=socket.getOutputStream(); //3.将数据写向服务器 out.write("服务器你好".getBytes()); //接收服务器端的回复 InputStream in=socket.getInputStream(); byte[] bytes=new byte[1024]; int len=in.read(bytes); System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len)); //释放资源 socket.close(); }
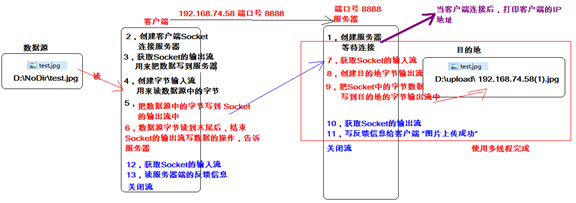
文件上传案例

代码演示:
public class TCPServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(5555); Socket socket=server.accept(); //明确数据源 InputStream in=socket.getInputStream(); //明确目的地 File file=new File("x:\\upload"); if(!file.exists()){ file.mkdirs(); } //域名+毫秒值 String filename="oracle"+System.currentTimeMillis()+".jpg"; FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(file+File.separator+filename); //复制 int len=0; byte[] bytes=new byte[1024]; while((len=in.read(bytes))!=-1){ fos.write(bytes,0,len); } //回复客户端 OutputStream out=socket.getOutputStream(); out.write("上传成功!".getBytes()); //释放资源 server.close(); fos.close(); } }
public class TCPClinet { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket=new Socket("192.168.1.171",7000); OutputStream out=socket.getOutputStream(); //明确数据源 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("x:\\test\\img1.jpg"); int len=0; byte[] bytes=new byte[1024]; //文件复制 while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ out.write(bytes,0,len); } //告诉服务器端不要在读了到末尾了 socket.shutdownOutput(); //服务器端回复 InputStream in=socket.getInputStream(); len=in.read(bytes); System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len)); //释放资源 fis.close(); socket.close(); } }
文件上传案例多线程版本
代码演示:
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(6000); while(true){ Socket socket=server.accept(); new Thread(new Upload(socket)).start(); } } }
public class Upload implements Runnable{ private Socket socket; public Upload(Socket socket){ this.socket=socket; } public void run() { //明确数据源 FileOutputStream fos=null; try { InputStream in= socket.getInputStream(); //明确目的地 File file=new File("x:\\upload"); if(!file.exists()){ file.mkdirs(); } //域名+毫秒值 String filename="oracle"+System.currentTimeMillis()+".jpg"; fos=new FileOutputStream(file+File.separator+filename); //复制 int len=0; byte[] bytes=new byte[1024]; while((len=in.read(bytes))!=-1){ fos.write(bytes,0,len); } //回复客户端 OutputStream out=socket.getOutputStream(); out.write("上传成功!".getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //释放资源 try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }

