005、列表的基本使用
列表 list [ ]
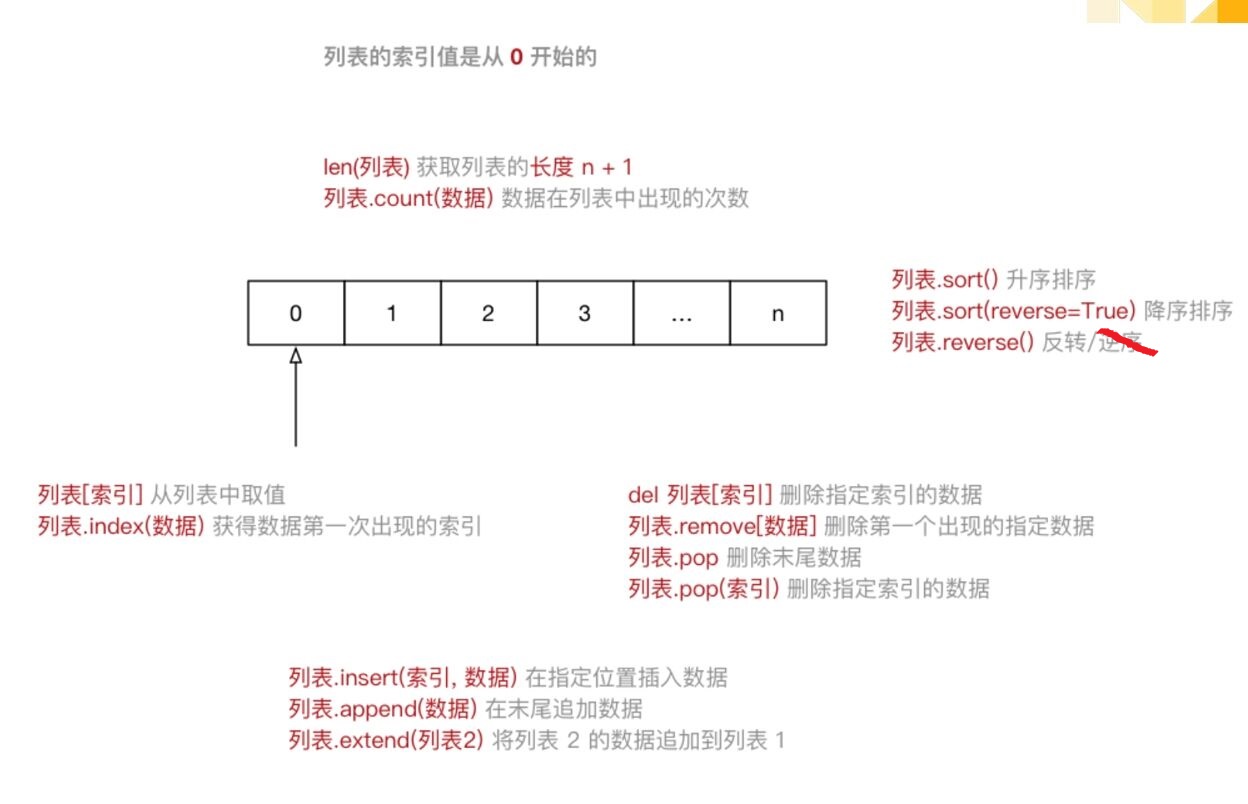
列表基本用法:
1、用 [ ] 定义,成员之间用 , 分隔, 成员可以是任意类型 ;
2、成员 可以重复 ;
3、获取某一个成员的下标: 列表名 . index('red') ,无find() 方法 ,字符串有 find() 方法;
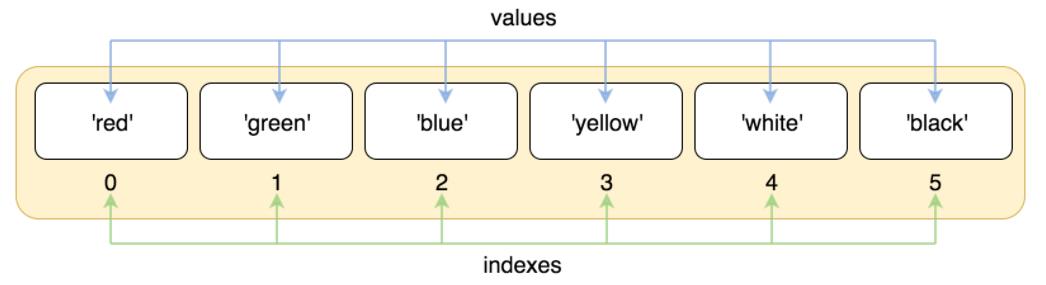
4、有序,通过下标索引 [1] ,从 0 开始 ,越界取值报错;
5、切片, 列表名[开始索引(默认为0) :结束索引 :步长(默认为 1)]
列表常用方法和函数:
列表.count(成员) :统计成员在列表中的次数 ;
列表.sort() / 列表.sort(reverse=True) : 升 / 降排序 ;
列表.reverse() : 反转 ;
列表[索引] : 取值,下表过界会报错 ;
列表.index(成员):获得成员第一次出现的位置 ;
列表.insert(索引,成员):在指定位置插入成员 ;
列表.append(成员):在末尾追加成员 ;
列表.extend(列表2):将列表2的数据追加到列表1;
len(列表) : 获取列表的长度 ;
del 列表[索引]:删除指定索引的数据 ;析构函数,垃圾回收;
列表.remove(成员):删除第一个出现成员的指定数据 ;
列表.pop:删除末尾成员;
列表.pop(索引):删除指定索引的数据;
列表名[1] = 'red' 修改 列表[1] 成员的值;
定义一个空列表,并用 append 追加值;

# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # @Author: Sky # @Email: 2780619724@qq.com # @Time: 2021/7/23 17:02 list = [] # 定义了一个空列表 list.append('bb') print(list) list[1] = 'aa' # 因为没有索引为 1的列表元素;给 [1] 赋值会报错,但是可以用 append 追加一个元素 print(list)
执行结果如下:

D:\SkyWorkSpace\WorkSpace\Pytest\Temp\day06\venv\Scripts\python.exe D:/SkyWorkSpace/WorkSpace/Pytest/Temp/day06/test_demo/test_07.py Traceback (most recent call last): File "D:/SkyWorkSpace/WorkSpace/Pytest/Temp/day06/test_demo/test_07.py", line 12, in <module> list[1] = 'aa' # 因为没有索引为 1的列表元素;给 [1] 赋值会报错,但是可以用 append 追加一个元素 IndexError: list assignment index out of range ['bb'] Process finished with exit code 1
列表基本用法

# 1、用 [ ] 定义,成员之间用 , 分隔, 成员可以是任意类型 ; # 2、成员 可以重复 ; # 3、获取某一个成员的下标: 列表名 . index('red') ,无find() 方法 ,字符串有 find() 方法; # 4、有序,通过下标索引 [1] ,从 0 开始 ,越界取值报错; # 5、切片, 列表名[开始索引(默认为0) :结束索引 :步长(默认为1)] list_all = [1, 3.14159, 'python', 'python', [1, 2, 3], (4, 5, 6), {'name': 'sky', 'age': 18}, {'red', 'green', 'blue', 'red'}] print(list_all) print(list_all.index('python')) # 获取第一个python的索引 print(list_all[1]) print(list_all[::-1]) print(list_all[1:7:2]) # 索引 1 开始,加2 ,一直到6, 1 ,3,5 list_2 = [1, 2, 3] print(len(list_2)) print("aa")
执行结果如下:

D:\SkyWorkSpace\WorkSpace\Pytest\Temp\day06\venv\Scripts\python.exe D:/SkyWorkSpace/WorkSpace/Pytest/Temp/day06/test_demo/test_08.py [1, 3.14159, 'python', 'python', [1, 2, 3], (4, 5, 6), {'name': 'sky', 'age': 18}, {'red', 'green', 'blue'}] 2 3.14159 [{'red', 'green', 'blue'}, {'name': 'sky', 'age': 18}, (4, 5, 6), [1, 2, 3], 'python', 'python', 3.14159, 1] [3.14159, 'python', (4, 5, 6)] 3 aa Process finished with exit code 0
列表常用方法和函数:

# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # @Author: Sky # @Email: 2780619724@qq.com # @Time: 2021/7/23 19:19 list_all = [1, 3.14159, 'python', 'python', [1, 2, 3], (4, 5, 6), {'name': 'sky', 'age': 18}, {'red', 'green', 'blue', 'red'}] print(list_all) print('============== 统计 ==============') print(list_all.count('python')) # 统计 print('=============== 排序 =============') nums_1 = [1, 3, 2, 5, 4] nums_1.sort() # 排序 print(nums_1) nums_1.sort(reverse=True) # 逆序 print(nums_1) print('=============== 排序 =============') nums_2 = [1, 3, 2, 5, 4] print(sorted(nums_2)) # 注意方法的作用域 print(nums_2) # 打印结果还是 [1, 3, 2, 5, 4] print(sorted(nums_2, reverse=True)) # 逆序 print(nums_2) print('=============== 排序 =============') names = ['jack', 'Tony', 'Lee', 'sky'] names.sort(key=lambda i: i[1]) # 指定排序规则,按照成员的第2个字母排序 print(names) print('=============== 反转 =============') nums_3 = [1, 3, 2, 5, 4] nums_3.reverse() # 列表反转,不等于逆序 print(nums_3) print('=============== 取值 =============') print(list_all[1]) print(list_all.index('python')) print('=============== 增加 =============') stu_names = ['jack', 'Tony', 'Lee', 'sky'] print(stu_names) stu_names.insert(0, 'Jane') print(stu_names) stu_names.append('Lilei') print(stu_names) stu_names_2 = ['勤学', '好学', '恒学'] stu_names.extend(stu_names_2) print(stu_names) print('=============== 删除 =============') stu_names_3 = ['克定', '克文', '克武', '克强', '克武', '徐世昌', '张勋', '世凯', '克武'] print(stu_names_3) del stu_names_3[2] print(stu_names_3) stu_names_3.remove('克武') print(stu_names_3) stu_names_3.pop() # 默认删除最后一个元素 print(stu_names_3) stu_names_3.pop(2) # 删除指定索引成员 print(stu_names_3)
执行结果如下:

D:\SkyWorkSpace\WorkSpace\Pytest\Temp\day06\venv\Scripts\python.exe D:/SkyWorkSpace/WorkSpace/Pytest/Temp/day06/test_demo/test_08.py [1, 3.14159, 'python', 'python', [1, 2, 3], (4, 5, 6), {'name': 'sky', 'age': 18}, {'red', 'blue', 'green'}] ============== 统计 ============== 2 =============== 排序 ============= [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] =============== 排序 ============= [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] [1, 3, 2, 5, 4] [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] [1, 3, 2, 5, 4] =============== 排序 ============= ['jack', 'Lee', 'sky', 'Tony'] =============== 反转 ============= [4, 5, 2, 3, 1] =============== 取值 ============= 3.14159 2 =============== 增加 ============= ['jack', 'Tony', 'Lee', 'sky'] ['Jane', 'jack', 'Tony', 'Lee', 'sky'] ['Jane', 'jack', 'Tony', 'Lee', 'sky', 'Lilei'] ['Jane', 'jack', 'Tony', 'Lee', 'sky', 'Lilei', '勤学', '好学', '恒学'] =============== 删除 ============= ['克定', '克文', '克武', '克强', '克武', '徐世昌', '张勋', '世凯', '克武'] ['克定', '克文', '克强', '克武', '徐世昌', '张勋', '世凯', '克武'] ['克定', '克文', '克强', '徐世昌', '张勋', '世凯', '克武'] ['克定', '克文', '克强', '徐世昌', '张勋', '世凯'] ['克定', '克文', '徐世昌', '张勋', '世凯'] Process finished with exit code 0
判断 某成员 是否 在列表中 in

names = ['克定', '克文', '克武', '徐世昌'] print('克文' in names) print('世凯' in names)
执行结果如下:

D:\SkyWorkSpace\WorkSpace\Pytest\Temp\day06\venv\Scripts\python.exe D:/SkyWorkSpace/WorkSpace/Pytest/Temp/day06/test_demo/test_08.py
True
False
Process finished with exit code 0
与列表相关的 , 字符串的 split('str') 和 str.join() 方法:

# 字符串的 split() 和 join() 方法 # 字符串是不可变序列 ; names = ['克定', '克文', '克武', '徐世昌'] names_all = '_'.join(names) print(names_all) print(names) sm = '民族,民权,民生' list_sm = sm.split(',') print(list_sm) print(sm)
执行结果如下:

D:\SkyWorkSpace\WorkSpace\Pytest\Temp\day06\venv\Scripts\python.exe D:/SkyWorkSpace/WorkSpace/Pytest/Temp/day06/test_demo/test_08.py 克定_克文_克武_徐世昌 ['克定', '克文', '克武', '徐世昌'] ['民族', '民权', '民生'] 民族,民权,民生 Process finished with exit code 0
字符串拼接的时候只能是同类型成员的字符串

# 字符串拼接的时候只能是同类型成员的字符串, # 有True,123 ,所以报错 TypeError: sequence item 4: expected str instance, bool found names = ['克定', '克文', '克武', '徐世昌', 123, True] names_all = '_'.join(names) print(names_all) print(names)
执行结果如下:

D:\SkyWorkSpace\WorkSpace\Pytest\Temp\day06\venv\Scripts\python.exe D:/SkyWorkSpace/WorkSpace/Pytest/Temp/day06/test_demo/test_08.py Traceback (most recent call last): File "D:/SkyWorkSpace/WorkSpace/Pytest/Temp/day06/test_demo/test_08.py", line 85, in <module> names_all = '_'.join(names) TypeError: sequence item 4: expected str instance, int found Process finished with exit code 1
补充知识:
1、函数和方法的作用域

# 从这一段代码可以体会到函数和方法有啥区别 ? # (1)函数作用域:从函数调用开始至函数执行完成,返回给调用者后,在执行过程中开辟的空间会自动释放, # 也就是说函数执行完成后,函数体内部通过赋值等方式修改变量的值不会保留,会随着返回给调用者后,开辟的空间会自动释放。 # (2)方法作用域:通过实例化的对象进行方法的调用,调用后开辟的空间不会释放,也就是说调用方法中对变量的修改值会一直保留。 colour_list = ['red', 'yellow', 'blue', 'green'] colour_list.sort() # 方法 print(colour_list) num_list = [3, 4, 2, 1, 5] sorted(num_list) # 函数的作用域,只在本行,执行后会释放,所以下面 print(num_list) 还是 [3, 4, 2, 1, 5] print(num_list)
执行结果如下:

D:\SkyWorkSpace\WorkSpace\Pytest\Temp\day06\venv\Scripts\python.exe D:/SkyWorkSpace/WorkSpace/Pytest/Temp/day06/test_demo/test_07.py ['blue', 'green', 'red', 'yellow'] [3, 4, 2, 1, 5] Process finished with exit code 0
2、del函数作用域

students = ['勤学', '好学', '敏学', '恒学'] print(students) print(id(students)) del students[2] # 用的是析构函数垃圾回收 students[2] 吧 ?调用del函数后,对象被回收; print(students) print(id(students)) print('==============================') students_2 = ['勤学', '好学', '敏学', '恒学'] print(students_2) print(id(students_2)) students_2.remove('敏学') print(students_2) print(id(students_2))
执行结果如下:

D:\SkyWorkSpace\WorkSpace\Pytest\Temp\day06\venv\Scripts\python.exe D:/SkyWorkSpace/WorkSpace/Pytest/Temp/day06/gggg/demo.py ['勤学', '好学', '敏学', '恒学'] 2294371583744 ['勤学', '好学', '恒学'] 2294371583744 ============================== ['勤学', '好学', '敏学', '恒学'] 2294372299072 ['勤学', '好学', '恒学'] 2294372299072 Process finished with exit code 0





