有一个按钮,想要单击并执行一个ViewModel的方法?Action可以解决这个问题。
Actions与方法
在传统的WPF中,你需要在ViewModel中创建一个属性并实现ICommand接口,然后将此属性绑定到按钮的Command属性上,这可以工作(不需要ViewModel与View的紧密联系,也不需要Code-behind.),但是这有点小麻烦,你只是想要调用ViewModel中的一个方法而已,不是在属性中调用方法。
Stylet优雅地解决了这个问题:
class ViewModel : Screen
{
public void DoSomething()
{
Debug.WriteLine("DoSomething called");
}
}
<UserControl x:Class="MyNamespace.View"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:s="https://github.com/canton7/Stylet">
<Button Command="{s:Action DoSomething}">Click me</Button>
</UserControl>
就是这么简单,点击按钮,执行方法!
如果方法还接受一个单一的参数,可以通过按钮的CommandParameter属性传递,如下例:
class ViewModel : Screen
{
public void DoSomething(string argument)
{
Debug.WriteLine(String.Format("Argument is {0}", argument));
}
}
<UserControl x:Class="MyNamespace.View"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:s="https://github.com/canton7/Stylet">
<Button Command="{s:Action DoSomething}" CommandParameter="Hello">Click me</Button>
</UserControl>
注意:Actions也支持ICommand属性的其他特性,例如KeyBinding.
守护属性
使用Stylet可以轻松控制是否使能按钮,我称之为守护属性(Guard Properties)。一个给定方法的守护属性是一个布尔型的属性,命名为"Can<方法名>",比如方法名为“DoSomething”,相应的守护属性为"CanDoSomething".
Stylet会检查守护属性是否存在,然后监测属性返回值,如果返回False,将会禁用按钮,反之使用能按钮。Stylet同时还会监测属性的PropertyChanged通知,从而可以更改按钮的使能状态。
比如:
class ViewModel : Screen
{
private bool _canDoSomething;
public bool CanDoSomething
{
get { return this._canDoSomething; }
set { this.SetAndNotify(ref this._canDoSomething, value); }
}
public void DoSomething()
{
Debug.WriteLine("DoSomething called");
}
}
事件
当事件发生时想要调用ViewModel的方法应该怎么做呢?Actions同样可以做到。语法是一样的,只是没有守护属性概念而已:
<UserControl x:Class="MyNamespace.View"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:s="https://github.com/canton7/Stylet">
<Button Click="{s:Action DoSomething}">Click me</Button>
</UserControl>
相对应的方法必须具有0-2个参数,可能的方法签名如下:
public void HasNoArguments() { }
// This can accept EventArgs, or a subclass of EventArgs
public void HasOneSingleArgument(EventArgs e) { }
// Again, a subclass of EventArgs is OK
public void HasTwoArguments(object sender, EventArgs e) { }
方法的返回类型
Action并不关心方法的返回类型,返回值会被丢弃。
例外的情况是如果返回值为Task(即方法是异步触发的)。这种情况下,Task等待async void方法的返回。如果方法返回Task并且包含异常,该异常会再次throw并且冒泡到Dispather,这会中断应用程序。除非处理这个异常,例如使用BootstrapperBase.OnUnhandledException。如果方法使用async void方式,但是这不利于单元测试。
Action目标
Action并非只能触发ViewModel中的方法,下面再详细讨论一下。
Stylet定义了一个继承的附加属性:View.ActionTarget。当View与其ViewModel相绑定,View根元素的 View.ActionTarget就被绑定到ViewModel,View中的所有元素也被继承了这个属性。当触发一个action,就触发相应的的 View.ActionTarget属性。
这就是说,默认情况下,actions都是由ViewModel的当前DataContext作为触发对象,这也是大多数我们期望的情况。
这一点很重要。在可视化树的多个层次里,DataContext可能会发生变化。但是,View.ActionTarget将保持一致(除非手动修改)。这就意味着action总是由ViewModel所处理,而不受所绑定对象的影响,这是绝大多数想要的情况。
当然你也可以修改View.ActionTarget针对单独的元素,像这样:
class InnerViewModel : Screen
{
public void DoSomething() { }
}
class ViewModel : Screen
{
public InnerViewModel InnerViewModel { get; private set; }
public ViewModel()
{
this.InnerViewModel = new InnerViewModel();
}
}
<UserControl x:Class="MyNamespace.View"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:s="https://github.com/canton7/Stylet">
<Button s:View.ActionTarget="{Binding InnerViewModel}" Command="{s:Action DoSomething}">Click me</Button>
</UserControl>
在这里,单击按钮,InnerViewModel.DoSomething将会被触发。并且由于View.ActionTarget是继承属性,Button的任何子元素也都会将View.ActionTargetr指向InnerViewModel.
你也可以覆写action的target(利用Target属性),但是由于WPF的限制,不能进行绑定,只能使用StaticResource, x:Static, x:Type等。
<Button Command="{s:Action DoSomething, Target={x:Static my:Globals.ButtonTarget}}">Click me</Button>
静态方法
Action也可以使用静态方法,如果Target是一个Type对象(在XAML中使用{x:Type ...}),你可以同时设置 View.ActionTarget和Action的Target属性。
public static class CommonButtonTarget
{
public static void DoSomething() { }
}
<Button Command="{s:Action DoSomething, Target={x:Type my:CommonButtonTarget}}">Click me</Button>
Action与样式
Action并不能与style setters一起工作。WPF中进行样式设置的类都是内部类,没有办法进行修改。
ContextMenu和Popup
对于ContextMenu,Popup,Frame,这些元素通常不属于可视化或逻辑树的元素,作为附加属性的View.ActionTarget需要根据要求作出调整,建议使用BindingProxy技术。
http://www.thomaslevesque.com/2011/03/21/wpf-how-to-bind-to-data-when-the-datacontext-is-not-inherited/
附加行为
有两种情况会阻止Action正确工作:View.ActionTarget为null或View.ActionTarget指定的方法并不存在,其默认的行为如下:
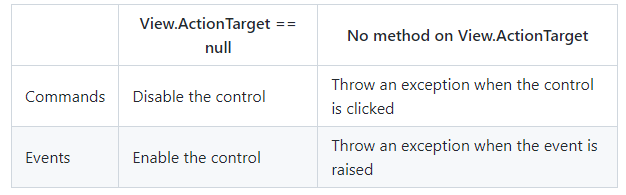
两种情况都应该加以解决,以使代码能够工作。
当然这种行为也是可配置的。为了控制View.ActionTarget为null的行为,设置NullTarget属性,如下:
<Button Command="{s:Action MyMethod, NullTarget=Enable}"/>
<Button Click="{s:Action MyMethod, NullTarget=Throw}"/>
为了控制View.ActionTarget指定的方法不存在的行为,设置ActionNotFound属性,如下所示:
<Button Command="{s:Action MyMethod, ActionNotFound=Disable}"/>
<Button Click="{s:Action MyMethod, ActionNotFound=Enable}"/>




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步