刷题篇--热题HOT 52-60
162.LRU缓存机制
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制。它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 get 和 写入数据 put 。获取数据 get(key) - 如果密钥 (key) 存在于缓存中,则获取密钥的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。写入数据 put(key, value) - 如果密钥不存在,则写入其数据值。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最近最少使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
进阶:你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
实例:LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* 缓存容量 */ );
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // 返回 1
cache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得密钥 2 作废
cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得密钥 1 作废
cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.get(3); // 返回 3
cache.get(4); // 返回 4
分析:O(1)时间复杂度=》主要有两个操作put&get,我们知道哈希表取数据理论上是O(1),链表插入数据是O(1)。那么就要牺牲空间将哈希表和链表结合起来。哈希表存入key和双向链表。使用双向链表是因为删除一个节点不需要格外信息,同时可以在常数时间内从头部或者尾部插入节点。
1 import java.util.Hashtable; 2 class LRUCache { 3 //创建一个内部类--双向链表,实现增加节点,删除节点,将节点调入头节点之后,删除尾节点之前的一个节点。双向链表的头结点和尾节点只是代表头尾,没有实际意义,头尾之间的才是实际节点。头节点--》尾节点:使用率 高---》低, 4 class DLinkedNode{ 5 int key; 6 int value; 7 DLinkedNode pre; 8 DLinkedNode next; 9 } 10 //在头节点右边添加结点,因为添加的节点看成是刚刚用过的 11 public void addNode(DLinkedNode node){ 12 node.pre = head; 13 node.next = head.next; 14 head.next.pre = node; 15 head.next = node; 16 } 17 //删除节点 18 public void removeNode(DLinkedNode node){ 19 node.next.pre = node.pre; 20 node.pre.next = node.next; 21 } 22 //将节点调入头节点右边 23 public void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node){ 24 removeNode(node); 25 addNode(node); 26 } 27 //删除尾节点左边,即删除不常用的 28 public DLinkedNode popTail(){ 29 DLinkedNode res = tail.pre; 30 removeNode(res); 31 return res; 32 } 33 34 private Hashtable<Integer,DLinkedNode> hashtable = new Hashtable<Integer,DLinkedNode>(); 35 private int size;//现在的元素数量 36 private int capacity; 37 private DLinkedNode head;//头节点 38 private DLinkedNode tail;//尾节点 39 40 public LRUCache(int capacity) { 41 this.size = 0; 42 this.capacity = capacity; 43 head = new DLinkedNode(); 44 tail = new DLinkedNode(); 45 head.next = tail; 46 tail.pre = head; 47 } 48 49 public int get(int key) { 50 DLinkedNode node = hashtable.get(key); 51 if(node==null) return -1; 52 moveToHead(node); 53 return node.value; 54 } 55 56 public void put(int key, int value) { 57 DLinkedNode node = hashtable.get(key); 58 if(node == null){ 59 //创建新节点 60 node = new DLinkedNode(); 61 node.value = value; 62 node.key = key; 63 addNode(node); 64 hashtable.put(key,node); 65 size++; 66 67 if(size > capacity){//如果添加后大于容量,那么删除尾节点左边,并且删除其在哈希表中对应的键值 68 DLinkedNode tailLeft = popTail(); 69 hashtable.remove(tailLeft.key); 70 size--; 71 }else{ 72 73 } 74 }else{//如果本来就存在,那么就更新,并且移动到头节点右边。 75 node.value = value; 76 moveToHead(node); 77 } 78 79 } 80 } 81 82 /** 83 * Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such: 84 * LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity); 85 * int param_1 = obj.get(key); 86 * obj.put(key,value); 87 */
148.排序链表
在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序。
示例 1:
输入: 4->2->1->3
输出: 1->2->3->4
示例 2:
输入: -1->5->3->4->0
输出: -1->0->3->4->5
分析:归并排序,先将链表分成小链表,在对每个小链表进行合并,
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } 7 * } 8 */ 9 class Solution { 10 public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { 11 if(head == null) return null; 12 return mergeSort(head); 13 } 14 //分,使用快慢指针,快指针一次走两步.函数返回小链表头指针 15 public ListNode mergeSort(ListNode head){ 16 if(head.next == null) return head; 17 ListNode slow = head; 18 ListNode fast = head.next; 19 //找中间点,即slow 20 while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){ 21 slow = slow.next; 22 fast = fast.next.next; 23 } 24 //右子链表头节点,重用fast 25 fast = slow.next; 26 //左子链表头节点即为head,但是要断尾 27 slow.next = null; 28 //递归分解左右子链表 29 head = mergeSort(head); 30 fast = mergeSort(fast); 31 //合并两个子链表,返回合并后的链表的头节点 32 ListNode newNode = merge(head,fast); 33 return newNode; 34 } 35 //合并 36 public ListNode merge(ListNode left, ListNode right){ 37 //数组合并时会新建一个数组临时存储数据,但是链表可以新建一个头节点 38 //维护头节点,取左右最小头节点 39 ListNode head; 40 if(left.val <= right.val){ 41 head = left; 42 left = left.next; 43 }else{ 44 head = right; 45 right = right.next; 46 } 47 //合并 48 ListNode temp = head; 49 while(left!=null && right!=null){ 50 if(left.val <= right.val){ 51 temp.next = left; 52 left = left.next; 53 temp = temp.next; 54 }else{ 55 temp.next = right; 56 right = right.next; 57 temp = temp.next; 58 } 59 } 60 //让子链表中剩下的连接至合并链表之后,下面两个if只会执行一个 61 if(left == null) temp.next = right; 62 if(right == null) temp.next = left; 63 return head; 64 } 65 }
152.乘积最大子序列
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找出一个序列中乘积最大的连续子序列(该序列至少包含一个数)。
示例 1:输入: [2,3,-2,4],输出: 6,解释: 子数组 [2,3] 有最大乘积 6。
示例 2:输入: [-2,0,-1],输出: 0,解释: 结果不能为 2, 因为 [-2,-1] 不是子数组。
分析:第一想法是动态规划,维护一个dpMax[i]数组表示以i结尾的乘积最大值(必须包含i)。则分成以下几种情况:
①nums[i] >=0:
dpMax[i-1]>0: dpMax[i] = nums[i] * dpMax[i-1]
dpMax[i-1]<=0: dpMax[i] = nums[i]
②nums[i] <=0:
dpMax[i-1]>=0: dpMax[i] = nums[i]
dpMax[i-1]<0: dpMax[i] = nums[i] * ?,dpMin[i-1]这里dpMin和dpMax相反,因为nums[i]小于0,那么再乘上最小的负数,就会得到最大的正数。所以这里应该判断dpMin的正负性。
dpMin[i-1]<=0 :dpMax[i] = nums[i] * dpMin[i-1]
dpMin[i-1]>0 : dpMax[i] =nums[i]
综上来看,dpMax无非就是三个值nums[i]、nums[i] * dpMax[i-1]、nums[i] * dpMin[i-1],那么只要在遍历过程中那个取最大值即可。同理,dpMin取nums[i]、nums[i] * dpMax[i-1]、nums[i] * dpMin[i-1]中的最小值即可。
动态规划优化,使用变量代替数组。
1 class Solution { 2 public int maxProduct(int[] nums) { 3 int dpMax = nums[0], dpMin = nums[0], max = nums[0]; 4 for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){ 5 int preMax = dpMax;//保存dpMax给dpMin使用 6 dpMax = Math.max(nums[i], Math.max(nums[i]*dpMax, nums[i]*dpMin)); 7 dpMin = Math.min(nums[i], Math.min(nums[i]*preMax, nums[i]*dpMin)); 8 max = Math.max(max, dpMax); 9 } 10 return max; 11 } 12 }
法二:具体问题具体分析

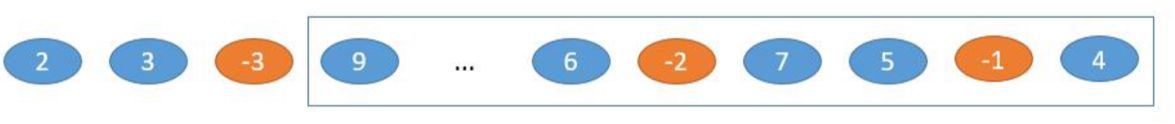
如果数组中有偶数个负数,那么最大值是所有元素相乘,如果有奇数个负数,那么最大值是除去第一个或最后一个负数的子数组相乘,如上图。只要从左到右和从右到左分别遍历一次,便可取出最大值。

但是,数组中的0如何处理呢?看作是0把数组分成若干个子数组,按照奇偶个奇数老办法继续计算
1 class Solution { 2 public int maxProduct(int[] nums) { 3 if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0; 4 int res = nums[0]; 5 int max = 1; 6 //从左往右 7 for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ 8 max = max * nums[i]; 9 res = Math.max(res, max); 10 if(max == 0){ 11 //如果max等于0,说明乘到了0,那么将max重新置为1,相当于分割数组作用 12 max = 1; 13 } 14 } 15 max = 1; 16 ////从右往左 17 for(int i=nums.length-1;i>=0;i--){ 18 max = max * nums[i]; 19 res = Math.max(res, max); 20 if(max == 0){ 21 max = 1; 22 } 23 } 24 return res; 25 26 } 27 }
155.最小栈
设计一个支持 push,pop,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
push(x) -- 将元素 x 推入栈中。pop() -- 删除栈顶的元素。 top() -- 获取栈顶元素。getMin() -- 检索栈中的最小元素。
示例:
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -3.
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); --> 返回 0.
minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -2.
分析:定义两个栈,一个数据栈data:正常操作,一个辅助栈helper:维持栈顶元素最小。当压栈时,data直接压入,helper如果为空或者压入元素小于栈顶才压入元素。当出栈时,data正常弹出,helper只有当data弹出元素和栈顶元素相同时才弹出。获取栈顶就直接返回data栈顶即可。
1 class MinStack { 2 Stack<Integer> data; 3 Stack<Integer> helper; 4 /** initialize your data structure here. */ 5 public MinStack() { 6 data = new Stack(); 7 helper = new Stack(); 8 } 9 10 public void push(int x) { 11 data.push(x); 12 if(helper.isEmpty() || helper.peek() >= x){ 13 helper.push(x); 14 } 15 } 16 17 public void pop() { 18 int pop = data.pop(); 19 int top = helper.peek(); 20 if(pop == top){ 21 helper.pop(); 22 } 23 } 24 25 public int top() { 26 return data.peek(); 27 28 } 29 30 public int getMin() { 31 return helper.peek(); 32 33 } 34 } 35 36 /** 37 * Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such: 38 * MinStack obj = new MinStack(); 39 * obj.push(x); 40 * obj.pop(); 41 * int param_3 = obj.top(); 42 * int param_4 = obj.getMin(); 43 */
160.相交链表
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:

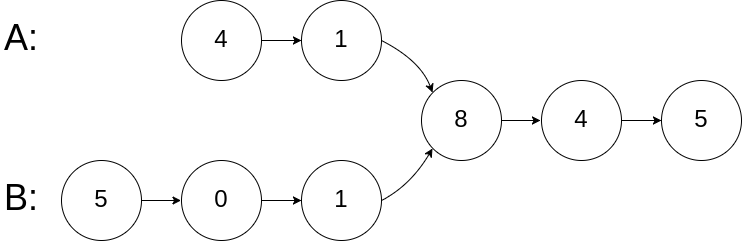
分析:如果两个链表相交,那么具有相同的尾巴。 剑指Offer
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } 7 * } 8 */ 9 class Solution { 10 public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode listA, ListNode listB) { 11 if(listA == null || listB == null) return null; 12 int ALen = 0, BLen = 0; 13 while(listA!=null){ 14 ALen++; 15 listA = listA.next; 16 } 17 while(listB!=null){ 18 BLen++; 19 listB = listB.next; 20 } 21 if((ALen - BLen) >= 0){ 22 return findCommonNode(listA, listB, ALen - BLen); 23 }else{ 24 return findCommonNode(listB, listA, BLen - ALen); 25 } 26 27 } 28 public ListNode findCommonNode(ListNode node1, ListNode node2,int k){ 29 while(k>0){//长的先走k步 30 node1 = node1.next; 31 k--; 32 } 33 //寻找公共点 34 while(node1 != null){ 35 if(node1 == node2) return node1; 36 node1 = node1.next; 37 node2 = node2.next; 38 } 39 return null; 40 } 41 }
169.多数元素
给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找到其中的多数元素。多数元素是指在数组中出现次数大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在多数元素。
示例 1:输入: [3,2,3]输出: 3
示例 2:输入: [2,2,1,1,1,2,2]输出: 2
方法1:哈希表
方法2:投票算法:多数元素是大于n/2的元素,如果把多数元素表示为+1,其他的表示为-1,那么之和一定是正数。我们设置一个整数count表示和,一个整数candidate表示候选者,当count = 0时,候选者就要换人。
1 class Solution { 2 public int majorityElement(int[] nums) { 3 Integer candidate = null; 4 int count = 0; 5 for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ 6 if(count == 0){ 7 candidate = nums[i];//更换候选人 8 } 9 //如果是候选人就加一,否则减一 10 count += (nums[i] == candidate) ? 1 : -1; 11 } 12 return candidate; 13 } 14 }
198.打家劫舍
你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你在不触动警报装置的情况下,能够偷窃到的最高金额
示例 1:输入: [1,2,3,1]输出: 4解释: 偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 1) ,然后偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 3)。偷窃到的最高金额 = 1 + 3 = 4 。
示例 2:输入: [2,7,9,3,1]输出: 12解释: 偷窃 1 号房屋 (金额 = 2), 偷窃 3 号房屋 (金额 = 9),接着偷窃 5 号房屋 (金额 = 1)。偷窃到的最高金额 = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12 。
分析:就是间隔(一个或多个)数组元素的最大值。第一反应是动态规划,建立数组dpMax[i]到i个房间的最大金额。则:
dpMax[i] = max{ dpMax[i-1] , dpMax[i-2] + nums[i]}
1 class Solution { 2 public int rob(int[] nums) { 3 if(nums == null || nums.length == 0) return 0; 4 if(nums.length == 1) return nums[0]; 5 int[] dpMax = new int[nums.length]; 6 dpMax[0] = nums[0]; 7 dpMax[1] = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]); 8 for(int i=2;i<nums.length;i++){ 9 dpMax[i] = Math.max(dpMax[i-1], dpMax[i-2]+nums[i]); 10 } 11 return dpMax[nums.length-1]; 12 } 13 }
200.岛屿数量
给定一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,计算岛屿的数量。一个岛被水包围,并且它是通过水平方向或垂直方向上相邻的陆地连接而成的。你可以假设网格的四个边均被水包围。
示例 1:输入:
11110
11010
11000
00000
输出: 1
示例 2:输入:
11000
11000
00100
00011
输出:3
分析:第一反应是使用动态规划,建立一个二维数组dp[i][j]表示(i,j)位置是否是岛屿。想了想不行啊。使用深度遍历搜索!遍历二维数组,如果是1,则以此点作深度遍历,每个访问过的被置为0。有1的地方肯定就有岛屿,深度遍历是将岛屿面积全都置为0,那么下次循环时跳过该岛屿。
1 class Solution { 2 public int numIslands(char[][] grid) { 3 if(grid == null || grid.length == 0) return 0; 4 int rl = grid.length; 5 int cl = grid[0].length; 6 int res = 0; 7 for(int i=0;i<rl;i++){ 8 for(int j=0;j<cl;j++){ 9 if(grid[i][j] == '1'){ 10 dfs(grid, i, j, rl, cl); 11 res++; 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 return res; 16 } 17 public void dfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j, int rl, int cl){ 18 if(i < 0 || i >= rl || j < 0 || j >= cl || grid[i][j] == '0') return; 19 //将岛屿置为0 20 grid[i][j] = '0'; 21 dfs(grid, i-1, j, rl, cl); 22 dfs(grid, i+1, j, rl, cl); 23 dfs(grid, i, j-1, rl, cl); 24 dfs(grid, i, j+1, rl, cl); 25 } 26 }
206.反转链表
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } 7 * } 8 */ 9 class Solution { 10 public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { 11 ListNode pre = null; 12 ListNode next; 13 while(head != null){ 14 next = head.next; 15 head.next = pre; 16 pre = head; 17 head = next; 18 } 19 return pre; 20 } 21 }
1 //递归 2 class Solution { 3 public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { 4 if(head == null || head.next == null) return head; 5 //p是最后一个节点,翻转后就是第一个头节点 6 ListNode p = reverseList(head.next); 7 head.next.next = head; 8 head.next = null; 9 return p; 10 } 11 }


