15. 时间空间效率的平衡(4)
题一:【丑数】
把只包含质因子2、3和5的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。例如6、8都是丑数,但14不是,因为它包含质因子7。 习惯上我们把1当做是第一个丑数。求按从小到大的顺序的第N个丑数。
分析:自己写了一个,算法复杂度太大了——写一个判断是否是丑数的函数,然后依次判断
1 public class Solution {
2 public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
3 if(index<=0) return 0;
4 int count=1;//计数
5 int res = 1;
6 while(count<=index){
7 if(isUgly(res)){
8 if(count==index) return res;
9 count++;
10 res++;
11 }else{
12 res++;
13 }
14 }
15 return 0;
16 }
17 public boolean isUgly(int num){
18 if(num==1) return true;
19 int res = num;
20 while(num!=0){
21 if(num%2==0){
22 num = num/2;
23 }else if(num%3==0){
24 num = num/3;
25 }else if(num%5==0){
26 num = num/5;
27 }else{
28 return false;
29 }
30 if(num==1) return true;
31 }
32 return false;
33 }
34 }
分析:DP

1 import java.lang.Math;
2 public class Solution {
3 public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
4 if(index<=0) return 0;
5 if(index<7) return index;
6 //后面的丑数是有前一个丑数乘以2,3,5中的一个得来。因此可以用动态规划去解
7 int t2=0,t3=0,t5=0;
8 int[] dp = new int[index];
9 dp[0] = 1;
10 for(int i=1;i<index;i++){
11 dp[i] = Math.min(dp[t2]*2,Math.min(dp[t3]*3,dp[t5]*5));
12 if(dp[i]==dp[t2]*2) t2++;
13 if(dp[i]==dp[t3]*3) t3++;
14 if(dp[i]==dp[t5]*5) t5++;
15 }
16 return dp[index-1];
17 }
18 }
题二:【第一个只出现一次的字符位置】
在一个字符串(0<=字符串长度<=10000,全部由字母组成)中找到第一个只出现一次的字符,并返回它的位置, 如果没有则返回 -1(需要区分大小写)。
分析:只能暴力解决;65~90为26个大写英文字母,97~122号为26个小写英文字母;
1 public class Solution {
2 public int FirstNotRepeatingChar(String str) {
3 if(str==null||str.length()==0) return -1;
4 int[] count = new int[123];//默认是0
5 for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++){
6 count[str.charAt(i)]++;
7 }
8 for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++){
9 if(count[str.charAt(i)]==1){
10 return i;
11 }
12 }
13 return 0;
14 }
15 }
题三:【数组中的逆序对】
在数组中的两个数字,如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,求出这个数组中的逆序对的总数P。并将P对1000000007取模的结果输出。 即输出P%1000000007
【输入描述】题目保证输入的数组中没有的相同的数字,数据范围:对于%50的数据,size<=10^4;对于%75的数据,size<=10^5;对于%100的数据,size<=2*10^5;
【示例】输入:1,2,3,4,5,6,7,0 输出:7
分析:暴力解决时间复杂度太高O(N^2);采用分治的思想,将数组不断一分为二,再合并排序,在合并排序的过程中,判断是否是逆序对。
归并排序:【图解】 【合并】
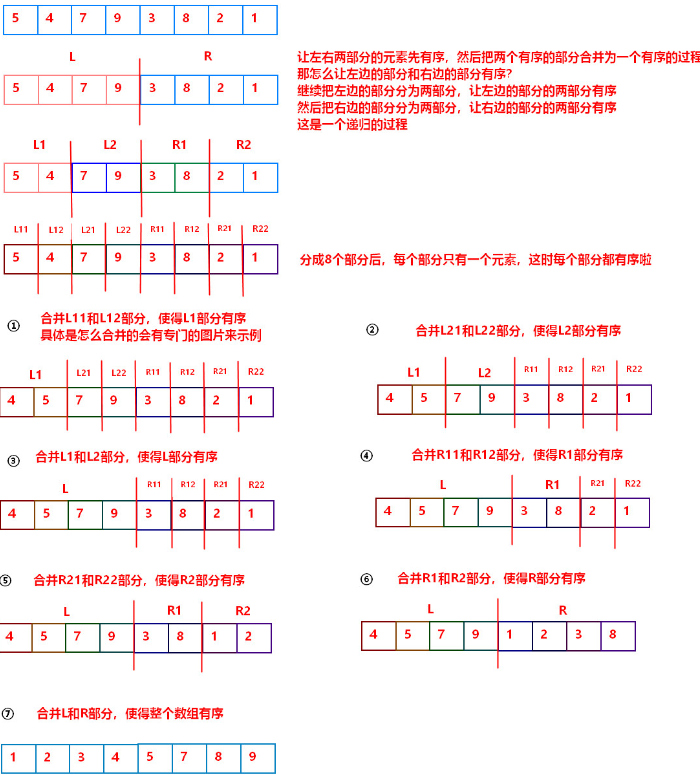
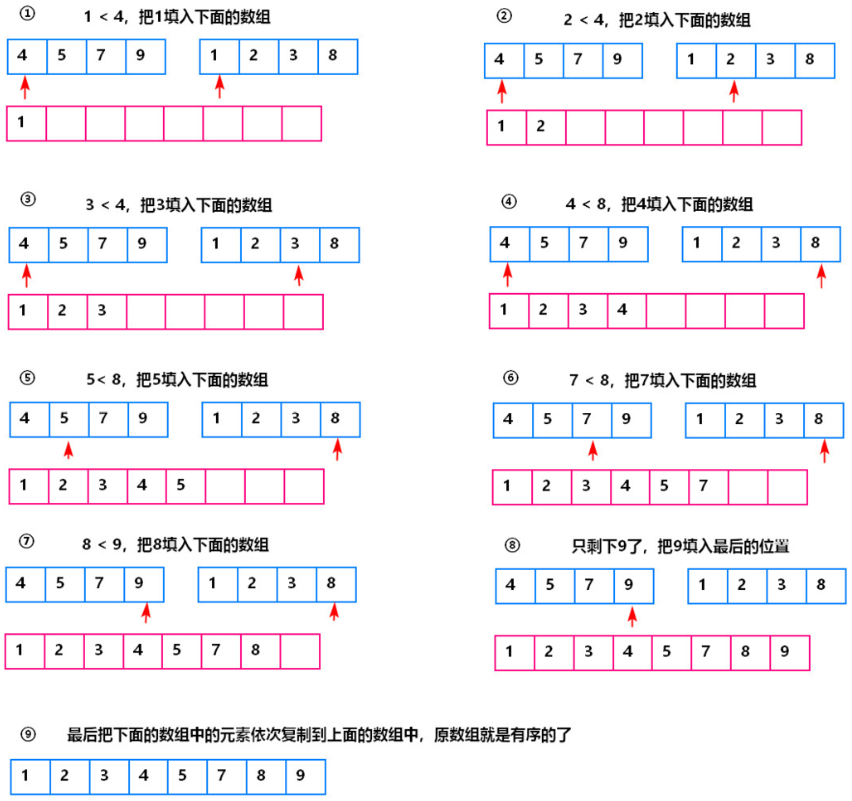
题
【注意】: count=count+mid-p1+1;//当左边有序小数组p1指向的元素大于p2指向的元素,这就说明p1~mid范围内的元素(有序,mid-p1+1)都大于p2指向的元素,所以有mid-p1+1个逆序对。例如下图,array[p1]=4 > array[p2]=1,这就是说p1~mid,即4、5、7、9都大于1,有mid-p1+1=3-0+1=4个。
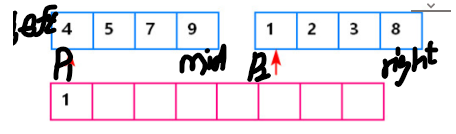
1 public class Solution { 2 private int count=0;//计数 3 private final int k = 1000000007; 4 public int InversePairs(int [] array) { 5 mergeSort(array,0,array.length-1); 6 return count; 7 } 8 //分解 9 public void mergeSort(int[] array, int left, int right){ 10 if(left>=right) return; 11 int mid = (left+right)/2; 12 mergeSort(array,left,mid); 13 mergeSort(array,mid+1,right); 14 merge(array,left,mid,right); 15 } 16 //合并 17 public void merge(int[] array, int left, int mid, int right){ 18 //建立两个指针P1,P2 19 int p1 = left;//第一个分数组开头 20 int p2 = mid+1;//第二个分数组开头 21 int i=0; 22 int[] temp = new int[right-left+1]; 23 while(p1<=mid&&p2<=right){ 24 if(array[p1]<=array[p2]){ 25 temp[i++] = array[p1++]; 26 }else{ 27 temp[i++] = array[p2++]; 28 count = (count+mid-p1+1)%k; 29 } 30 } 31 while(p1<=mid){ 32 temp[i++]=array[p1++]; 33 } 34 while(p2<=right){ 35 temp[i++]=array[p2++]; 36 } 37 for(int j=0;j<temp.length;j++){ 38 array[left+j]=temp[j]; 39 } 40 } 41 }
四:【两个链表的第一个公共结点】
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
分析:公共节点,即两个结点相同(p1.val=p2.val并且p1.next=p2.next)。因此,如果有公共节点,那么就会有相同的尾部。
法一:暴力,循环嵌套 O(m*n);m是pHead1长度,n是pHead2长度。
法二:从尾部向后遍历,遍历的最后一个公共节点就是我们想要的,但是题目中给的是单向链表,先进后出=》使用队列存放公共节点,当p1!=p2时,则两个队列头(相等)就是我们想要的。时间和空间复杂度都是O(m+n)。
法三:首先遍历两个链表的长度,计算长的比短的长多少(k),先让长的链表先走k步,然后再同时遍历两个链表找到公共节点。时间复杂度O(m) ,m是较长链表的长度,空间复杂度O(1)。
1 /* 2 public class ListNode { 3 int val; 4 ListNode next = null; 5 6 ListNode(int val) { 7 this.val = val; 8 } 9 }*/ 10 public class Solution { 11 public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) { 12 if(pHead1==null||pHead2==null) return null; 13 int i = 0;//第一个链表长度 14 int j = 0;//第二个链表长度 15 ListNode head1 = pHead1; 16 ListNode head2 = pHead2; 17 //计算两链表长度 18 while(head1!=null){ 19 i++; 20 head1=head1.next; 21 } 22 while(head2!=null){ 23 j++; 24 head2=head2.next; 25 } 26 if((i-j)>=0){ 27 return fingCommonNode(pHead1,pHead2,i-j); 28 }else{ 29 return fingCommonNode(pHead2,pHead1,j-i); 30 } 31 } 32 public ListNode fingCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2, int k){ 33 while(k>0){ 34 pHead1 = pHead1.next; 35 k--; 36 } 37 while(pHead1!=null){ 38 if(pHead1==pHead2) return pHead1; 39 pHead1=pHead1.next; 40 pHead2=pHead2.next; 41 } 42 return null; 43 } 44 }



