javascript数据结构与算法学习笔记
1. 栈结构
1.1 栈的介绍
栈是一种遵循后进先出(Last In First Out / LIFO) 原则的一种有序集合。
新添加或者要删除的元素都会保存在栈的同一端,我们把它叫做栈顶,另外一端叫做栈底。
1.2 栈的方法
- push:将数据压入栈
- pop:删除并返回栈顶元素(此方法会修改栈)
- peek:返回栈顶元素,但不修改栈
- size:查看栈内的数据个数
- isEmpty:判断栈内是否为空
- isString:将栈内的数据转化为字符串输出
- clear:清空栈
1.3 栈的封装
/* 栈结构封装 */
export class Stack {
#items = [] // 添加#表示私有属性
// 出栈
pop() {
return this.#items.pop()
}
// 压栈/入栈
push(element) {
this.#items.push(element)
}
// 返回栈顶元素
peek() {
// return this.#items[#items.length - 1]
return this.#items.at(-1)
}
// 判断栈是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.#items.length === 0
}
// 栈的元素个数
size() {
return this.#items.length
}
// 清空栈
clear() {
this.#items = []
}
// 转换成字符串
toString() {
return this.#items.join(" ")
}
}
1.4 示例
/* 十进制转二/八/十六进制
@params {number} num 需转换的数值
@param {number=} base 转换的进制,默认为二进制
*/
function convert(num, base = 2) {
const stack = new Stack();
const baseStringMap = '0123456789ABCDEF';
let result = '';
while (num > 0) {
stack.push(num % base);
num = Math.floor(num / base);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
result += baseStringMap[stack.pop()];
}
return result;
}
2. 队列
2.1 队列是什么
队列是是一种受限的线性表,特点为先进先出(FIFO:first in first out)。
- 受限之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作;
- 在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作;
2.2 队列的方法
- enqueue(element):向队列尾部添加一个(或多个)新的项;
- dequeue:移除队列的第一(即排在队列最前面的)项,并返回被移除的元素;
- front:返回队列中的第一个元素——最先被添加,也将是最先被移除的元素。队列不做任何变动(不移除元素,只返回元素信息与Stack类的peek方法非常类似);
- isEmpty:如果队列中不包含任何元素,返回true,否则返回false;
- size:返回队列包含的元素个数,与数组的length属性类似;
- toString:将队列中的内容,转成字符串形式;
2.3 队列的封装
2.3.1 基于数组封装
删除前面元素时,后边元素都会移动,性能不好
class Queue {
#items = [];
// 出列
dequeue() {
return this.#items.shift();
}
// 入列
enqueue(element) {
this.#items.push(element);
}
// 返回队头
front() {
return this.#items[0];
}
// 判断队列是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.#items.length === 0;
}
// 队列的元素个数
size() {
return this.#items.length;
}
// 清空队列
clear() {
this.#items = [];
}
// 转换成字符串
toString() {
return this.#items.join(' ');
}
}
2.3.2 基于对象封装
class Queue {
#items = {};
#headIndex = 0; // 记录队头索引
#index = 0;
// 出列
dequeue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) return;
const res = this.#items[this.#headIndex];
delete this.#items[this.#headIndex];
this.#headIndex++;
return res;
}
// 入列
enqueue(element) {
this.#items[this.#index] = element;
this.#index++;
}
// 返回队头
front() {
return this.#items[this.#headIndex];
}
// 判断队列是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0;
}
// 队列的元素个数
size() {
return this.#index - this.#headIndex;
}
// 清空队列
clear() {
this.#items = {};
this.#headIndex = 0;
this.#index = 0;
}
// 转换成字符串
toString() {
let str = ''
for (let i = this.#headIndex; i < this.#index; i++) {
str += `${this.#items[i]} `;
}
return str
}
}
3. 链表
3.1 链表介绍
链表用来存储有序的元素集合,与数组不同,链表中的元素并非保存在连续的存储空间内,每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的指针构成。当要移动或删除元素时,只需要修改相应元素上的指针就可以了。对链表元素的操作要比对数组元素的操作效率更高。下面是链表数据结构的示意图:
3.2 链表的特点
- 插入、删除数据效率高O(1)级别(只需要更改指针指向即可),随机访问效率低O(n)级别(需要从链头至链尾进行遍历)
- 和数组相比,内存空间消耗更大,因为每个存储数据的节点都需要额外的空间存储后继指针
3.3 单链表
3.3.1 单列表的特点
每个节点只包含一个指针,即后级指针
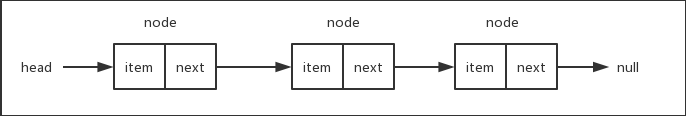
3.4.2 单列表的封装
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.length = 0
this.head = null
}
append(element) {
const node = new Node(element);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next !== null) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = node;
}
this.length++;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.length) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next;
} else {
let previous = this.getNodeAt(index - 1);
current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next; // 跳过/删除当前元素
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
}
}
getNodeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.length) {
let node = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
return this.head.element;
} else {
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
}
}
getElementAt(index) {
return this.getNodeAt(index).element;
}
equalFn(a, b) {
return JSON.stringify(a) === JSON.stringify(b);
}
indexOf(element) {
let node = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (this.equalFn(node.element, element)) {
return i;
} else {
node = node.next;
}
}
return -1;
}
remove(element) {
const index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
insert(element, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.length) {
const node = new Node(element);
if (index === 0) {
const current = this.head;
this.head = node;
node.next = current;
} else {
const current = this.getNodeAt(index);
const previous = this.getNodeAt(index - 1);
previous.next = node;
node.next = current;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
getHead() {
return this.head;
}
clear() {
this.length = 0;
this.head = null;
}
toString() {
let node = this.head;
let str = '';
while (node) {
str += `${node.element} `;
node = node.next;
}
str = str.slice(0, -1);
return str;
}
}
3.4 双列表
3.4.1 双列表介绍
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据节点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。一般我们都构造双向循环链表。
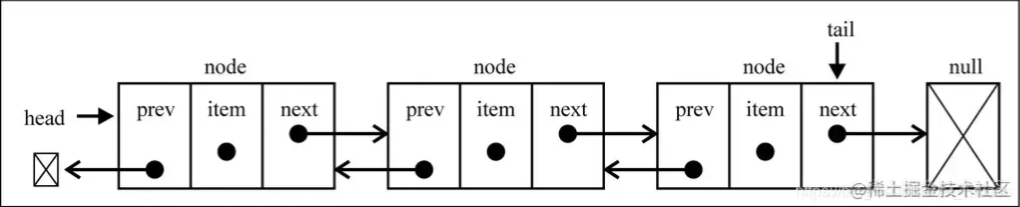
3.4.2 双向列表的特点
- 可以使用head和一个tail分别指向头部和尾部的节点
- 每个节点都由三部分组成:前一个节点的指针,后一个节点的指针,元素
- 双向链表的第一个节点prev是null
- 双向链表的最后的节点next是null;
3.4.3 双向列表的方法
-
append(element):向链表尾部添加一个新的项
-
insert(position,element):向链表的特定位置插入一个新的项
-
get(position):获取对应位置的元素
-
indexOf(element):返回元素在列表上的索引。如果链表上没有该元素则返回-1
-
updata(position,element):更新某个元素
-
removeAt(position):从链表的特定位置移除一项(根据位置)
-
remove(element):从链表移除一项(根据元素)
-
isEmpty():如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回true,如果链表长度大于0则返回false。
-
size():返回链表包含的元素个数。
-
tostring():输出
-
forwardString():返回正向遍历的节点字符串形式
-
backwarkString():返回反向遍历的节点字符串形式
3.4.4 双向列表的封装
class DoublyNode {
constructor(element) {
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
this.element = element;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.length = 0;
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
append(element) {
const node = new DoublyNode(element);
if (this.length === 0) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
this.tail.next = node;
node.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = node;
}
this.length++;
}
insert(index, element) {
// 越界判断
if (index < 0 || index > this.length) throw Error('输入的 index 无效');
const node = new DoublyNode(element);
// 1.添加的位置在链表头
if (index === 0) {
if (this.length === 0) {
// a.链表原本为空
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
// b.链表原本有结点
node.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
} else if (index === this.length) {
// 2.添加的位置在链表尾
this.tail.next = node;
node.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = node;
} else {
// 3.添加的位置在中间
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
current.prev.next = node;
node.prev = current.prev;
node.next = current;
current.prev = node;
}
this.length++;
}
getNode(index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.length) return new Error('无效index');
let current;
if (index < this.length / 2) {
current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
} else {
current = this.tail;
for (let i = this.length - 1; i > index; i--) {
current = current.prev;
}
}
return current;
}
get(index) {
return this.getNode(index).element;
}
indexOf(element) {
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (current.element === element) {
return i;
}
current = current.next;
}
}
update(index, element) {
const node = this.getNode(index);
node.element = element;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.length) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
if (this.length === 1) {
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.head.prev = null;
}
} else if (index === this.length - 1) {
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
current = this.getNode(index);
const prevNode = current.prev;
const nextNode = current.next;
prevNode.next = nextNode;
nextNode.prev = prevNode;
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
}
return false;
}
remove(element) {
const index = this.indexOf(element);
this.removeAt(index);
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
clear() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
}
3.5 循环列表
3.5.1 循环列表介绍
循环列表和单向列表的区别在于,最后一个元素指向下一个元素的指针,不是引用undefined,而是指向第一个元素
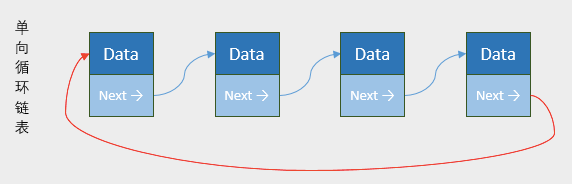
3.5.2 循环列表封装
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
}
class CircularLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor() {
super();
}
append(element) {
const node = new Node(element);
let current;
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.getNodeAt(this.size() - 1);
current.next = node;
}
node.next = this.head;
this.count++;
}
insert(element, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.length) {
const node = new Node(element);
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
node.next = this.head;
} else {
node.next = current;
current = this.getNodeAt(this.size() - 1);
this.head = node;
current.next = this.head;
}
} else {
prevNode = this.getNodeAt(index - 1);
node.next = prevNode.next;
prevNode.next = node;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.length) {
let current = this.head;
if (index === 0) {
if (this.length === 1) {
this.head = null;
} else {
const tailNode = this.getNodeAt(this.length - 1)
this.head = this.head.next
tailNode.next = this.head
}
} else {
const prevNode = this.getNodeAt(index - 1)
current = prevNode.next
prevNode.next = current.next
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
}
return;
}
}
4. 集合(Set)
集合是一组无需且唯一的项组成的
class Set {
items = {};
add(element) {
if (this.has(element)) return false;
this.items[element] = element;
return true
}
delete(element) {
if (this.has(element)) {
delete this.items[element]
return true
}
return false
}
has(element) {
return element in this.items;
}
clear() {
this.items = {}
}
size() {
return Object.keys(this.items).length
}
values() {
return Object.values(this.items)
}
}
5. 字典(Map)
字典和集合很相似,集合以[值,值]的形式存储元素,字典则是以[键,值]的形式存储元素。字典也称作映射、符号表或关联数组
class KeyValue {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
class Map {
table = {};
toStringFn(item) {
if (item === null) {
return 'null';
} else if (item === undefined) {
return 'undefined';
} else if (typeof item === 'string' || item instanceof String) {
return item;
}
return JSON.stringify(item);
}
hasKey() {
return this.table[this.toStringFn(key)] !== null;
}
get() {
const keyValue = this.table[this.toStringFn(key)];
return keyValue == null ? undefined : keyValue.value;
}
set(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
const tableKey = this.toStringFn(key);
this.table[tableKey] = new KeyValue(key, value);
return true;
}
return false;
}
delete(key) {
if (this.hasKey(key)) {
delete this.table[this.toStringFn(key)];
return true;
}
return false;
}
keys() {
return Object.vlaues(this.table).map((item) => item.key);
}
values() {
return Object.vlaues(this.table).map((item) => item.value);
}
entries() {
return Object.values(this.table);
}
size() {
return Object.keys(this.table).length
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0
}
clear() {
this.table = {}
}
}
6. 散列表
HashMap类,它是Dictionary类的一种散列表实现方式。散列算法的作用是尽可能快的在数据结构中找到一个值
class KeyValue {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
class HashMap {
hashTable = {};
toStringFn(item) {
if (item === null) {
return 'null';
} else if (item === undefined) {
return 'undefined';
} else if (typeof item === 'string' || item instanceof String) {
return item;
}
return JSON.stringify(item);
}
hashCode(key) {
if (typeof key === 'number') {
return key;
}
const tableKey = this.toStringFn(key);
let hash = 5381;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash += (hash * 33) + tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 1013;
}
set(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
this.hashTable[position] = new KeyValue(key, value);
return true;
}
return false;
}
get(key) {
const keyValue = this.hashTable[this.hashCode(key)];
return keyValue == null ? undefined : keyValue.value;
}
remove(key) {
const hash = this.hashCode(key);
const keyValue = this.hashTable[hash];
if (keyValue != null) {
delete this.hashTable(hash);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
7. 树
树是一种分层数据的抽象模型
7.1 二叉树
二叉树中的节点最多只能有两个子节点:一个是左侧子节点,另一个是右侧子节点
7.2 二叉搜索树
7.2.1 二叉搜索树介绍
二叉搜索树(BST)是二叉树的一种,但是只允许你左侧节点存储(比父节点)小的值,右侧节点存储比父节点大的值
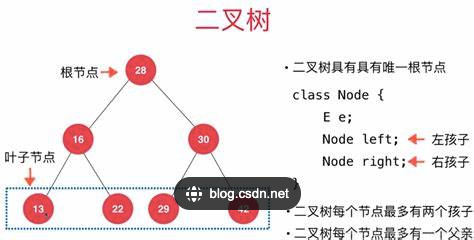
7.2.2 二叉搜索树封装
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.key = key;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
const Compare = {
less: -1,
bigger: 1,
equal: 0,
};
function compareFn(a, b) {
return a === b ? Compare.equal : a < b ? Compare.less : Compare.bigger;
}
class BST {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
insert(key) {
if (this.root == null) {
this.root = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(this.root, key);
}
}
insertNode(node, key) {
if (compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.less) {
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, key);
}
} else {
if (node.right == null) {
node.right = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, key);
}
}
}
// 中序遍历
inOrderMap(callback) {
this.inOrderMapNode(this.root, callback);
}
inOrderMapNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
this.inOrderMapNode(node.left, callback);
callback(node.key);
this.inOrderMapNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
// 先序遍历
preOrderMap(callback) {
this.#preOrderMapNode(this.root, callback);
}
#preOrderMapNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
callback(node.key);
this.#preOrderMapNode(node.left, callback);
this.#preOrderMapNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
// 后序遍历
postOrderMap(callback) {
this.#postOrderMapNode(this.root, callback);
}
#postOrderMapNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
this.#postOrderMapNode(node.left, callback);
this.#postOrderMapNode(node.right, callback);
callback(node.key);
}
}
min() {
return this.#minNode(this.root);
}
#minNode(node) {
let current = node;
while (current != null && current.left != null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current;
}
max() {
return this.#maxNode(this.root);
}
#maxNode(node) {
let current = node;
while (current != null && current.right != null) {
current = current.right;
}
return current;
}
search(key) {
return this.#searchNode(this.root, key);
}
#searchNode(node, key) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.less) {
return this.#searchNode(node.left, key);
} else if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.bigger) {
return this.#searchNode(node.right, key);
} else {
return true;
}
}
remove(key) {
this.#removeNode(this.root, key);
}
#removeNode(node, key) {
if (node === null) {
return null;
}
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.less) {
node.left = this.#removeNode(node.left, key);
return node;
} else if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.bigger) {
node.right = this.#removeNode(node.right, key);
return node;
} else {
// 位于树末端,左右子节点为空
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
node = null;
return node;
}
// 左子节点或右子节点为空
if (node.left == null) {
node = node.right;
return node;
} else if (node.right == null) {
node = node.left;
return node;
}
// 左右子节点都不为空
const target = this.#minNode(node.right);
node.key = target.key;
node.right = this.#removeNode(node.right, target.key);
return node;
}
}
}
7.2.3 遍历
- 中序遍历是一种以上行顺序访问BST所有节点的遍历方式,也就是从最小到最大的顺序访问所有节点。中序遍历的一种应用就是对树进行排序操作
- 先序遍历是以优先于后代节点的顺序访问每个节点的。先序遍历的一种应用是打印一个结构化的文档。
- 后序遍历则是先访问节点的后代节点,再访问节点本身。后序遍历的一种应用是计算一个目录及其子目录中所有文件所占空间的大小
7.2.4 移除
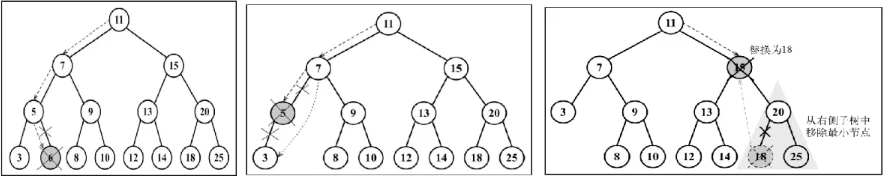
8. 二叉堆
二叉堆是一种特殊的二叉树,有以下两个特性
- 它是一颗完全的二叉树,表示树的每一层都有左侧和右侧子节点(除了最后一层的叶节点),并且最后一层的叶节点尽可能都是左侧子节点,这叫做结构特性
- 二叉堆不是最小堆就是最大堆。最小堆允许你快速导出树的最小值, 最大堆允许你快速导出树的最大值。所有的节点都大于等于(最大堆)或小于等于(最小堆)每个它的子节点。这叫做堆特性
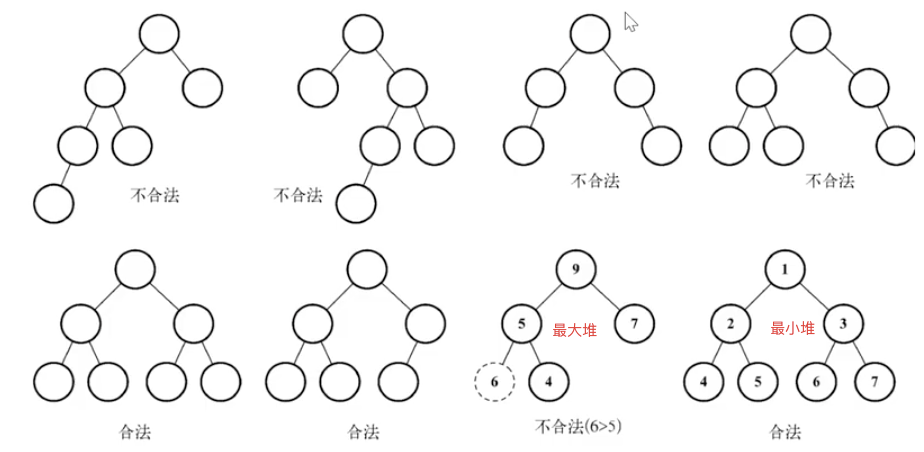
8.1 最小堆
所有的节点都小于等于每个它的子节点
const Compare = {
less: -1,
bigger: 1,
equal: 0,
};
function compareFn(a, b) {
return a === b ? Compare.equal : a < b ? Compare.less : Compare.bigger;
}
// 交换位置
function swap(array, index1, index2) {
const temp = array[index1];
array[index1] = array[index2];
array[index2] = temp;
}
class MinHeap {
heap = []; // 数组管理数据
// 左侧子节点的索引
#getLeftIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 1;
}
// 右侧子节点的索引
#getRightIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 2;
}
#getParentIndex(index) {
return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
}
#shiftUp(index) {
let parentIndex = this.#getParentIndex(index);
while (
index > 0 &&
compareFn(this.heap[parentIndex], this.heap[index]) === Compare.bigger
) {
swap(this.heap, parentIndex, index);
index = parentIndex;
parentIndex = this.#getParentIndex(index);
}
}
insert(value) {
if (value != null) {
this.heap.push(value);
// 与父节点对比,如果比父节点小,交换位置
this.#shiftUp(this.heap.length - 1);
return true;
}
}
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
findTarget() {
return this.heap[0];
}
// 导出最小值
extract() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (this.size() === 1) {
return this.heap.shift();
}
const removed = this.heap[0];
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
return removed;
}
// 向下交换位置
shiftDown(index) {
let current = index
let left = this.#getLeftIndex(index)
let right = this.#getRightIndex(index)
if (this.compareFn(this.heap[current], this.heap[left]) === Compare.bigger) {
current = left
}
if (
this.compareFn(this.heap[current], this.heap[right]) === Compare.bigger
) {
current = right;
}
if (index !== current) {
swap(this.heap, index, current)
this.shiftDown(current)
}
}
}
8.2 最大堆
所有的节点都大于等于每个它的子节点
const Compare = {
less: -1,
bigger: 1,
equal: 0,
};
function compareFn(a, b) {
return a === b ? Compare.equal : a < b ? Compare.less : Compare.bigger;
}
// 交换位置
function swap(array, index1, index2) {
const temp = array[index1];
array[index1] = array[index2];
array[index2] = temp;
}
class MinHeap {
heap = []; // 数组管理数据
// 左侧子节点的索引
#getLeftIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 1;
}
// 右侧子节点的索引
#getRightIndex(index) {
return 2 * index + 2;
}
#getParentIndex(index) {
return Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
}
#shiftUp(index) {
let parentIndex = this.#getParentIndex(index);
while (
index > 0 &&
compareFn(this.heap[parentIndex], this.heap[index]) === Compare.bigger
) {
swap(this.heap, parentIndex, index);
index = parentIndex;
parentIndex = this.#getParentIndex(index);
}
}
insert(value) {
if (value != null) {
this.heap.push(value);
// 与父节点对比,如果比父节点小,交换位置
this.#shiftUp(this.heap.length - 1);
return true;
}
}
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
findTarget() {
return this.heap[0];
}
// 导出最大值
extract() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (this.size() === 1) {
return this.heap.shift();
}
const removed = this.heap[0];
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
return removed;
}
// 向下交换位置
shiftDown(index) {
let current = index;
let left = this.#getLeftIndex(index);
let right = this.#getRightIndex(index);
if (
this.compareFn(this.heap[current], this.heap[left]) === Compare.bigger
) {
current = left;
}
if (
this.compareFn(this.heap[current], this.heap[right]) === Compare.bigger
) {
current = right;
}
if (index !== current) {
swap(this.heap, index, current);
this.shiftDown(current);
}
}
}
9. 排序算法
9.1 冒泡排序
冒泡排序比较所有相邻的两个项,如果第一个比第二个大,则交换它们。元素项向上移动至正确的顺序,就好像气泡升至表面一样
function bubblesort(array) {
const { length } = array;
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
// 每循环一次,就会将最大值放置在最后面,因此不必再循环后面已经确定好的值
for (let j = 0; j < length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// 交换位置
swap(array, j, j+1);
}
}
}
}
// 交换位置
function swap(array, index1, index2) {
const temp = array[index1];
array[index1] = array[index2];
array[index2] = temp;
// [array[a], array[b]] = [array[b], array[a]];
}
9.2 选择排序
选择排序算法是一种原址比较排序算法。选择排序大致的思路是找到数据结构中的最小值并将其放置在第一位,接着找到第二小的值并将其放在第二位,依次类推
// 交换位置
function swap(array, index1, index2) {
const temp = array[index1];
array[index1] = array[index2];
array[index2] = temp;
}
// 选择排序
function selectionSort(arr) {
const { length } = arr;
let minIndex;
for (let i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
for (let j = i; j < length; j++) {
if (arr[minIndex] > arr[j]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
if (i !== minIndex) {
swap(arr, minIndex, i);
}
}
return arr
}
9.3 插入排序
// 插入排序
function insertSort(arr) {
const { length } = arr;
let temp;
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
let j = i;
while (j > 0) {
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
j--;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
return arr;
}
9.4 归并排序
归并排序是一种分而治之算法。其思想是将原始数组切分成较小的数组,直到每个小数组只有一个位置,接着将小数组归并成较大的数组,直到最后一个排序完毕的大数组
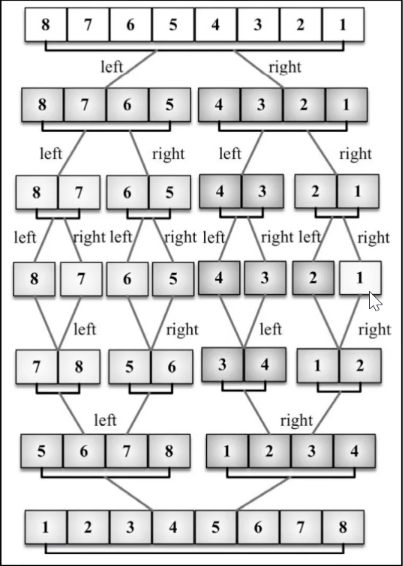
// 归并排序
function mergeSort(array) {
const { length } = array;
if (length > 1) {
const middle = Math.floor(length / 2);
const left = mergeSort(array.slice(0, middle))
const right = mergeSort(array.slice(middle, length))
array = merge(left, right)
}
return array
}
function merge(left, right) {
let i = 0;
let j = 0;
const result = [];
while (i < left.length && j < right.length) {
result.push(left[i] < right[j] ? left[i++] : right[j++])
}
return result.concat(i < left.length ? left.slice(i): right.slice(i))
}
9.5 快速排序
function quickSort(arr) {
const { length} = arr
if (length < 2) {
return arr
}
let base = arr[0]
let minArr = arr.slice(1).filter(item => item <= base)
let maxArr = arr.slice(1).filter(item => item > base)
minArr = quickSort(minArr)
maxArr = quickSort(maxArr)
return minArr.concat(base).concat(maxArr)
}
9.6 计数排序
计数排序使用一个用来存储每个元素在原始数组中出现次数的临时数组。在所有元素都计数完成后,临时数组已排好序并可迭代以构建排序后的结果数组
// 计数排序
function countSort(arr) {
if (arr.length < 2) {
return arr;
}
const maxValue = Math.max(...arr);
const counts = new Array(maxValue + 1);
arr.forEach((item) => {
if (!counts[item]) {
counts[item] = 0;
}
counts[item]++;
});
let newArr = [];
let sortIndex = 0;
counts.forEach((item, index) => {
while (item > 0) {
newArr[sortIndex++] = index;
item--;
}
});
return newArr;
}
9.7 桶排序
桶排序(箱排序)也是分布式排序算法,它将元素分为不同的桶(较小的数组),再使用一个简单的排序算法,例如插入排序(用来排序小数组的不错的算法),来对每个桶进行排序,然后,它将所有的桶合并为结果数组
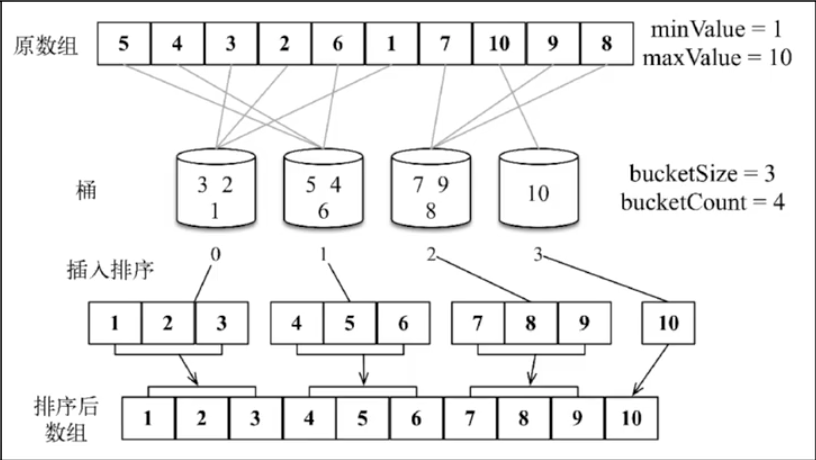
function bucketSort(arr, bucketSize = 3) {
if (arr.length < 2) {
return arr;
}
// 创建几个小桶
const buckets = createBucket(arr, bucketSize);
// 小桶排序(插入排序算法),合并concat
return sortBuckets(buckets);
}
function createBucket(arr, bucketSize) {
minValue = Math.min(...arr);
maxValue = Math.max(...arr);
const bucketCount = Math.floor((maxValue - minValue) / bucketSize) + 1;
const buckets = [...Array(bucketCount)].map(() => []);
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
const index = Math.floor((arr[i] - minValue) / bucketSize);
buckets[index].push(arr[i]);
}
return buckets;
}
function sortBuckets(arr) {
let sortArr = [];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i]) {
insertSort(arr[i]);
sortArr = sortArr.concat(arr[i]);
}
}
}
// 插入排序
function insertSort(arr) {
const { length } = arr;
let temp;
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
temp = arr[i];
let j = i;
while (j > 0) {
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
j--;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
return arr;
}
9.8 基数排序
基数排序是一种非比较型整数排序算法,其原理是将整数按位数切割成不同的数字,然后按每个位数分别比较。由于整数也可以表达字符串(比如名字或日期)和特定格式的浮点数,所以基数排序也不是只能使用于整数。

// 基数排序
function radixSort(arr) {
const base = 10;
let divider = 1;
const maxValue = Math.max(...arr);
while (divider <= maxValue) {
// 构建二维数组
let buckets = [...Array(10)].map(() => []);
for (let val of arr) {
buckets[Math.floor(val / divider) % base].push(val);
}
console.log(buckets);
arr = [].concat(...buckets);
divider *= base;
}
return arr
}
10. 搜索算法
10.1 顺序搜索
顺序或线性搜索是最基本的搜索算法。它的机制是,将每一个数据结构中的元素和我们要找的元素作比较。顺序搜索是最低效的一种搜索算法
function sequentialSearch(arr, val) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == val) {
return i
}
return -1
}
}
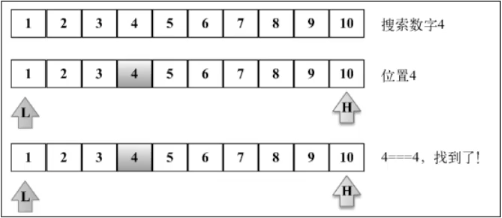
10.2 二分搜索
在计算机科学中,二分搜索(英语:binary search),也称折半搜索(英语:half-interval search)、对数搜索(英语:logarithmic search),是一种在有序数组中查找某一特定元素的搜索算法。搜索过程从数组的中间元素开始,如果中间元素正好是要查找的元素,则搜索过程结束;如果某一特定元素大于或者小于中间元素,则在数组大于或小于中间元素的那一半中查找,而且跟开始一样从中间元素开始比较。如果在某一步骤数组为空,则代表找不到。这种搜索算法每一次比较都使搜索范围缩小一半。
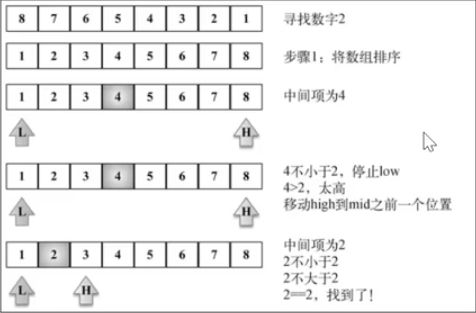
10.3 内插搜索
内插搜索是改良的二分搜索。二分搜索总是检查mid位置上的值,而内插搜索可能会根据要搜索的值检查数组的不同地方
function quickSort(arr) {
const { length } = arr;
if (length < 2) {
return arr;
}
let base = arr[0];
let minArr = arr.slice(1).filter((item) => item <= base);
let maxArr = arr.slice(1).filter((item) => item > base);
minArr = quickSort(minArr);
maxArr = quickSort(maxArr);
return minArr.concat(base).concat(maxArr);
}
// 内插搜索
function insertSearch(val, arr, start, end) {
start = start || 0;
end = end || arr.length - 1;
arr = quickSort(arr);
if (start <= end && val >= arr[start] && val <= arr[end]) {
if (arr[start] === val) {
return start;
}
if (arr[end] === val) {
return end;
}
// 适用于分布比较均匀
let mid = start + (val - arr[start]) / (arr[end] - arr[start]) * (end - start)
if (arr[mid] === val) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] > val) {
return binarySearch(val, arr, start, mid - 1);
} else {
return binarySearch(val, arr, mid + 1, end);
}
}
return -1;
}
11. 随机算法
迭代数组,从最后一位开始并将当前位置和一个随机位置进行交换。这个随机位置比当前位置小。这样,这个算法可以保证随机过的位置不会再被随机一次
// 交换位置
function swap(array, index1, index2) {
const temp = array[index1];
array[index1] = array[index2];
array[index2] = temp;
}
function shuffle(array) {
for (let i = array.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
const randomIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * (i + 1));
swap(array, i, randomIndex);
}
}
12. 算法设计
12.1 分而治之
分而治之是算法设计中的一种方法。它将一个问题分成多个原问题相似的小问题,递归解决小问题,再将解决方式合并以解决原来的问题
分而治之算法可以分成三个部分:
- 分解原问题为多个子问题(原问题的多个小实例)
- 解决子问题,用返回解决子问题的方式的递归算法。递归算法的基本情形可以用来解决子问题
- 组合这些子问题的解决方式。得到原问题的解
12.2 动态规划
动态规划(dynamic programming,DP)是一种将复杂问题分解成更小的子问题来解决的优化技术
用动态规划解决问题时,需要尊徐三个重要步骤:
- 定义子问题
- 实现要反复执行来解决子问题的部分
- 识别并求解出基线条件
12.2.1 背包问题
// 背包问题
function knapSack(weights, values, totalWeight) {
var n = weights.length - 1;
var f = [[]];
for (var j = 0; j <= totalWeight; j++) {
if (j < weights[0]) {
f[0][j] = 0;
} else {
f[0][j] = values[0];
}
}
for (var j = 0; j <= totalWeight; j++) {
for (var i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!f[i]) {
f[i] = [];
}
if (j < weights[i]) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
} else {
// f[i - 1][j] 上一行的最优解
// f[i - 1][j - weights[i]] + values[i] 减去当前重量后,剩下重量的最优解 + 当前重量的价值
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i - 1][j], f[i - 1][j - weights[i]] + values[i]);
}
}
}
return f[n][totalWeight]
}
12.2.2 最长公共子序列
找出两个字符串序列的最长子序列的长度。最长子序列是指,在两个字符串序列中以相同顺序出现,但不要求连续(非字符串子串)的字符串序列
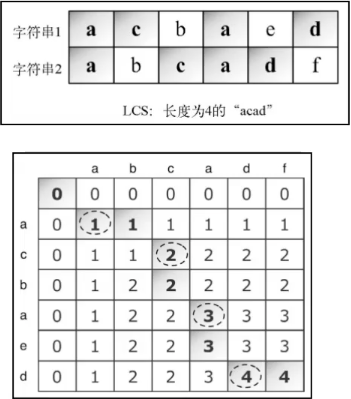
// 最长公共子序列
function LCS(str1, str2) {
var m = str1.length; // 行数
var n = str2.length; // 列数
var dp = [new Array(n + 1)].fill(0); // 第一行全是0
for (var i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
// 一共有m+1行
dp[i] = [0]; // 第一列全是0
for (var j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (str1[i - 1] === str2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
printLCS(dp, str1, str2, m, n);
return dp[m][n];
}
function printLCS(dp, str1, str2, i, j) {
if (i === 0 || j === 0) {
return '';
}
if (str1[i - 1] === str2[j - 1]) {
return printLCS(dp, str1, str2, i - 1, j - 1) + str1[i - 1];
} else {
if (dp[i][j - 1] > dp[i - 1][j]) {
return printLCS(dp, str1, str2, i, j - 1);
} else {
return printLCS(dp, str1, str2, i - 1, j);
}
}
}
12.3 贪心算法
在对问题求解时,总是做出在当前看来是最好的选择。也就是说,不从整体最优上加以考虑,他所做出的仅是在某种意义上的局部最优解。贪心算法不是对说有问题都能得到整体最优解,但对范围相当广泛的许多问题他能产生整体最优解或者整体最优解的近似解
// 贪心算法
// 背包问题
function greedy(capacity, weights, values) {
var list = [];
for (var i = 0; i < weights.length; i++) {
list.push({
num: i + 1,
w: weights[i],
v: values[i],
rate: values[i] / weights[i],
});
}
list.sort((a, b) => b.rate - a.rate);
var selects = []
var total = 0
for (let i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
var item = list[i]
if (item.w <= capacity) {
selects.push({
num: item.num,
rate: 1,
v: item.v,
w: item.w
})
total += item.v
capacity -= item.w
} else if (capacity > 0) {
var rate = capacity / item.w
var v = item.v * rate
selects.push({
num: item.num,
rate,
v: item.v * rate,
w: item.w * rate,
});
}
}
}
12.2.4 回溯算法
回溯法采用试错的思想,它尝试分步的去解决一个问题。在分步解决问题的过程中,当它通过尝试发现现有的分步答案不能得到有效的正确的解答的时候,它将取消上一步甚至上几步的计算,再通过其他的可能的分布解答再次尝试寻找问题的答案
示例:
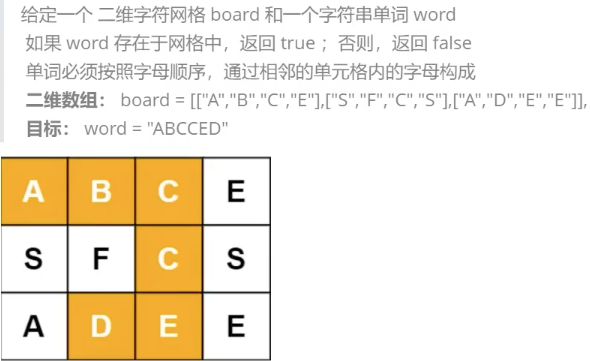
// 回溯算法
function backTracking(board, word) {
// 设置行列数
let row = board.length;
let col = board[0].length;
// 双循环,每个坐标都尝试,作目标的第1个元素
for (let i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < col; j++) {
// 从宫格图中第一个开始找(i, j),找目标第一个字母(word[0])
const result = find(i, j, 0); // 返回true或false
if (result) {
return result;
}
}
// 结束了都没找到,返回false
return false;
}
function find(r, c, cur) {
if (r >= row || r < 0) return false;
if (c >= col || c < 0) return false;
if (board[r][c] !== word[cur]) return false; // 不是目标元素则返回false
// 执行到这,说明rc坐标是目标元素
// 先判断,如果是最后一个也找到了,返回true结束
if (cur === word.length - 1) return true;
let letter = board[r][c]; // 赋值给临时变量
board[r][c] = null; // 用null作替换标记,避免下一个找上下左右时重复
// 进行下一步,上下左右查找
const result =
find(r - 1, c, cur + 1) ||
find(r + 1, c, cur + 1) ||
find(r, c + 1, cur + 1) ||
find(r, c - 1, cur + 1);
// 用null作标记是避免重复,但双for的find结束就需要恢复
board[r][c] = letter;
return result;
}
}
var res = backTracking(
[
['A', 'B', 'C', 'E'],
['S', 'F', 'C', 'S'],
['A', 'D', 'E', 'F'],
],
'ABCCED'
);
console.log(res);
13. 算法复杂度
O表示法用于藐视算法的性能和复杂程度。O表示法将算法按照消耗的时间进行分类,依据随输入增大所需要的空间/内存;可根据循环的次数判断其复杂度

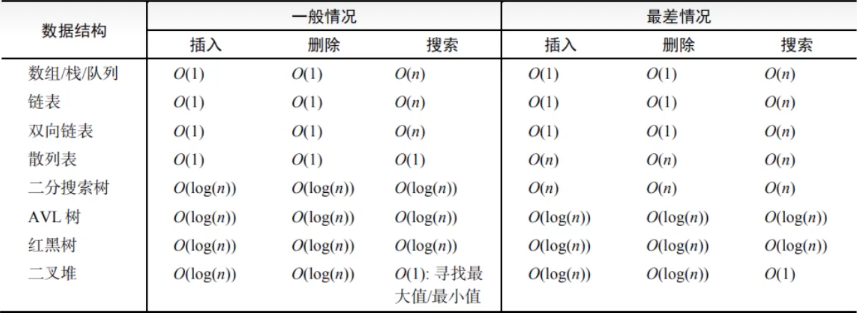
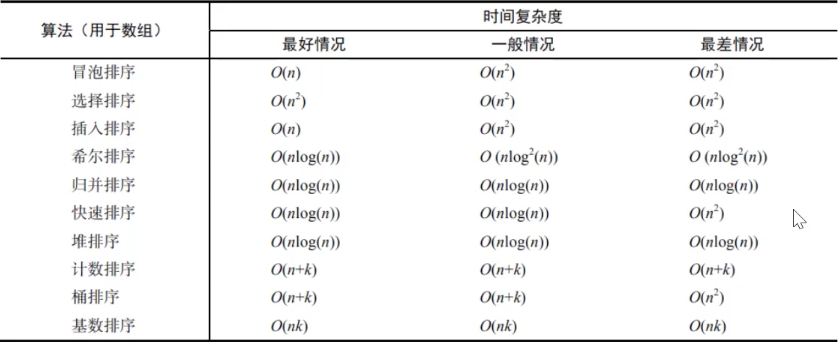
- 常数阶O(1)
无论代码执行了多少行,只要是没有循环等复杂结构,那这个代码的时间复杂度就都是O(1)
function inc(n) {
return ++n
}
- 对数阶O(logN)
在while循环里面,每次都将 i 乘以 2,乘完之后,i 距离 n 就越来越近了。假设循环x次之后,i 就大于 2 了,此时这个循环就退出了,也就是说 2 的 x 次方等于 n,那么 x = log2n也就是说当循环 log2n 次以后,这个代码就结束了。因此这个代码的时间复杂度为:O(log2n) 。 O(log2n) 的这个2 时间上是根据代码变化的,i = i * 3 ,则是 O(log3n) .
int i = 1;
while(i < n) {
i = i * 2;
}
- 线性阶O(n)
这段代码,for循环里面的代码会执行n遍,因此它消耗的时间是随着n的变化而变化的,因此这类代码都可以用O(n)来表示它的时间复杂度
for(i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
j = i;
j++
}
- 线性对数阶O(nlogN)
线性对数阶O(nlogN) 其实非常容易理解,将时间复杂度为O(logn)的代码循环N遍的话,那么它的时间复杂度就是 n * O(logN),也就是了O(nlogN)
for(m = 1; m < n; m++) {
i = 1;
while(i < n) {
i = i * 2;
}
}
- O(n^2)
平方阶O(n²) 就更容易理解了,如果把 O(n) 的代码再嵌套循环一遍,它的时间复杂度就是 O(n²),这段代码其实就是嵌套了2层n循环,它的时间复杂度就是 O(nn),即 O(n²) 如果将其中一层循环的n改成m,那它的时间复杂度就变成了 O(mn)
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < n; j++) {
console.log(i, j)
}
}
- 立方阶O(n³)、K次方阶O(n^k)
参考上面的O(n²) 去理解就好了,O(n³)相当于三层n循环,其它的类似




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异