Spring注解@Resource和@Autowired区别对比、spring扫描的默认bean的Id、程序获取spring容器对象
-------------------------注解扫面的bean的ID问题--------------------------
0.前提需要明白注解扫描出来的bean的id默认是类名首字母小写,当然可以指定id:
(1)只写注解不指定id
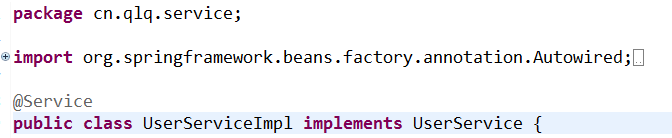
上面实际上是等价于xml中的下面配置:
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="cn.qlq.service.UserService"></bean>
测试:(程序中获取spring容器中的bean)
@Action("saveUser")
public String saveUser() {
userService.saveUser();
// 代码中获取容器中bean(依赖于web容器)
WebApplicationContext wac = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
Object bean = wac.getBean("userServiceImpl");
return "json";
}
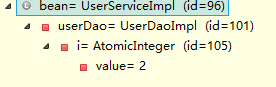
打断点查看bean:(获取到的是容器中的唯一bean的引用,且此对象的依赖关系也会取出来)
(2)指定id属性:
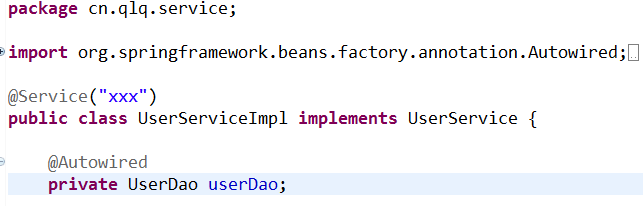
上面等价于:
<bean id="xxx" class="cn.qlq.service.UserService"></bean>
测试代码:
@Action("saveUser")
public String saveUser() {
userService.saveUser();
// 代码中获取容器中bean(依赖于web容器)
WebApplicationContext wac = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
Object bean = wac.getBean("xxx");
return "json";
}
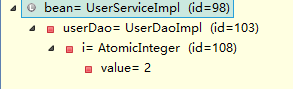
打断点查看bean:
(3)按照上面的思路,我们在不同的包下如果不指定id是不允许有类名字相同的类存在的,测试
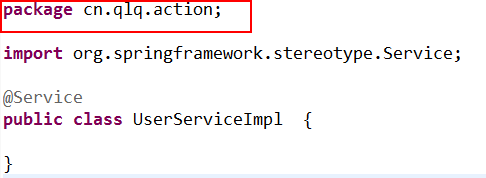
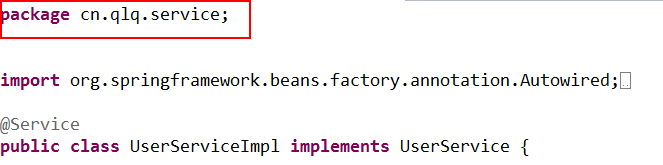
启动容器报错:(注解冲突)
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException: Unexpected exception parsing XML document from class path resource [applicationContext.xml]; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalStateException: Annotation-specified bean name 'userServiceImpl' for bean class [cn.qlq.service.UserServiceImpl] conflicts with existing, non-compatible bean definition of same name and class [cn.qlq.action.UserServiceImpl]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.doLoadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:412)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:334)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:302)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java:143)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java:178)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java:149)
at org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions(XmlWebApplicationContext.java:124)
at org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions(XmlWebApplicationContext.java:93)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.refreshBeanFactory(AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java:130)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.obtainFreshBeanFactory(AbstractApplicationContext.java:467)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:397)
at org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.createWebApplicationContext(ContextLoader.java:276)
at org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(ContextLoader.java:197)
at org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener.contextInitialized(ContextLoaderListener.java:47)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext.listenerStart(StandardContext.java:5118)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext.startInternal(StandardContext.java:5634)
at org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase.start(LifecycleBase.java:145)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.addChildInternal(ContainerBase.java:899)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.addChild(ContainerBase.java:875)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHost.addChild(StandardHost.java:652)
at org.apache.catalina.startup.HostConfig.deployDescriptor(HostConfig.java:679)
at org.apache.catalina.startup.HostConfig$DeployDescriptor.run(HostConfig.java:1966)
at java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter.call(Executors.java:471)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:262)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1145)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:615)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
----------------研究Autowired和Resource两者不同----------------
@Resource和@Autowired都是做bean的注入时使用,其实@Resource并不是Spring的注解,它的包是javax.annotation.Resource,需要导入,但是Spring支持该注解的注入。
1、共同点
两者都可以写在字段和setter方法上。两者如果都写在字段上,那么就不需要再写setter方法。
2、不同点
(1)@Autowired
查看源码:
package org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD}) public @interface Autowired { boolean required() default true; }
@Autowired为Spring提供的注解,需要导入包org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;只按照byType注入。
public class TestServiceImpl { // 下面两种@Autowired只要使用一种即可 @Autowired private UserDao userDao; // 用于字段上 @Autowired public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { // 用于属性的方法上 this.userDao = userDao; } }
@Autowired注解是按照类型(byType)装配依赖对象,默认情况下它要求依赖对象必须存在,如果允许null值,可以设置它的required属性为false。如果我们想使用按照名称(byName)来装配,可以结合@Qualifier注解一起使用。如下:
public class TestServiceImpl { @Autowired @Qualifier("userDao") private UserDao userDao; }
当然,您也可以通过 @Autowired 对方法或构造函数进行标注,如果构造函数有两个入参,分别是 bean1 和 bean2,@Autowired 将分别寻找和它们类型匹配的 Bean,将它们作为 CountryService (Bean1 bean1 ,Bean2 bean2) 的入参来创建 CountryService Bean。来看下面的代码: 对方法
public class Boss { private Car car; private Office office; @Autowired public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } @Autowired public void setOffice(Office office) { this.office = office; } … }
这时,@Autowired 将查找被标注的方法的入参类型的 Bean,并调用方法自动注入这些 Bean。而下面的使用方法则对构造函数进行标注:
public class Boss { private Car car; private Office office; @Autowired public Boss(Car car ,Office office){ this.car = car; this.office = office ; } … }
(2)@Resource
查看源码:
package javax.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.*; import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*; import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.*; @Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD}) @Retention(RUNTIME) public @interface Resource { String name() default ""; String lookup() default ""; Class type() default java.lang.Object.class; enum AuthenticationType { CONTAINER, APPLICATION } AuthenticationType authenticationType() default AuthenticationType.CONTAINER; boolean shareable() default true; String mappedName() default ""; String description() default ""; }
@Resource的作用相当于@Autowired,只不过@Autowired按byType自动注入,而@Resource默认按 byName自动注入罢了。@Resource有两个属性是比较重要的,分是name和type,Spring将@Resource注解的name属性解析为bean的名字,而type属性则解析为bean的类型。所以如果使用name属性,则使用byName的自动注入策略,而使用type属性时则使用byType自动注入策略。如果既不指定name也不指定type属性,这时将通过反射机制使用byName自动注入策略。
注:最好是将@Resource放在setter方法上,因为这样更符合面向对象的思想,通过set、get去操作属性,而不是直接去操作属性。
@Resource装配顺序:
①如果同时指定了name和type,则从Spring上下文中找到唯一匹配的bean进行装配,找不到则抛出异常。
②如果指定了name,则从上下文中查找名称(id)匹配的bean进行装配,找不到则抛出异常。
③如果指定了type,则从上下文中找到类似匹配的唯一bean进行装配,找不到或是找到多个,都会抛出异常。
④如果既没有指定name,又没有指定type,则自动按照byName方式进行装配;如果没有匹配,则回退为一个原始类型进行匹配,如果匹配则自动装配。
例如以下写法都对:(当然下面只是写在成员变量中,也可以写在set方法上)
@Resource(type = cn.qlq.service.UserService.class) private UserService userService;
@Resource(name="userServiceImpl") private UserService userService;
@Resource private UserService userService;
总结:
- @Resource默认按照名称方式进行bean匹配(byName),@Autowired默认按照类型方式进行bean匹配(byType)
- @Resource(import javax.annotation.Resource;)是J2EE的注解,@Autowired( import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;)是Spring的注解
Spring属于第三方的,J2EE是Java自己的东西。使用@Resource可以减少代码和Spring之间的耦合
----------------程序中获取spring容器中对象----------------
我们知道在spring中容器启动有BeanFactory和ApplicationContext(其实现有ClassPathXmlApplicationContext、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 、XmlWebApplicationContext、AnnotationConfigApplicationContext四种基本是),所以我们首先获取到ApplicationContext,然后获取对象:(可以根据类型获取,也可以根据bean的Id获取)
// 获取webApplicationContext进而获取对象 WebApplicationContext currentWebApplicationContext = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext(); TestUtils bean = currentWebApplicationContext.getBean(TestUtils.class);// 根据类型获取对象 UserService bean2 = (UserService) currentWebApplicationContext.getBean("userService");// 根据id获取
我们打断点查看上面获取的bean:
(1)currentWebApplicationContext是取的XmlWebApplicationContext

(2)bean是获取容器的原生对象(通过IOC反射创建的)
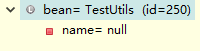
(3)bean2是获取的AOP增强的代理对象。

通过上面明白了spring ioc默认的都是原生对象 只有通过aop增强的对象才是代理对象。代理对象也是在原来的反射创建的对象上进行增强。
实际上在web应用中,我们的dao层用的ORM框架,例如mybatis、hibernate与spring整合之后都获取的是增强过的代理对象;我们的service层一般也会用aop增强事务等操作。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix